Dispatching and route-planning method for multiple AGVs used for material transportation in factory
A technology for path planning and running paths, which is applied in the direction of navigation calculation tools, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
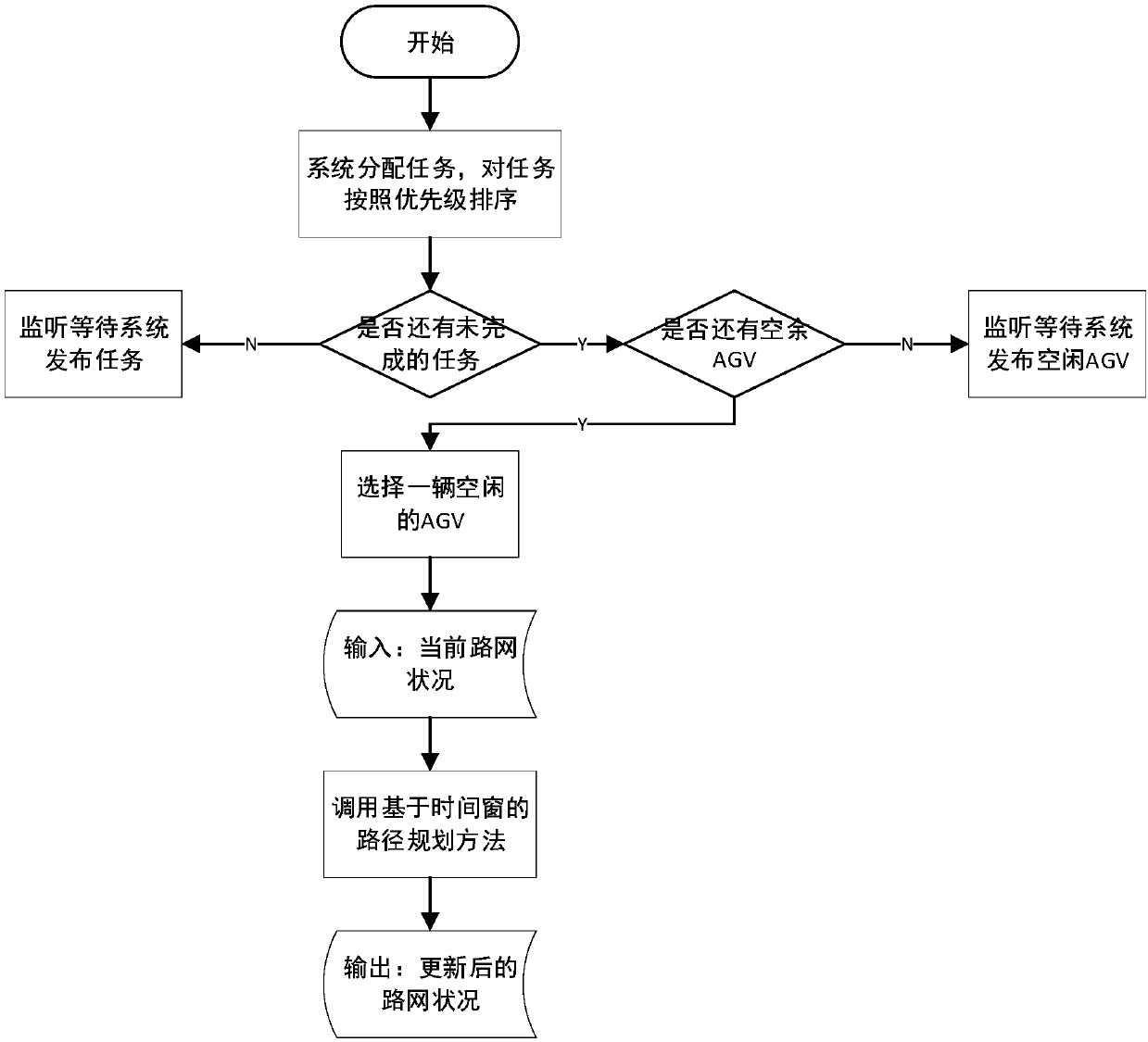
[0058] A multi-AGV scheduling and path planning method for material transportation in a factory, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0059] (1) Model the material transportation scene in the factory, including AGV driving path, AGV charging point, loading and unloading point, and AGV standby area;
[0060] (2) Store the allocated tasks in the queue; put the allocated tasks into the blocking queue according to the priority from high to low. According to different evaluation criteria, the priority scheduling method is used to set the priority for each task, that is, the priority of each task is evaluated according to the time when the task is released and whether the task is urgent or not. The tasks are put into the blocking queue in an asynchronous manner, and in the blocking queue, the AGVs are assigned in order of priority from high to low.
[0061] The scheduling system reads tasks from the head of the blocking queue and adds tasks to the tail of the q...
Embodiment 2
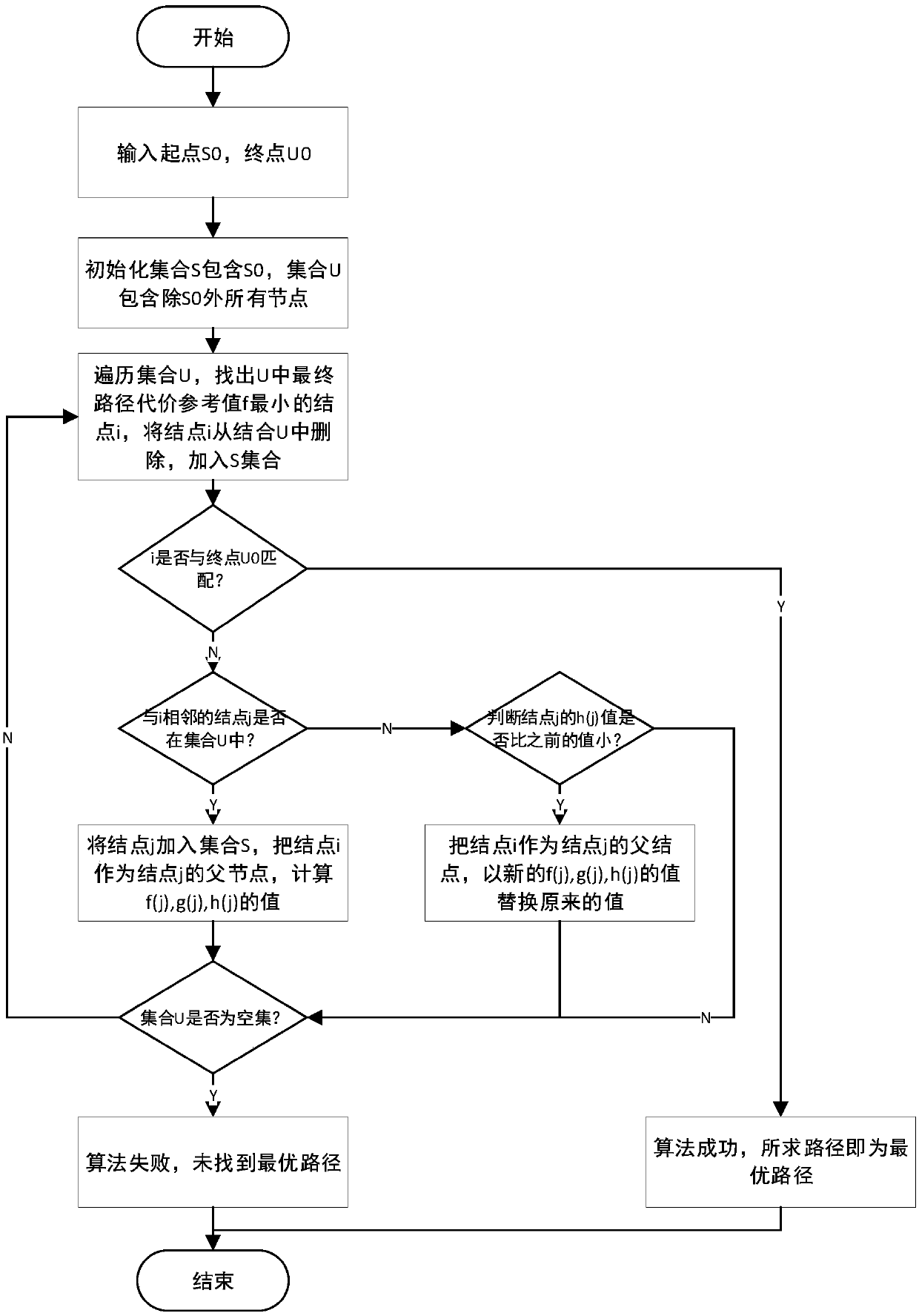
[0066] According to the multi-AGV scheduling and path planning method for material transportation in a factory described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that in step (1), the grid map method is used to establish the working environment model of the AGV in the material transportation workshop in the factory, including :
[0067] Design the map road network of the workshop in the factory, mark the coordinates of the AGV charging point, loading and unloading point, and node (Node), and the two AGV driving paths intersect at a certain point on the map road network, then the point is called a node;
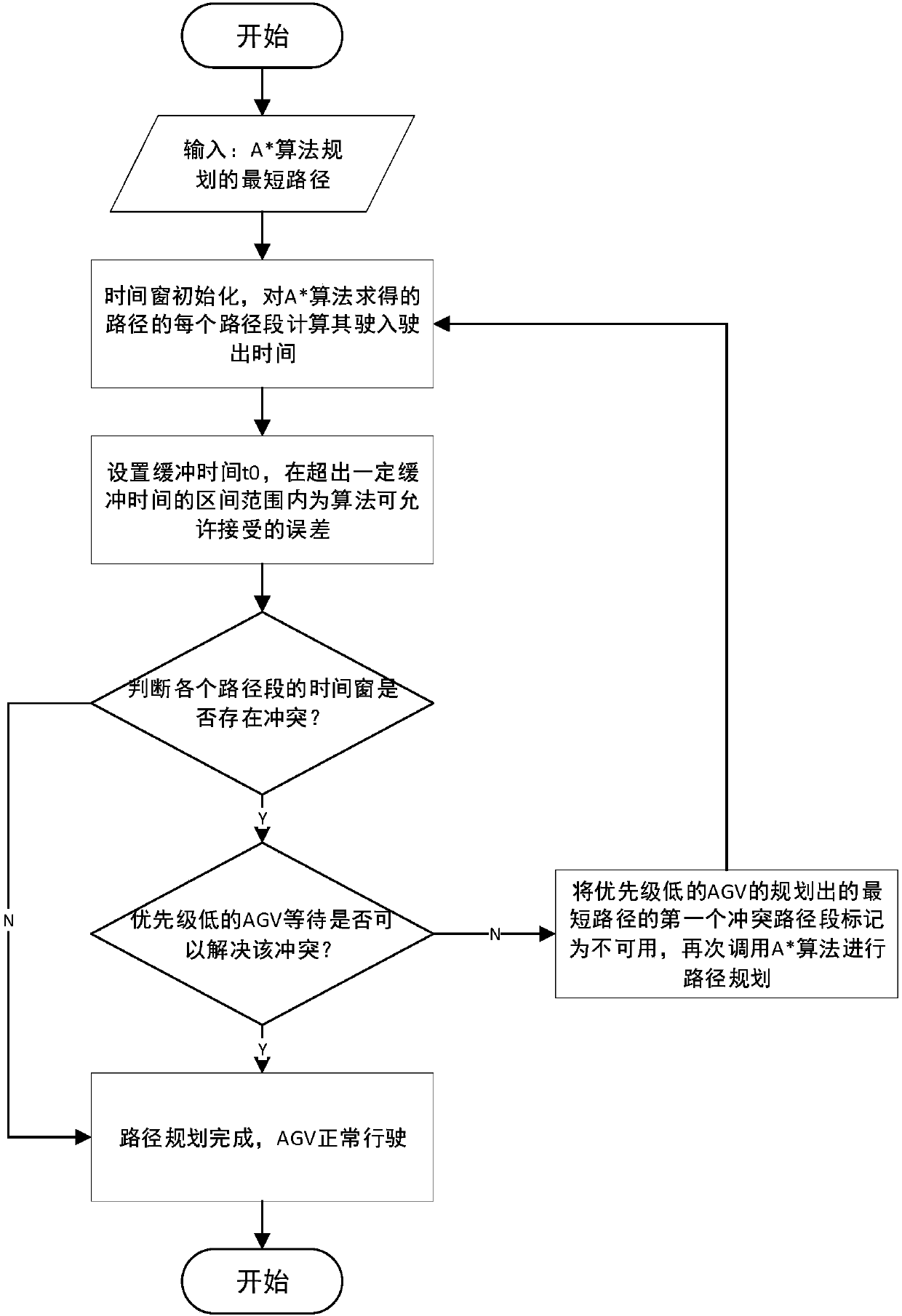
[0068] Design the AGV driving path and the AGV standby area. The AGV driving path is two-way driving. The width of the AGV driving path can only accommodate one AGV, that is, 1 unit length; in the same time period, the AGV can only accept one task; in the AGV During the execution of the current task, the scheduling system cannot issue tasks to this AGV; at a certain moment or within...
Embodiment 3
[0070] According to the multi-AGV scheduling and path planning method for material transportation in a factory described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that in step (3), the attributes of all AGVs are stored in the AGV array, and the attributes of the AGV include the AGV number, AGV Status, AGV current power, whether AGV is available, each AGV corresponds to an AGV number; AGV status includes three states: driving, stopping, and turning; and the number of currently available AGVs is set as a memory visible variable suitable for concurrent situations. The memory visible variable is obtained by the following method: traverse the attribute of whether the AGV is available in the AGV array, and the statistical attribute is the number of available AGVs. The number of available AGVs can be obtained by traversing the AGV array and judging whether the number of AGVs whose attribute is false is available in the AGV array. When reading and writing the number of AGVs concurrently, in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com