Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Realize path planning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
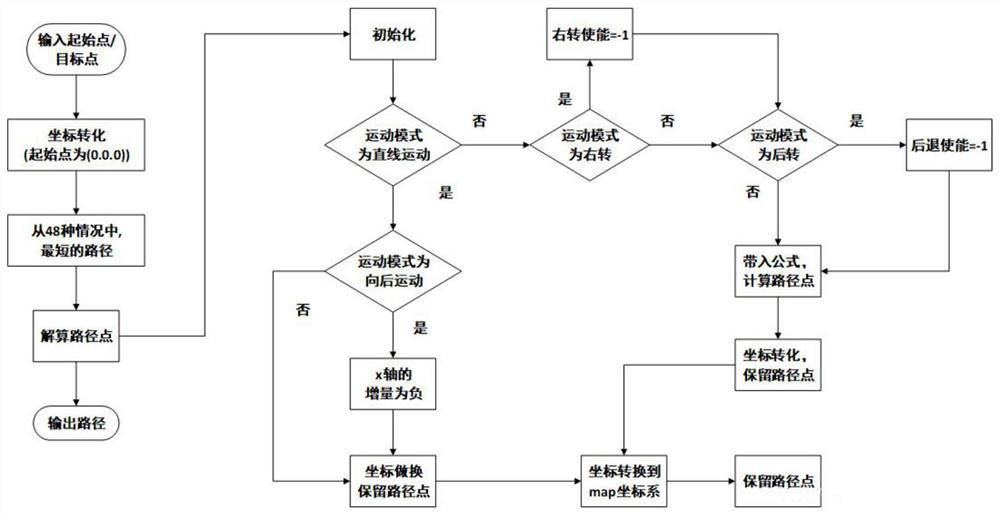
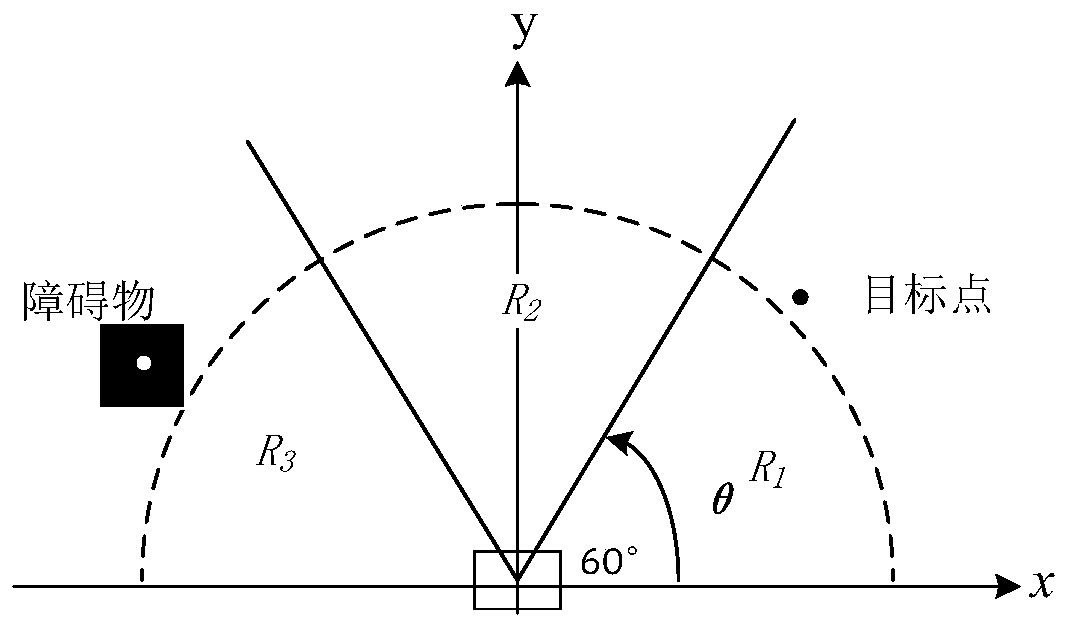
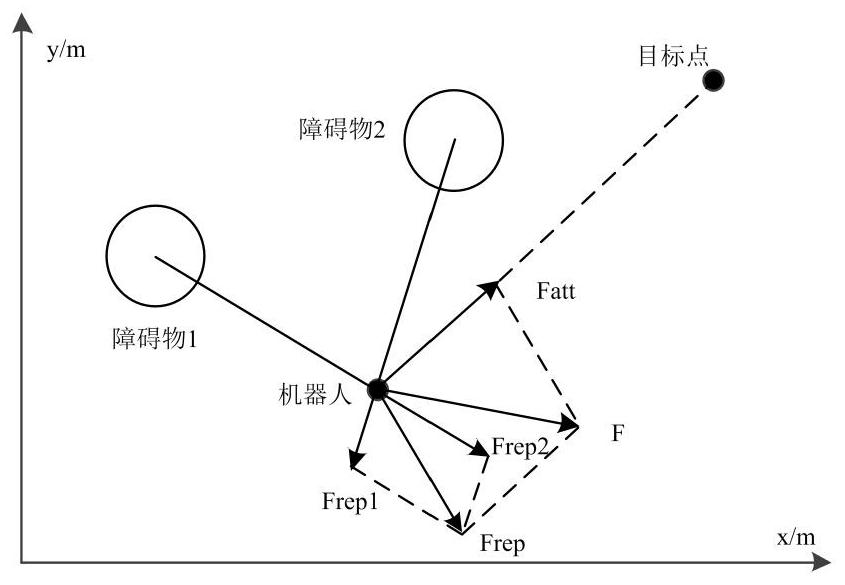
Path planning method for mobile robot in dynamic environment
ActiveCN103823466AOptimization principleRealize path planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationPath plan
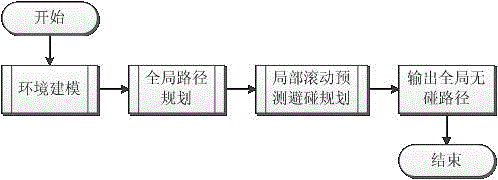
The invention discloses a double-layer planning method based on the combination of global path planning and local rolling prediction collision avoidance planning, so as to solve the problem of path planning for a mobile robot in a dynamic environment. The method mainly comprises two parts: the global path planning and the local rolling prediction collision avoidance planning. The path planning method can better realize robot navigation, and improve intelligence of the robot. The double planning method can be utilized to prevent the blindness of planning in the beginning, and searching space of the problem is reduced; based on the uncertainty of the moving direction of a dynamic barrier and by utilizing the two collision prediction strategies and two corresponding collision avoidance strategies, the dynamic barrier can be avoided well; and particularly, in order to adapt to the change of environment better, in the second layer of planning, a Follow_wall behavior based on behavior method is added, so that when the environment changes, the mobile robot can still arrive at the target without touching the barriers safely.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Path planning method for vertical automatic parking and system
The invention discloses a path planning method for vertical automatic parking comprising creating an overall coordinate system by using surrounding environment information of a vehicle needing for parking obtained by a sensor, determining whether the vehicle needing for parking can accomplish automatic parking in the current overall coordinate system by combining with vehicle steering characteristics based on an Ackermann steering mechanism and carrying out a vertical parking path planning. By using a simple geometric construction method for the vertical parking path planning, the path planning method for the vertical automatic parking has the advantages of successfully accomplishing the parking in three times, improving the efficiency of the vertical parking path planning, possessing better robustness and rapidly realizing path planning when the parking is only obstructed by obstacle garages.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Reinforced learning path planning algorithm based on potential field
InactiveCN110794842ARealize path planningGuaranteed randomnessPosition/course control in two dimensionsReinforcement learning algorithmEngineering
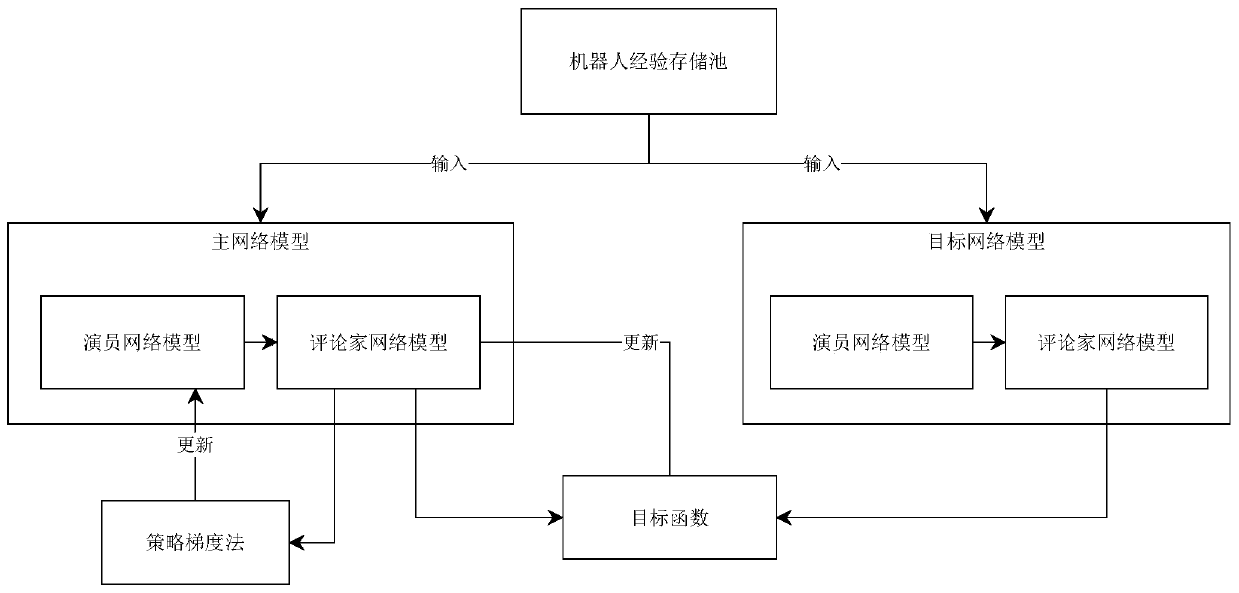
The invention, which belongs to the field of intelligent algorithm optimization, provides a reinforced learning robot path planning algorithm based on a potential field in a complex environment, thereby realizing robot path planning in a complex dynamic environment under the environmental condition that a large number of movable obstacles exist in a scene. The method comprises the following steps:modeling environment space by utilizing the traditional artificial potential field method; defining a state function, a reward function and an action function in a Markov decision-making process according to a potential field model, and training the state function, the reward function and the action function in a simulation environment by utilizing a reinforcement learning algorithm of a depth deterministic strategy gradient; and thus enabling a robot to have the decision-making capability of performing collision-free path planning in a complex obstacle environment. Experimental results showthat the method has advantages of short decision-making time, low system resource occupation, and certain robustness; and robot path planning under complex environmental conditions can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Mobile robot path planning method in complex environment
InactiveCN104516350AImprove operational efficiencyMeet operational needsAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationArtificial immune algorithm
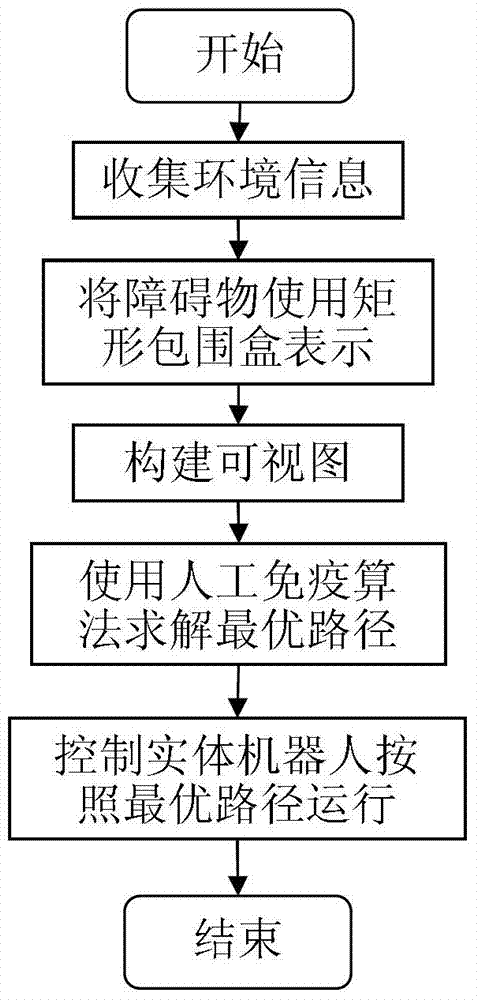
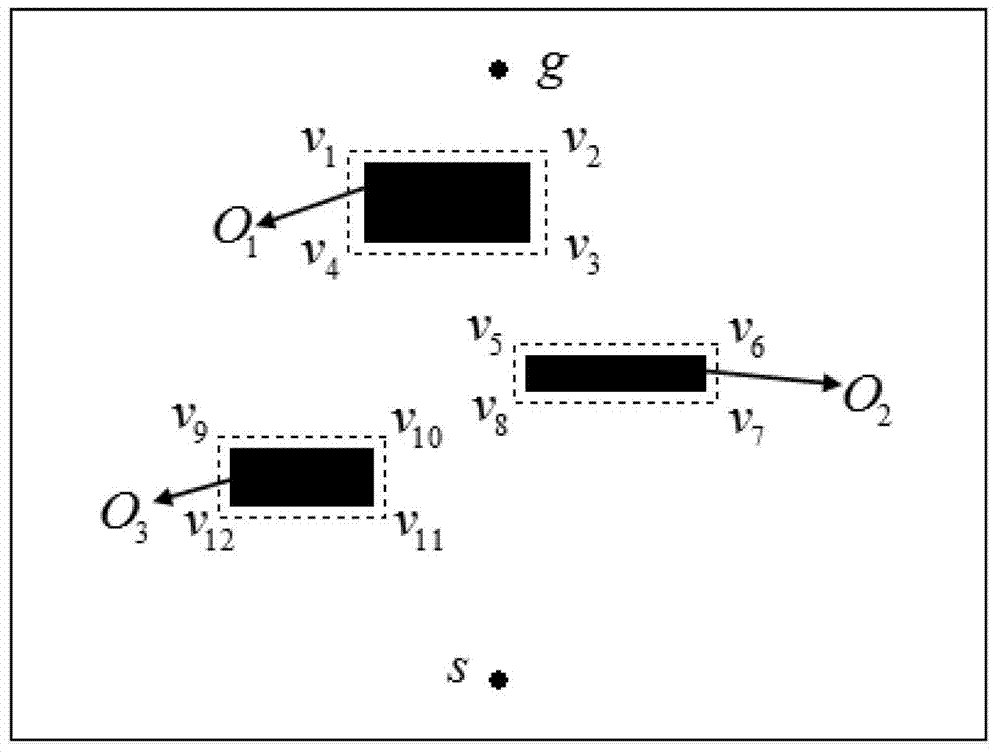
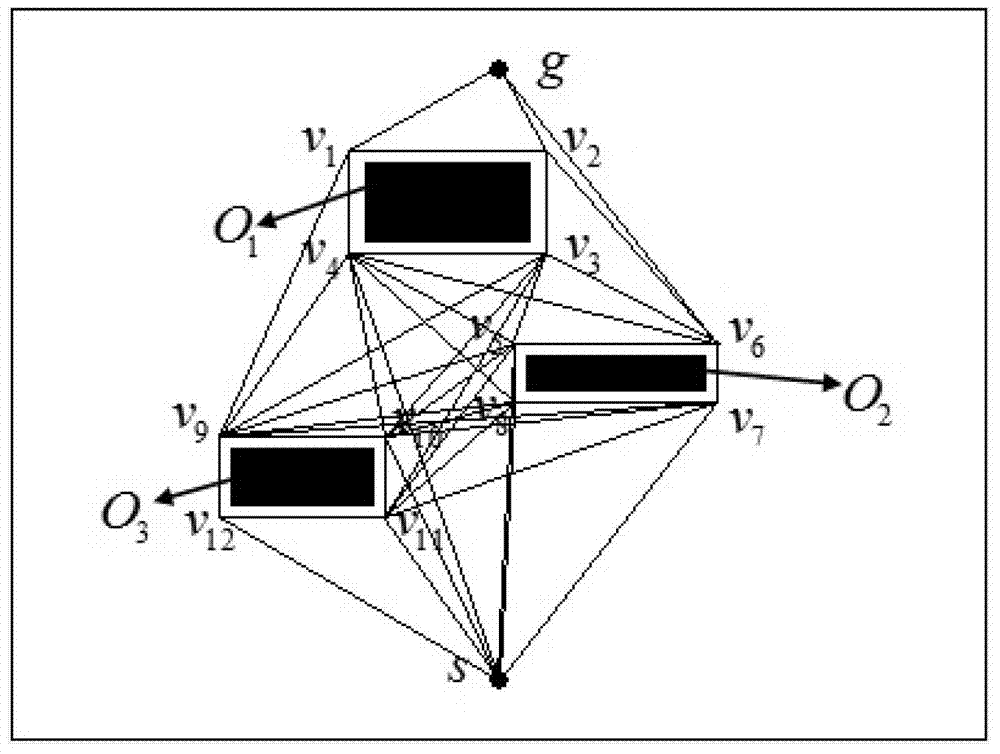
The invention provides a mobile robot path planning method in a complex environment. The method is characterized in that 1. information of environment in which a robot is positioned is acquired, and obstacles in the environmental space are indicated by using rectangular enclosing boxes after processing and displayed on a human-computer interaction module; 2. the initial position of the robot is confirmed and recorded as an initial point; a target position expected to be reached by the robot is confirmed and recorded as a target point; 3. the initial point, the target point and the vertexes of all the obstacle enclosing boxes meeting the condition are connected by using line segments, wherein the requirement indicates that the connecting line of any two points does not penetrate through the enclosing boxes, based on which a visual graph is constructed; 4. the optimal path is planned in the visual graph via an artificial immune algorithm, and key nodes in the optimal path are stored; and 5. The entity robot is controlled to start from the initial point, pass the key nodes in the optimal path one by one and finally reach the target point. Algorithm efficiency and convergence rate can be effectively enhanced under the premise of guaranteeing solution of the optimal path.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
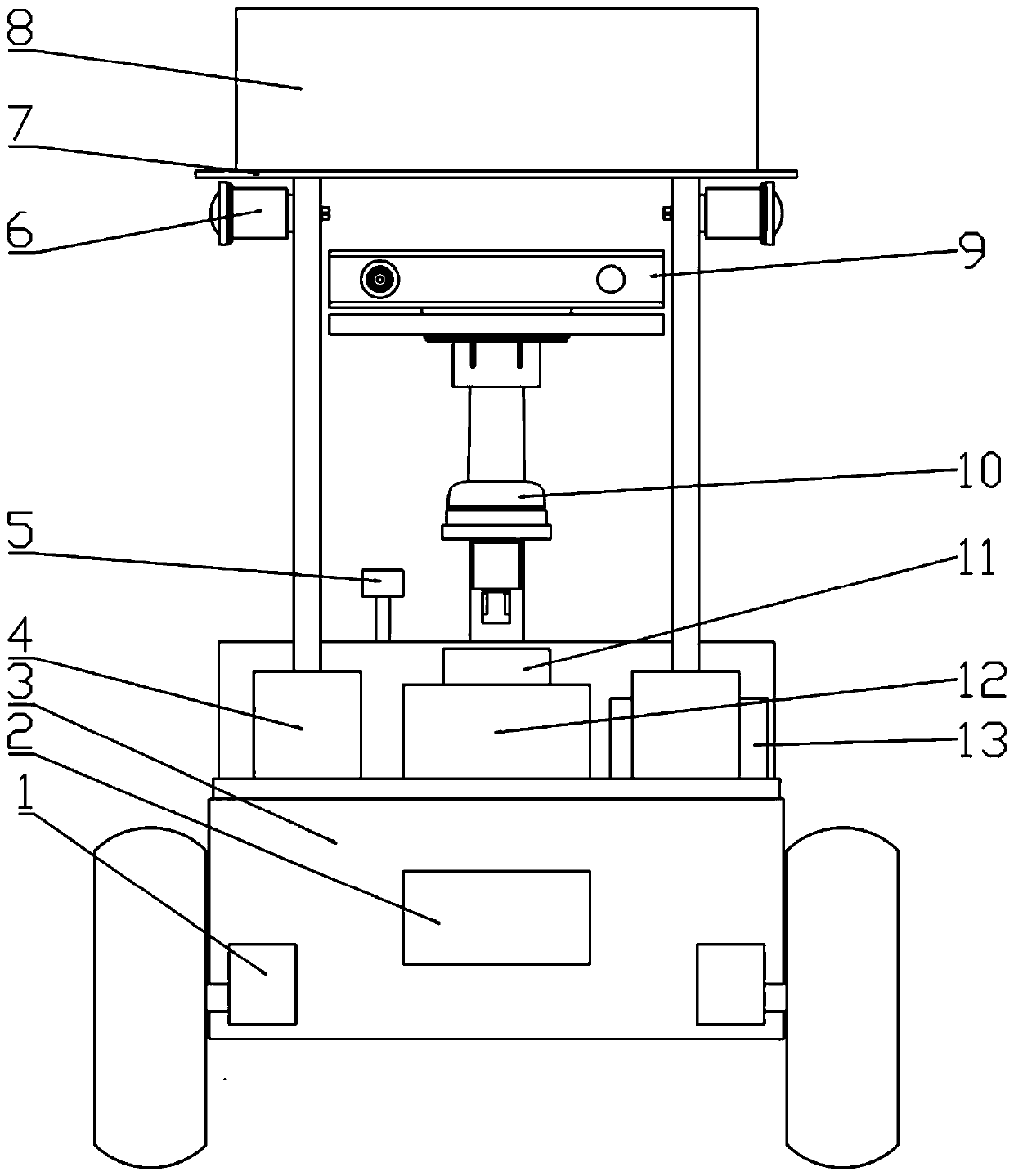
Livestock and poultry information sensing robot based on autonomous navigation and map construction method
ActiveCN109900280AImplement automatic detectionRealize automatic collectionImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationMicrocontrollerLivestock
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
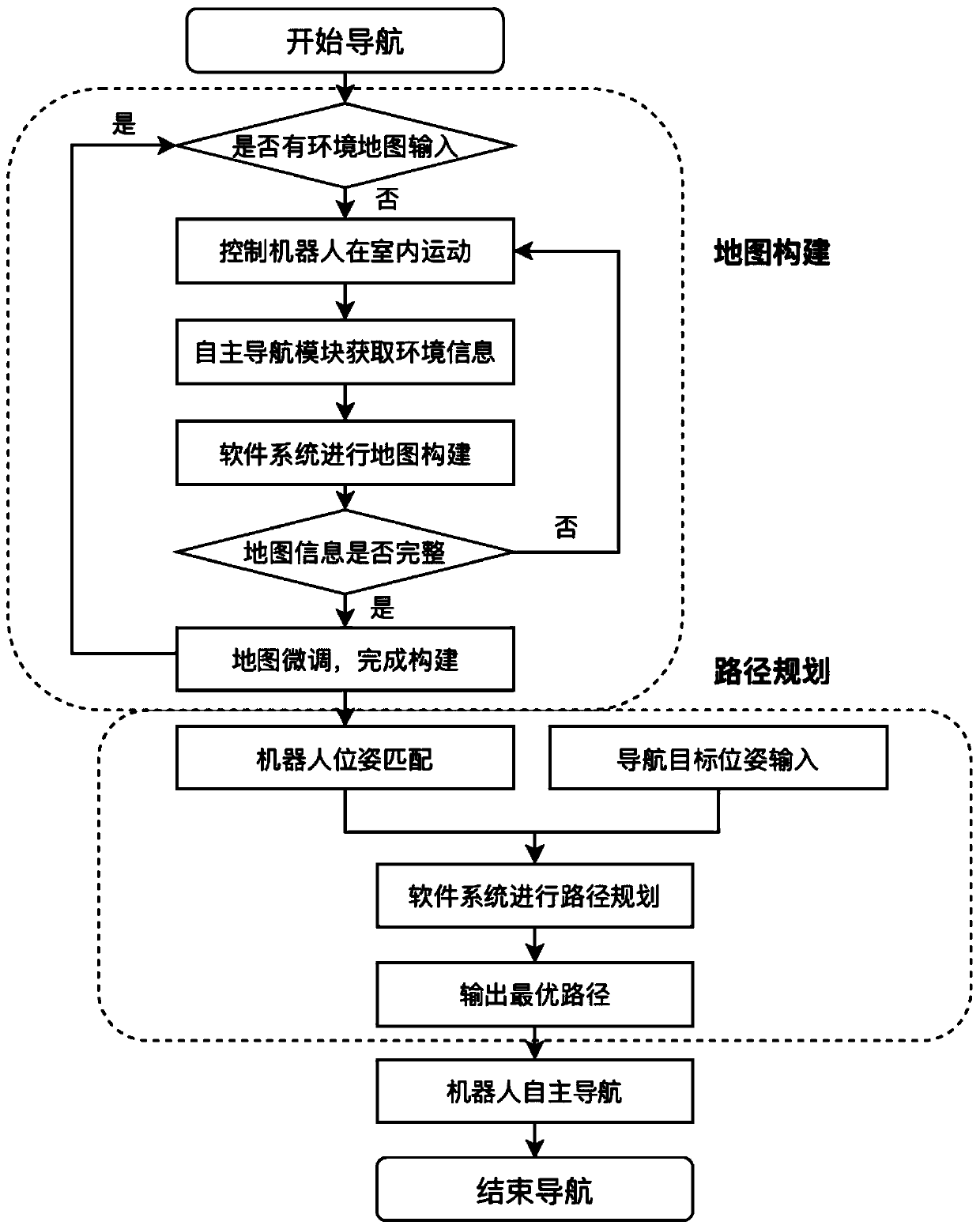
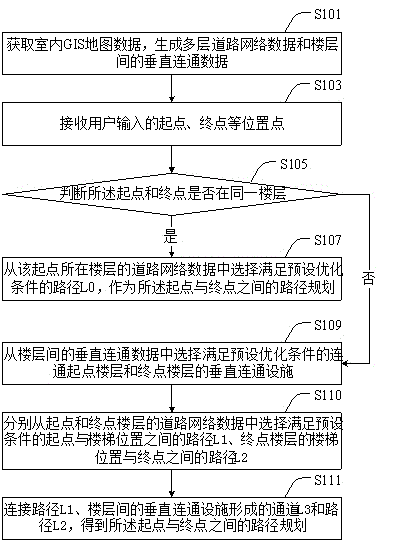
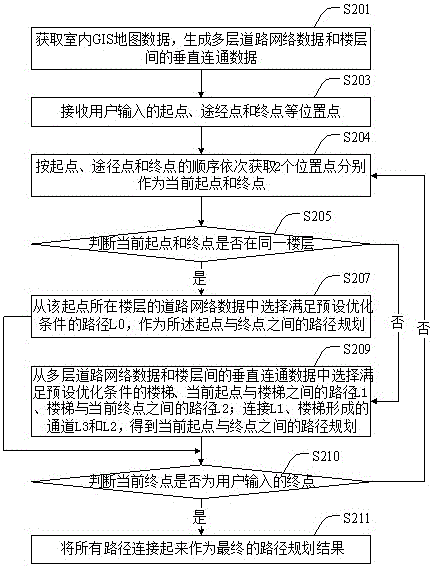
Indoor floor-spanning path planning method and indoor floor-spanning path planning device
ActiveCN106441305ARealize path planningSolve the route planning that can only achieve a single floorNavigational calculation instrumentsUser inputRoad networks
The invention provides an indoor floor-spanning path planning method and an indoor floor-spanning path planning device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring indoor GIS (Geographic Information System) map data, and generating multilayer road network data and vertical communication data among floors; receiving a starting point and an ending point inputted by a user; judging whether the starting point and the ending point are at the same floor or not; if not, selecting a vertical communication facility meeting a preset optimized condition, a path L1 between the starting point and the vertical communication facility and a path L2 between the vertical communication facility and the ending point from the vertical communication data among the floors and the multilayer road network data; connecting the L1, a channel L3 formed by the vertical communication facility and the L2 to obtain a path planning between the starting point and the ending point. According to the indoor floor-spanning path planning method and the indoor floor-spanning path planning device disclosed by the invention, the path planning of all the floors is realized on the basis of a method for analyzing layer by layer, and the path planning among floor-spanning position points is realized by using connection information among the floors.
Owner:BEIJING SUPERMAP SOFTWARE CO LTD
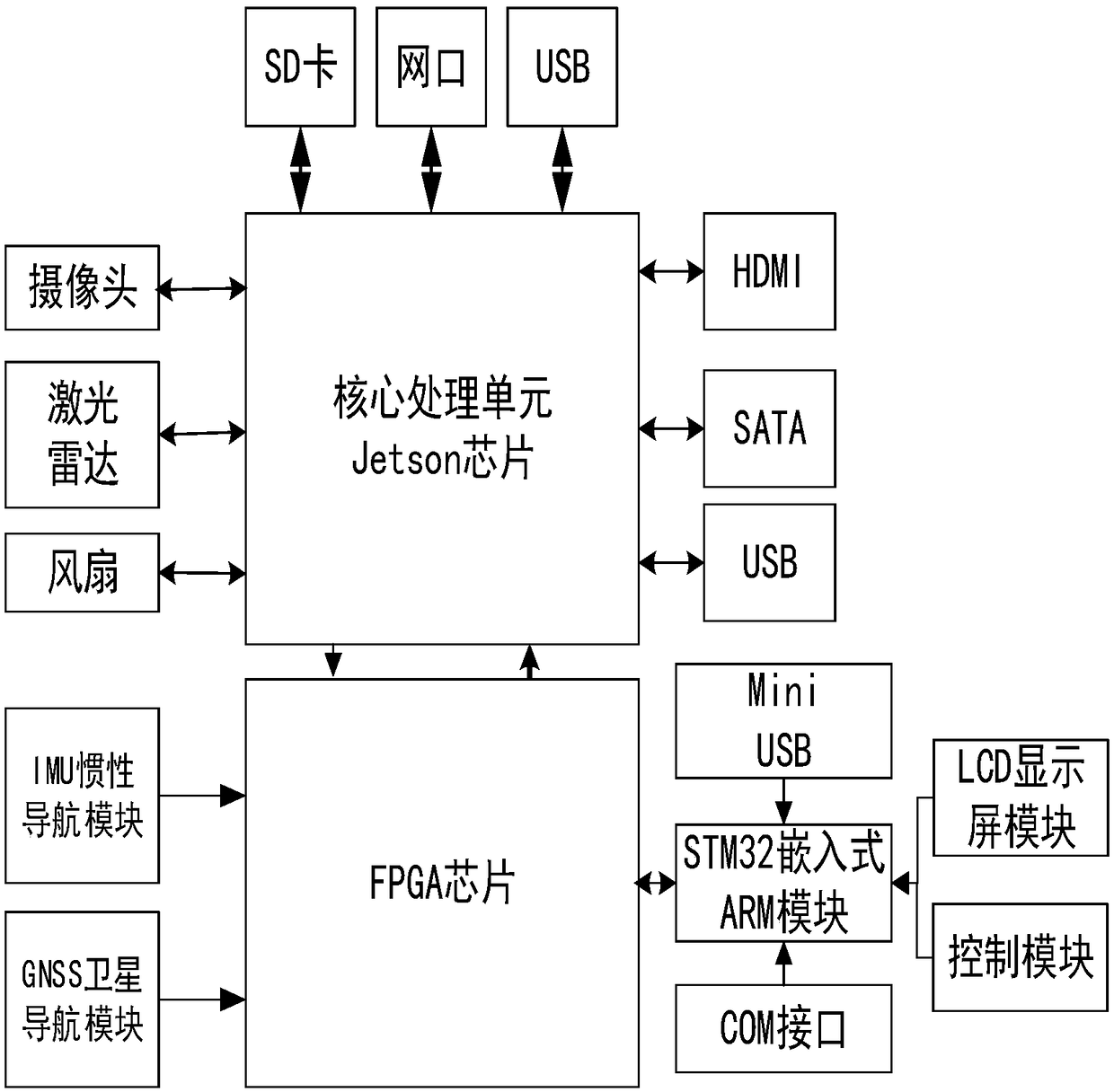
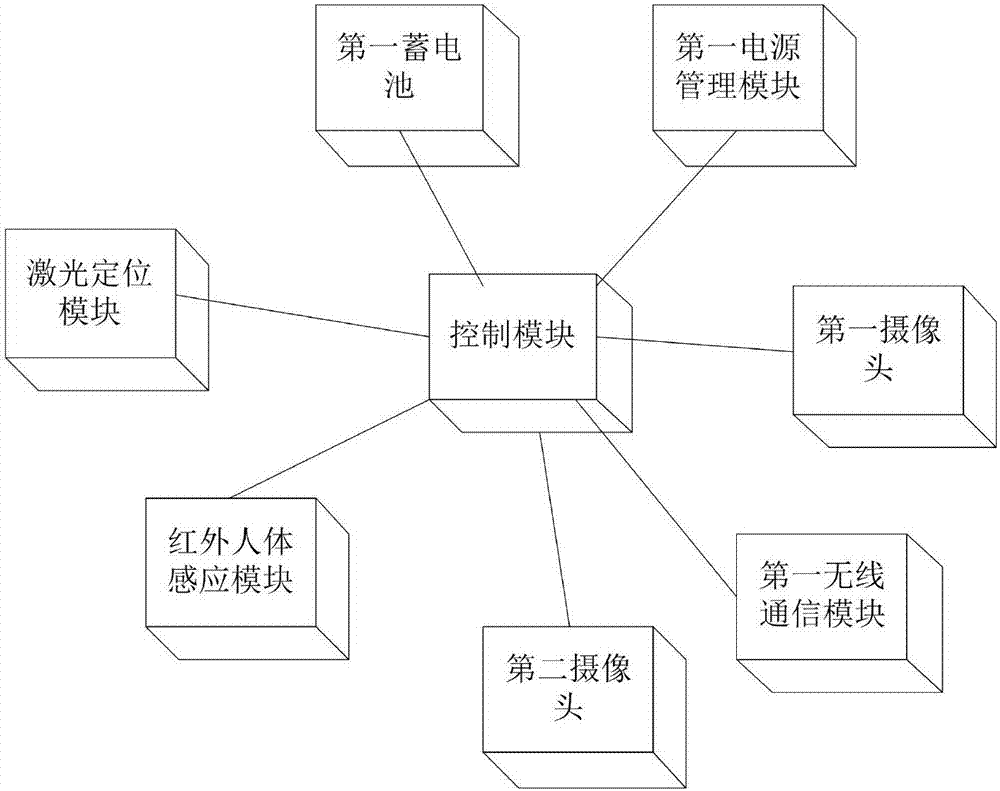
Robot embedded computing terminal integrated with high precision navigation positioning and deep learning
ActiveCN108776474AContinuous real-time positioningContinuous real-time path planningAutonomous decision making processPosition/course control in two dimensionsRadarComputer terminal
The invention relates to a robot embedded computing terminal integrated with high precision navigation positioning and deep learning. The embedded computing terminal is characterized by comprising a core processing unit Jetson chip, an FPGA chip, an embedded ARM module and multiple types of sensors which are integrated, wherein the sensors comprise a GNSS satellite navigation module, an IMU inertial navigation module, a laser radar device and a camera, the core processing unit Jetson chip is connected with the camera and the laser radar device, the FPGA chip is connected with the GNSS satellite navigation module, the IMU inertial navigation module and the embedded ARM module, and the embedded ARM module is connected with a servo motor of a control robot. The embedded computing terminal isadvantaged in that realization of the real-time high-precision positioning result solution can be supported, and environment sensing and mission planning of the robot are realized.
Owner:中山赛伯坦智能科技有限公司 +2
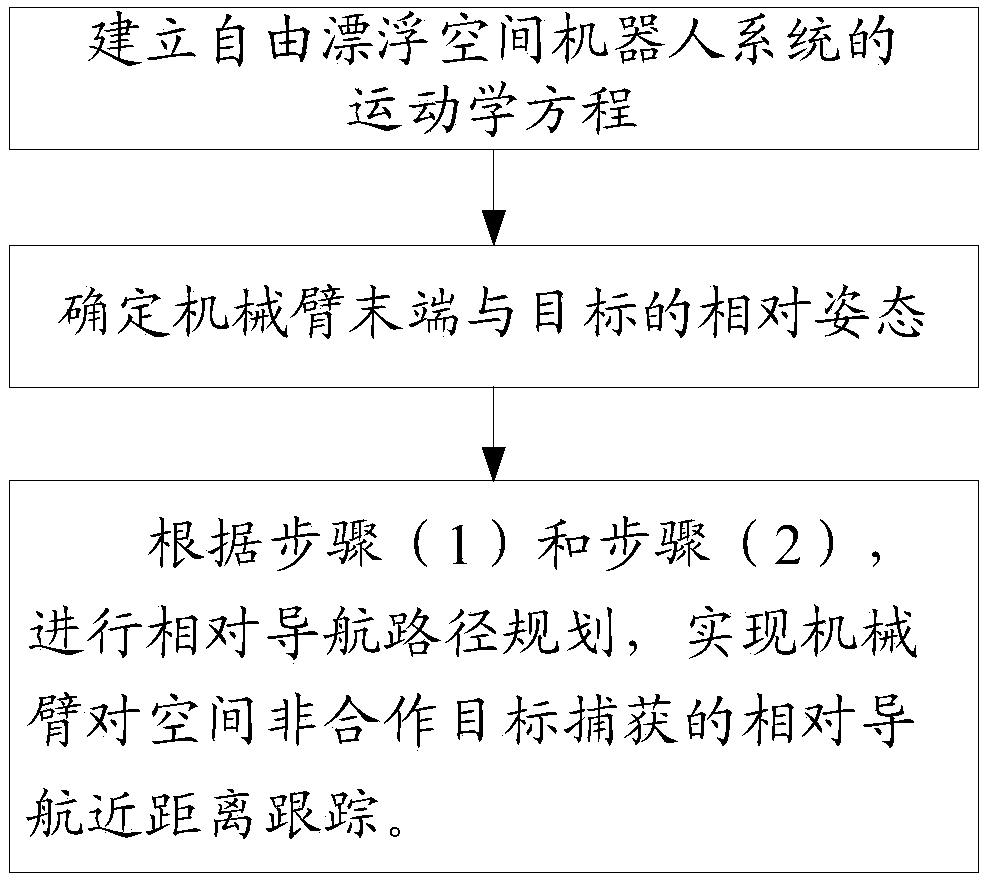
Relative navigation close range tracking method and system for space noncooperative target capturing
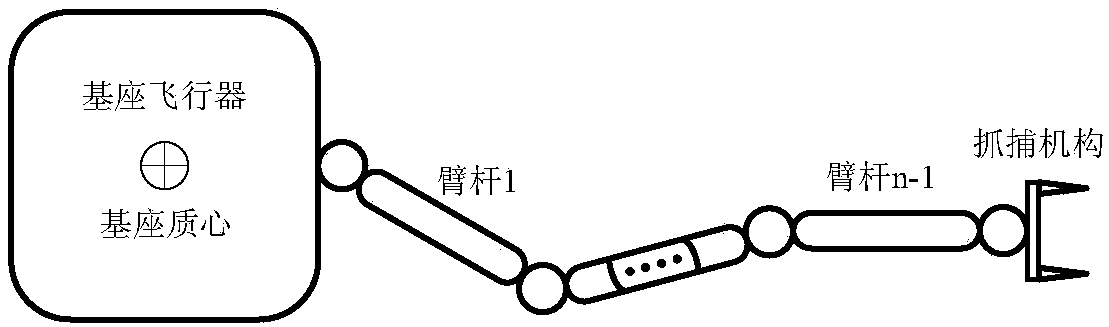
ActiveCN108381553ARealize autonomous relative navigationReal-time plan motion pathProgramme-controlled manipulatorToolsKinematics equationsJoint spaces
The invention provides a relative navigation close range tracking method and system for space noncooperative target capturing. According to the relative navigation close range tracking method and system for space noncooperative target capturing, a kinematical equation of a free-floating space robot system is utilized to deduce and obtain a path planning method for a mechanical arm capturing a moving target, the relative speed and relative posture of the tail end of the mechanical arm and the target are taken as input, joint angle commands controlling the mechanical arm to move can be calculated and obtained, so that capturing operations of the mechanical arm on the moving target can be realized. By means of the relative navigation close range tracking method, in the process of close rangerelative navigation of a space robot on the moving noncooperative target, path planning for the relative position and posture of the tail end of the mechanical arm and the target and continuous inverse kinematics solution from Cartesian space to mechanical arm joint space can be independently realized, and especially for redundant mechanical arms, posture undisturbed planning for a base seat relative to inertial space can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
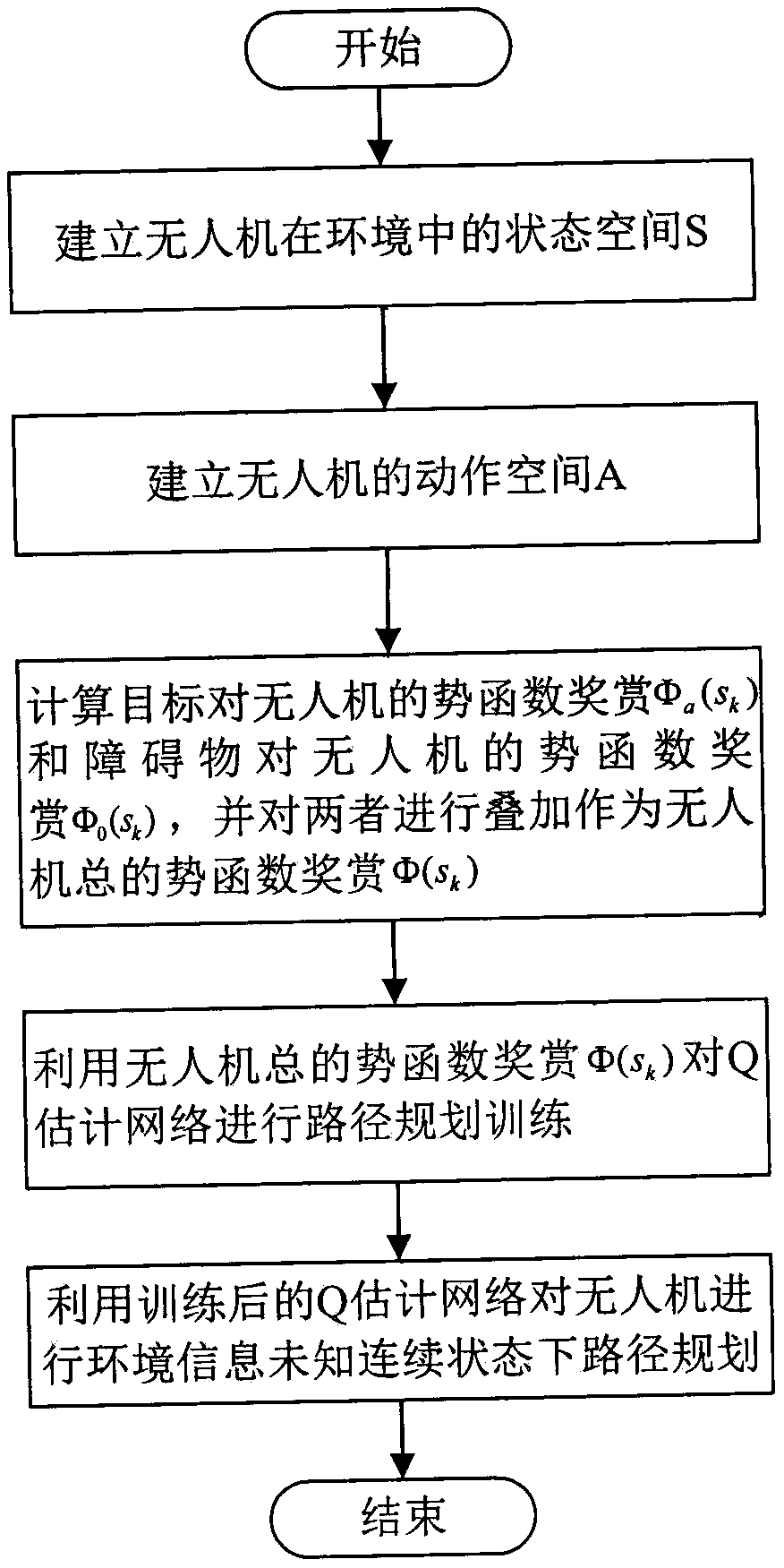
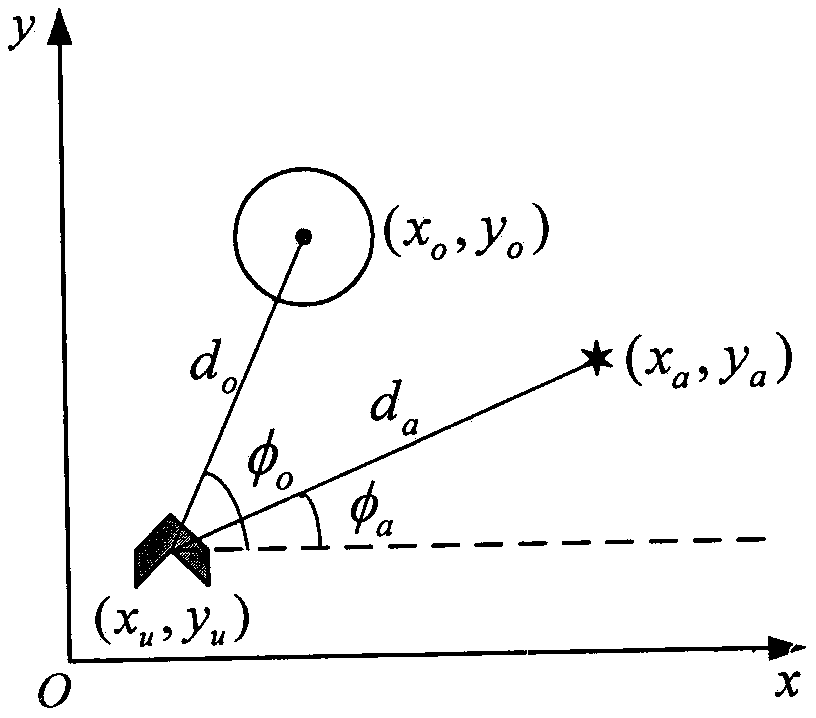
Unmanned aerial vehicle path planning method based on potential function reward DQN under environmental information unknown continuous state
ActiveCN110134140AHigh speedFast convergencePosition/course control in three dimensionsPlanning methodReal-time computing
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle path planning method based on potential function reward DQN under environmental information unknown continuous state. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing state space of an unmanned aerial vehicle in an environment, wherein the state space is a continuous state space and contains infinitely many states of the unmanned aerial vehicle; secondly, equally dividing 360 degrees into n angles and taking the angles as heading angles of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and establishing an action space of the unmanned aerial vehicle; then, calculating potential function reward of a target to the unmanned aerial vehicle and the potential function reward of an obstacle to the unmanned aerial vehicle, and superposing the rewardsand taking the superposed rewards as total potential function reward of the unmanned aerial vehicle; then, performing path planning training for a Q estimation network through the total potential function reward of the unmanned aerial vehicle; and finally, performing path planning under environment information unknown continuous state for the unmanned aerial vehicle through the trained Q estimation network. The method mainly solves a problem of path planning of the unmanned aerial vehicle without an environment model, satisfies requirements on state continuity of the environment, where the unmanned aerial vehicle is, when the unmanned aerial vehicle executes tasks; and the potential function reward accelerates path planning of the unmanned aerial vehicle, thus, the method has better applicability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Laser-navigation-based omnibearing motion mechanism control system
PendingCN106647741AImplement obstacle detectionAchieve positioningPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesRadarControl system
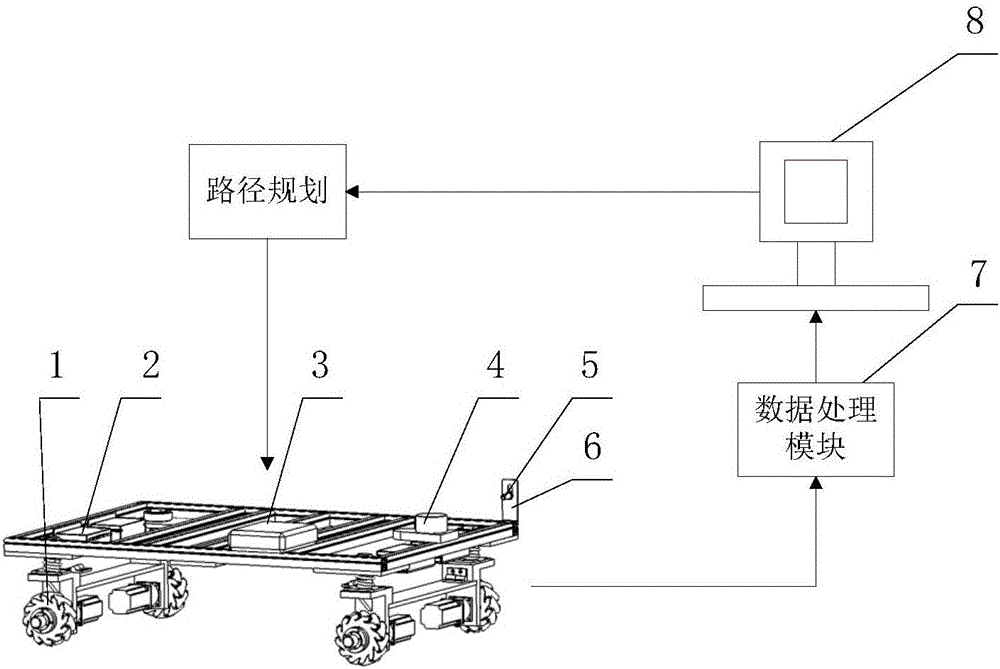
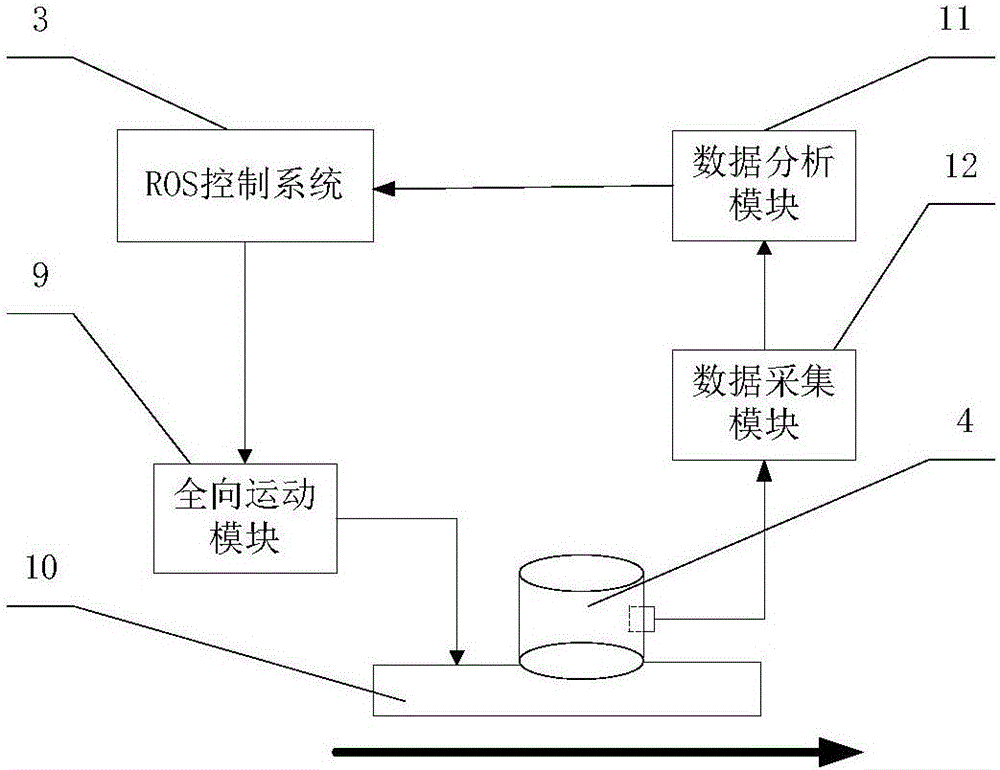
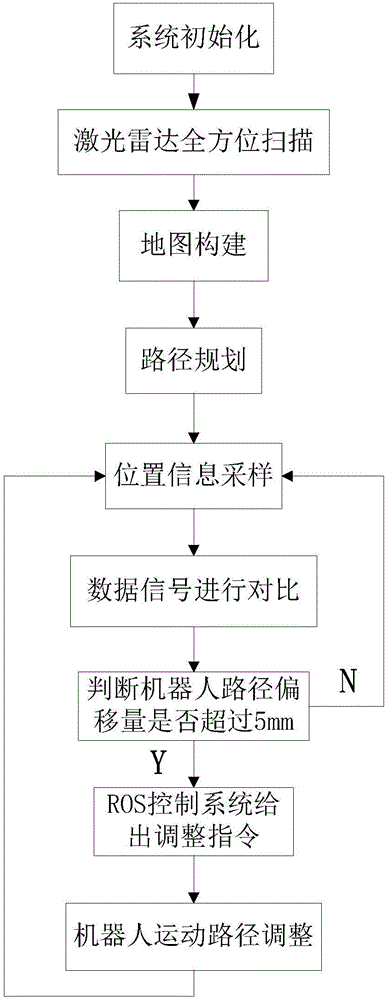
The invention discloses a laser-navigation-based omnibearing motion mechanism control system. The system comprises an omnibearing movement module based on an ROS four-axis control system and an RPLIDAR-laser-radar-based navigation module. The ROS four-axis control system feeds back location information in real time by the RPLIDAR laser radar; and a rotating speed and a turning direction of a detection robot are controlled by a driver to realize traverse movement, oblique movement, and in-situ rotation movement around the axis of the detection robort, so that the detection robot can walk along a predetermined path. The RPLIDAR laser radar is connected with a PC machine by a matched USB connecting wire; the PC machine uses the RPLIDAR laser radar to realize map building and path planning of the detection robot and stores the planned path information into the omnibearing movement module; the RPLIDAR laser radar carries out navigation positioning on the detection robot in real time and transmits the collected location information to the omnibearing movement module; and on the basis of the feedback location information, the ROS four-axis control system adjusts the omnibearing movement module continuously to enable the detection robot to walk along a predetermined track.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
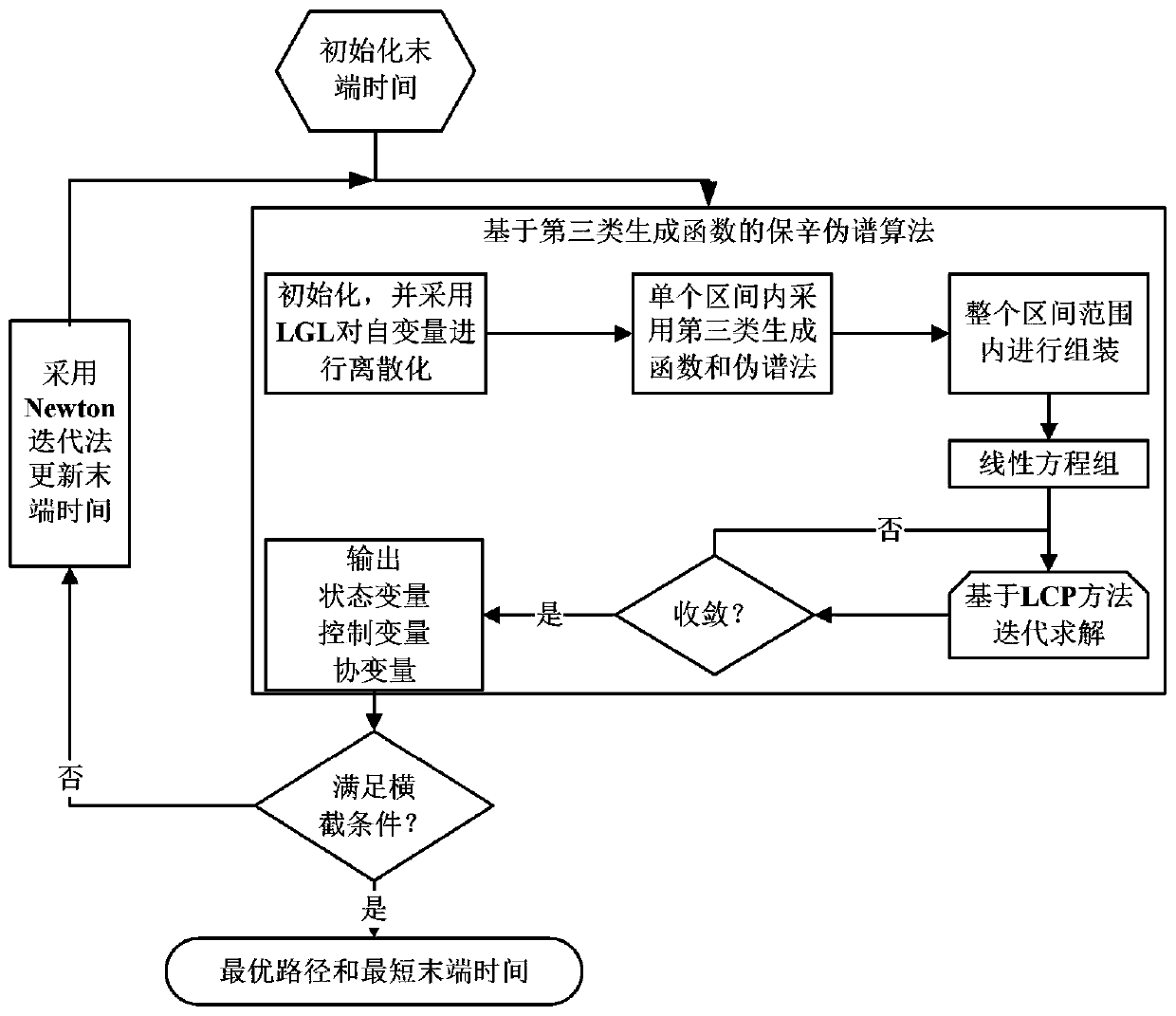
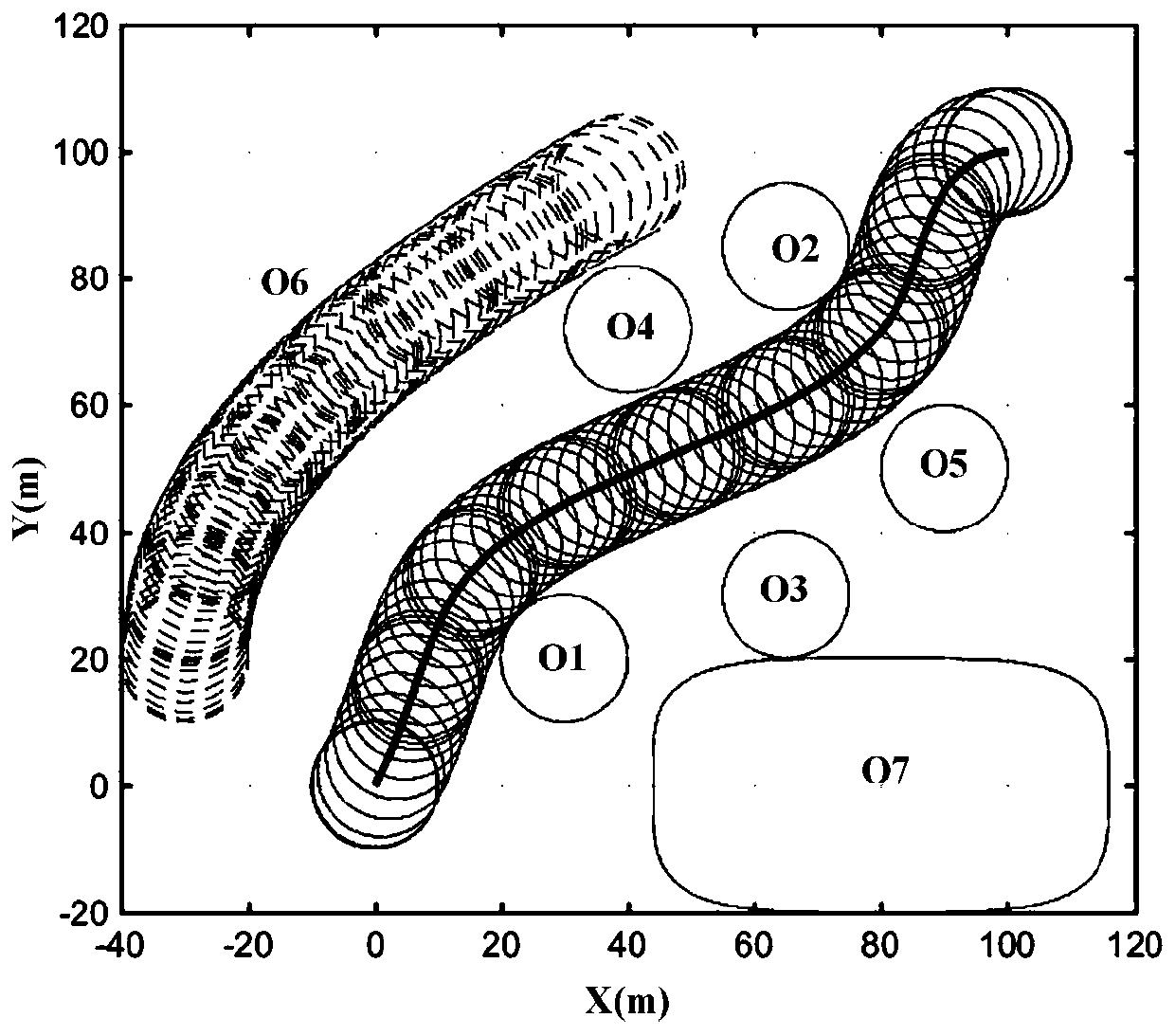
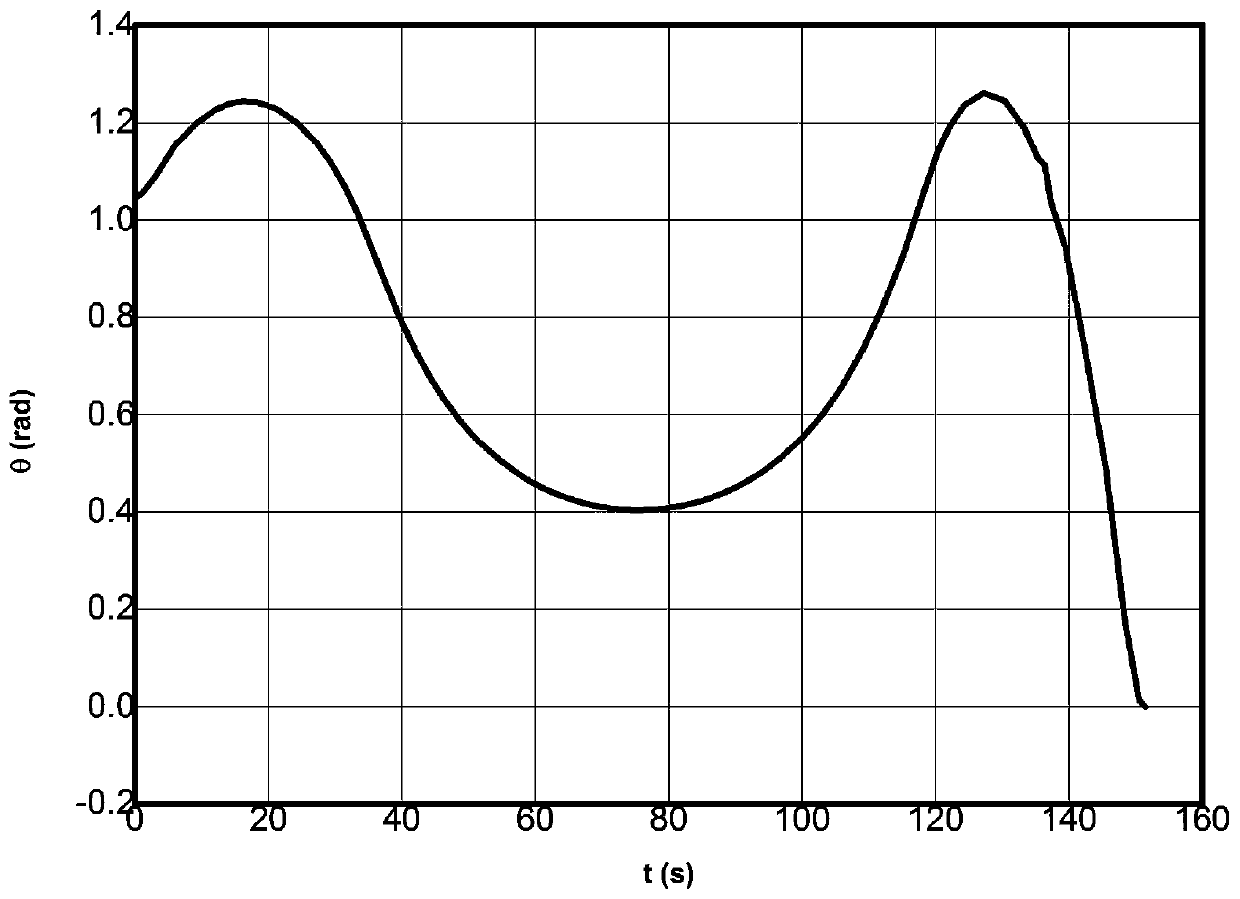
Path planning optimum control method for deck of ship-based aircraft based on NSP algorithm
ActiveCN110412877ASolve precise path planningSolving Optimal Control ProblemsNavigational calculation instrumentsAdaptive controlState variableOptimal control
The invention discloses a path planning optimum control method for a deck of a ship-based aircraft based on an NSP algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of automation and optimum control overship-based aircrafts. Based on analysis of deck path planning of the ship-based aircraft and optimum control over deck path planning, the problem of an original method is solved that path planning andcontrol cannot be combined, and the deficiency is overcome that an obtained path cannot easily meet terminal constraint, and in combination with motion constraint, barrier constraint, control variable and state variable constraint and terminal constraint of sliding of the ship-based aircraft, a path planning optimum control model of the deck of the ship-based aircraft is constructed; based on a Newton iteration method, a symplectic algorithm and a pseudo-spectral method, the NSP algorithm is provided for quickly solving the optimum control model, the problems exist in accurate path planning and control of the deck of the ship-based aircraft are effectively solved, the calculation efficiency and precision are improved, and the obtained path can strictly meet the terminal constraint. According to the path planning optimum control method, a reasonable solution can be provided for the problems existing in path planning and control of the deck of the ship-based aircraft.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV +3
Visual localization system of industrial robots and method
InactiveCN106965179ARealize automatic controlAchieve positioningProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual localizationSimulation
The present invention relates to a visual positioning system and method for industrial robots, wherein the system includes a plurality of industrial robots, a plurality of unmanned aerial vehicles corresponding to the industrial robots and a host computer, and each of the industrial robots passes through the The drone communicates with the host computer to exchange position data and request data. The industrial robot is equipped with a first battery and a first power management module, and the drone is equipped with a second battery and a second power management module. . The present invention can obtain position information through binocular recognition of industrial robots, and obtain position data through GPS positioning through drones, and correct and transmit data to the positions of landmark buildings in the map stored in the host computer. Multiple industrial robots It can cooperate with each other, and is especially suitable for the unified management of large-scale group robots. The upper computer can realize map update and path planning. The structure is simple, the application is convenient, and it is suitable for large-scale promotion and application.
Owner:浙江谱麦科技有限公司
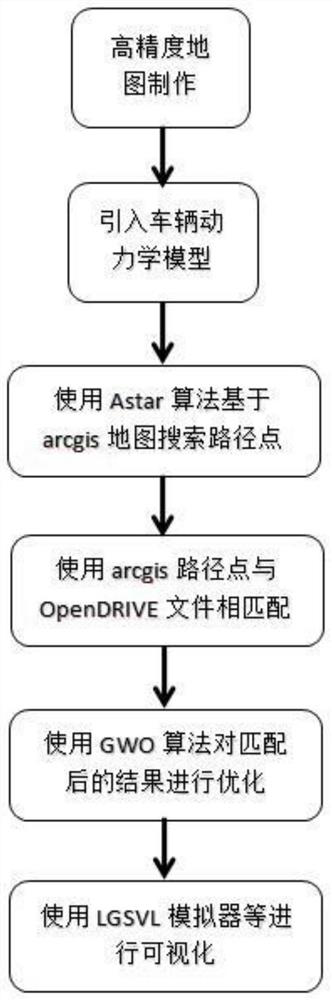
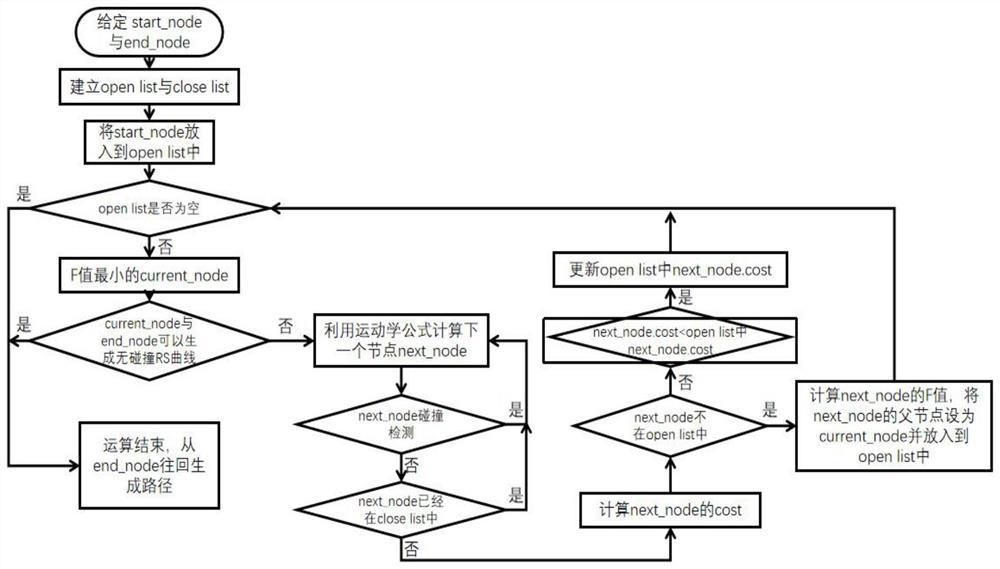
Map path planning method based on combination of improved Astar algorithm and grey wolf algorithm
PendingCN112082567ARealize path planningInstruments for road network navigationForecastingVisualizationVisulation
The invention discloses a map path planning method based on combination of an improved Astar algorithm and a grey wolf algorithm. The map path planning method specifically comprises the following steps: constructing a high-precision map based on data acquisition equipment; introducing a vehicle kinematics model into the Astar algorithm, and importing the vehicle kinematics model into an xml file of the OpenDRIVE; searching an optimal path point in the arcgis derived map data by using the Atar algorithm, and generating a traceable motion track of the vehicle by combining an RS curve with the optimal path point searched by the Atar algorithm; matching the point, line and plane data of the arcgis with thexml file of the OpenDRIVE; performing safety and comfort optimization on a matched resultby using a GWO algorithm, and selecting an optimal path; after the optimal path is selected from the OpenDRIVE file, the color of a root and the like on the corresponding optimal path can be changed,and performing visualization by using an LGSVL simulator and the like.
Owner:上海智驾汽车科技有限公司
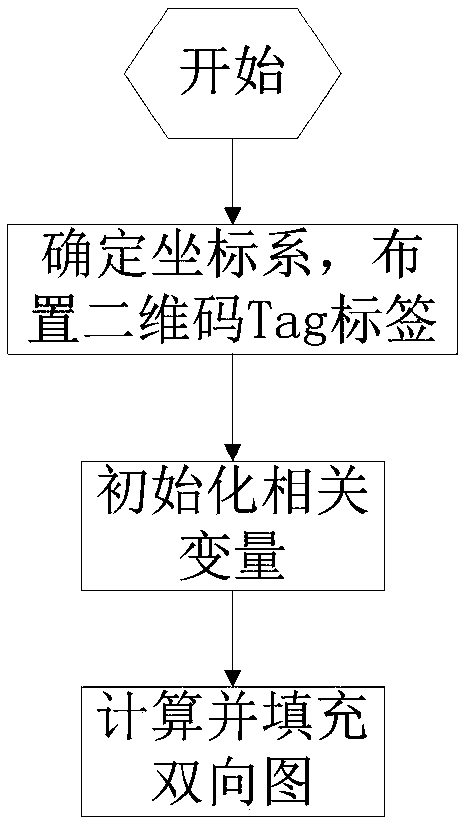
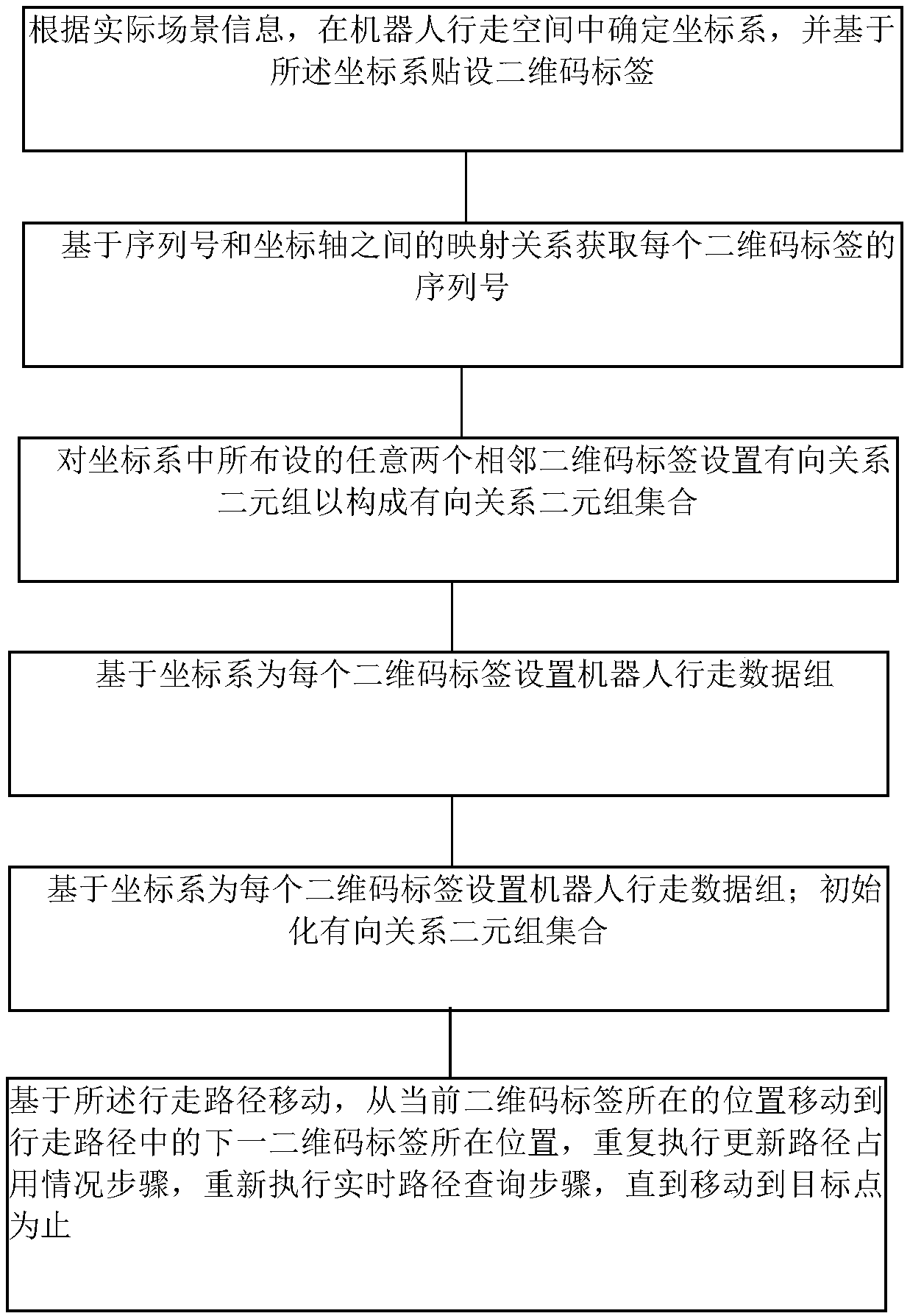
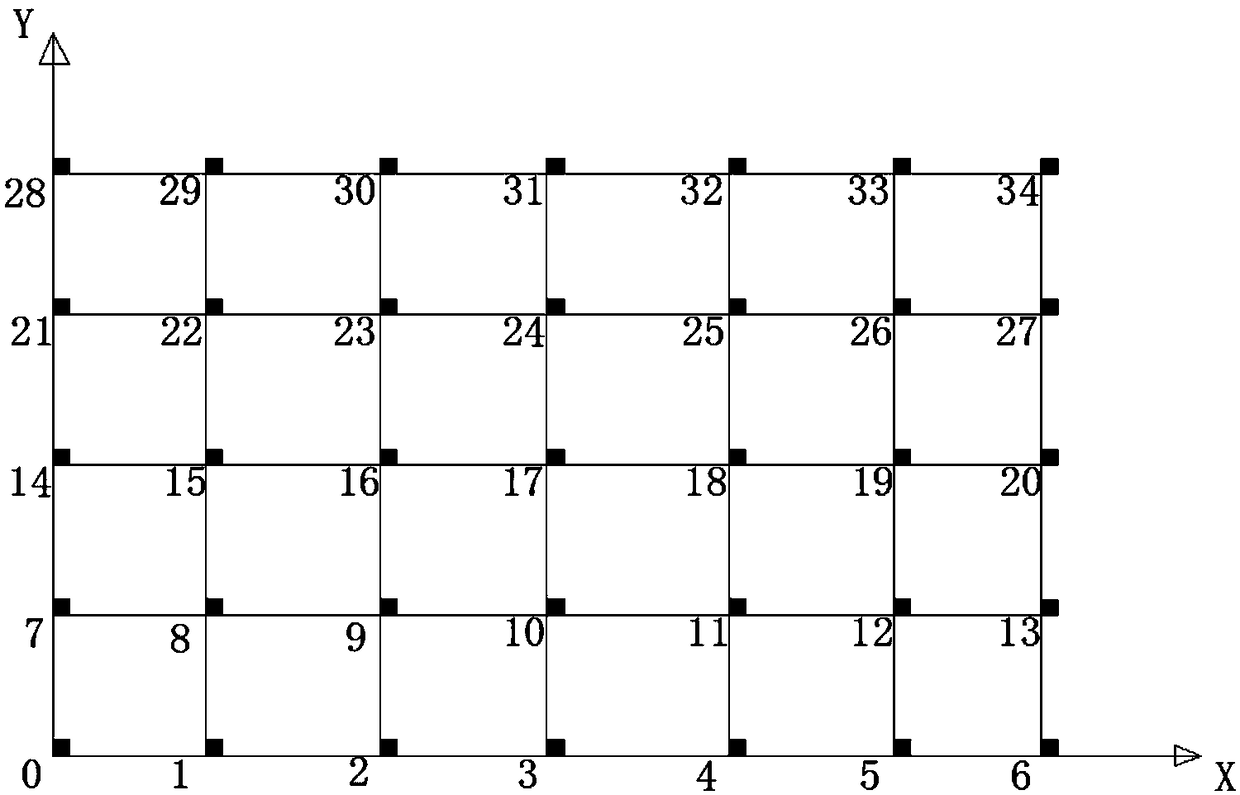
Multi-robot path dynamic planning method
ActiveCN108107895ASmall amount of calculationRealize path planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsRobot path planningDynamic programming
The present invention relates to a multi-robot path dynamic planning method, and the objective of the invention is to solve the problem of multi-robot path dynamic planning in a grid map. The method comprises the steps of: 1, pasting two-dimensional code tags according to an actual condition, and ensuring unique tag numbers, the same direction and the same spacing of the two-dimensional code tags;2, recording and initializing the tag numbers and index serial numbers, and forming a one-to-one correspondence relation; 3, constructing a digraph in a data structure according to two-dimensional data in an actual map; 4, initializing a correlation matrix to calculate the shortest path; 5, initializing a variable, arranging record data and employing the record data to fill in the digraph; 6, employing a Floyd algorithm to calculate the shortest path; 7, when a robot reads the two-dimensional codes to perform path request, adding partial graph boundary weight values; 8, allowing the robot toobtain a total path to a terminal point and performing execution in order; and 9, reducing a partial graph boundary weight value when the robot starts, adding another partial graph boundary weight value, performing reciprocating in this way, and continuously achieving the dynamic path planning of the robot. The multi-robot path dynamic planning method can solve the multi-robot path planning problem in the grid map, and is simple, small in computing amount and good in dynamics.
Owner:HEFEI HRG XUANYUAN INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
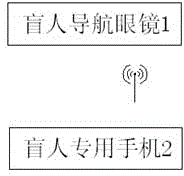
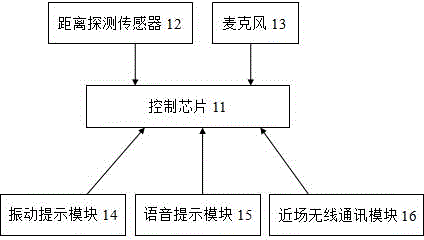
Blind navigation system
InactiveCN104921908ARealize early warningRealize traffic light recognitionWalking aidsRoute planningNavigation function
The invention discloses a blind navigation system, and relates to the technical field of navigation for the blind going out. A pair of blind navigation glasses and a blind special cell phone are connected through a glasses near-field wireless communication module and a cell phone near-field wireless communication module and are combined with a remote data processing center so that an intelligent blind navigation function can be achieved; an obstacle is detected through distance detection devices such as an ultrasonic distance detection device and an infrared distance detection device; when the blind encounters the obstacle in front, the distance and direction of the obstacle are measured through a distance detection sensor and then transmitted to a distance detection module of the blind special cell phone through the glasses near-field wireless communication module, and the blind is informed of the obstacle in front through a vibration prompting module and a voice prompting module after processing. Functions of obstacle early warning, traffic light recognizing, route planning, real-time positioning, distress information sending and additional information inquiring can be achieved.
Owner:常州市瑞君医疗科技有限公司
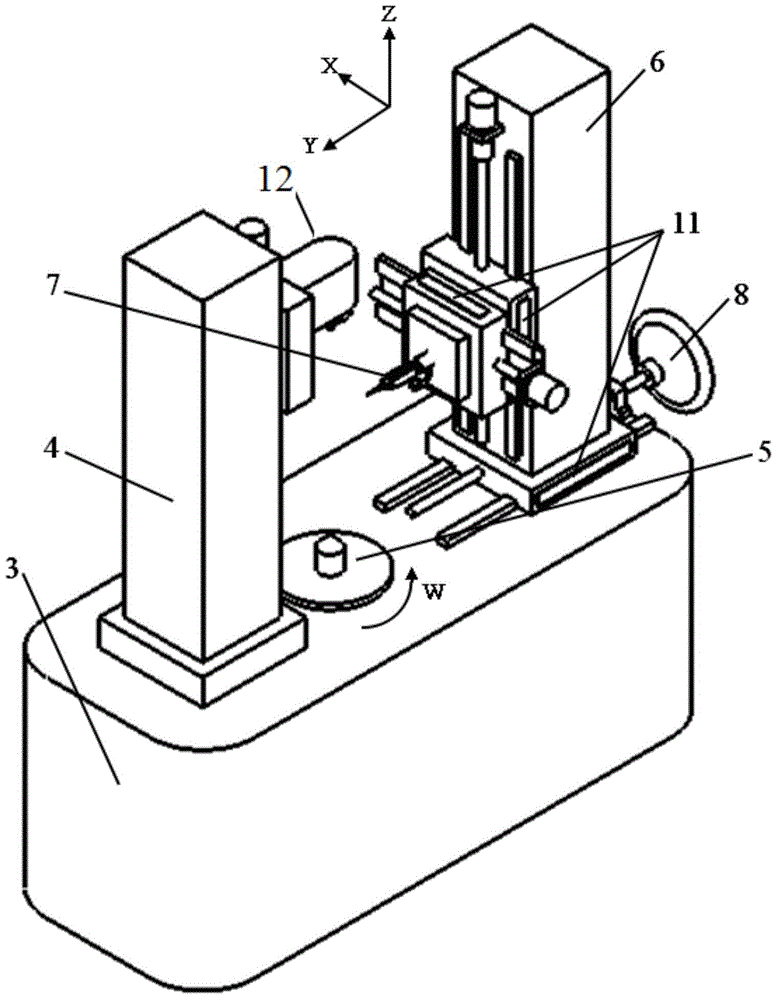
Three-axis linkage-based complicated part accurate measurement central path planning realizing method and device
ActiveCN104154849ARealize stepless adjustmentEasy to detectUsing electrical meansUsing optical meansCircular discElectric sense
The invention provides a three-axis linkage-based complicated part accurate measurement central path planning realizing method and a device. the device comprises a base, a workpiece vertical column, and a measurement vertical column, wherein the measurement vertical column is provided with an electric sensing head capable of moving vertically and horizontally. Horizontal movement of the measurement vertical column is used for contotrlling the distance between the measuring head and the center of a spindle rotating shaft system, stepless adjustment of a basic circle can be realized, a series of basic circle discs do not need to assist measurement of a gear, the detection process is simplified, and detection errors due to wear of the basic circle discs can be solved. Through controlling vertical movement, horizontal movement of the measuring head and linkage of the spindle rotating shaft system, control of the measuring trajectory of the measuring head can be realized respectively, and helix, tooth profile and pitch error of the gear with any base circle radius value within the measuring range can be fully automatically measured. In addition, path planning of an eccentric gear can be realized, and full-automatic measurement on helix, tooth profile and pitch error of the eccentric gear can be realized.
Owner:西安秦川思源测量仪器有限公司
Path planning method based on DBQ algorithm
InactiveCN110389591AHigh precisionFast convergencePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPlanning approachRobot path planning
The invention belongs to the field of robot path planning, and particularly relates to a path planning method based on DBQ algorithm. The path planning method provided by the invention performs improvement by reinforced learning of the action selection mechanism in the Dyna-Q algorithm, and mainly solves the following three path planning problems: 1, solving the problem of low learning efficiencyof the robot in the early stages when learning in the environment; 2, improving the accuracy of robot path planning; and 3, speeding up the convergence of the algorithm.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
AGV system path planning method and system
InactiveCN108253985ARealize path planningReduce manufacturing costInstruments for road network navigationVehicle position/course/altitude controlPlanning methodComputer science
The invention discloses an AGV system path planning method and system. According to the AGV system path planning method and the system, the article is transported through an AGV, the latest state information of the AGV is acquired in real time, the control range includes a crossroad or a preset avoiding road when the AGV reaches the control range; the AGV reaching the control range is controlled in a way that the AGV arriving earlier goes into the control range earlier and the AGV arriving late keeps clear, so that the path of an AGV system is planned, the production cost of a battery is lowered, and the production efficiency of the battery is also improved.
Owner:安徽谦如智能科技有限公司
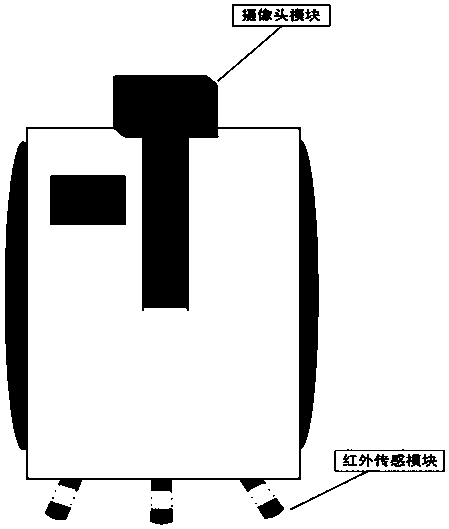
Implementation method of agricultural robot based on GPS positioning and automatic obstacle avoidance
PendingCN111077890ARealize path planningRealize automatic drivingPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesAgricultural engineeringRoad surface
The invention discloses an agricultural robot implementation method based on GPS positioning and automatic obstacle avoidance. The method comprises the steps: obtaining positioning information througha GPS positioning module, carrying out path planning, and obtaining an optimal path; acquiring road condition image information right ahead the agricultural robot by using a camera module, and acquiring the road condition information right below the agricultural robot by using an infrared sensing module; calculating a relative position of an obstacle and the agricultural robot and progressible positions in a road surface, and screening out an optimal position from the multiple progressible positions; making the agricultural robot avoid the obstacle to reach the optimal position; and in combination with path information of the GPS positioning module, making the agricultural robot continue to advance to the next optimal position point till that the agricultural robot reaches a target position. The agricultural robot can be ensured to work normally when facing the obstacle, and working efficiency of the agricultural robot is improved.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
High-speed rotor aircraft path planning method based on BBO optimized artificial potential field
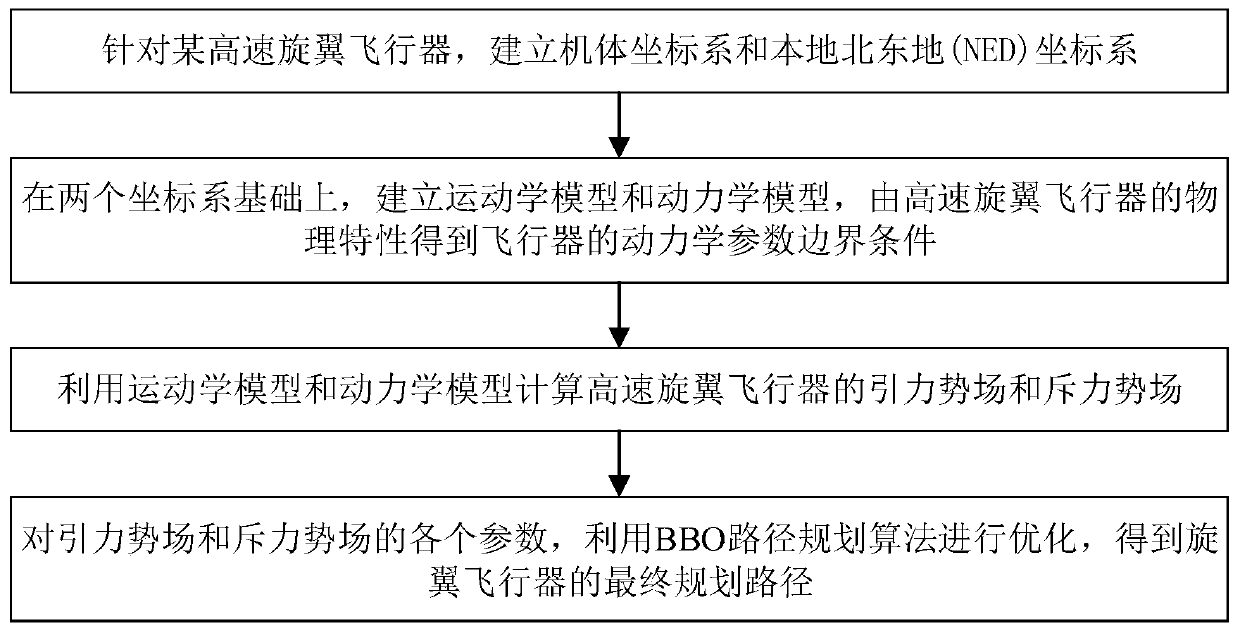
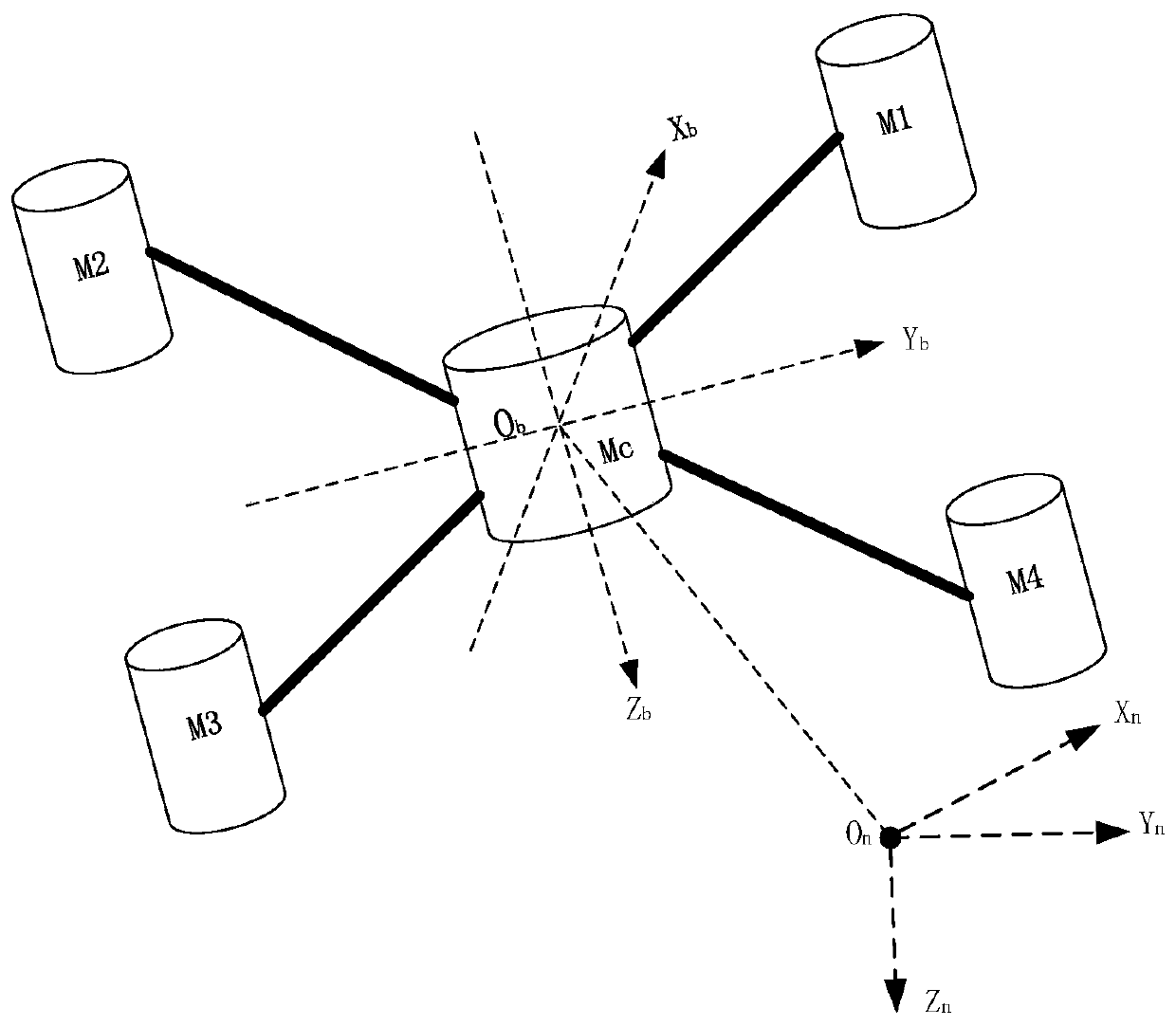
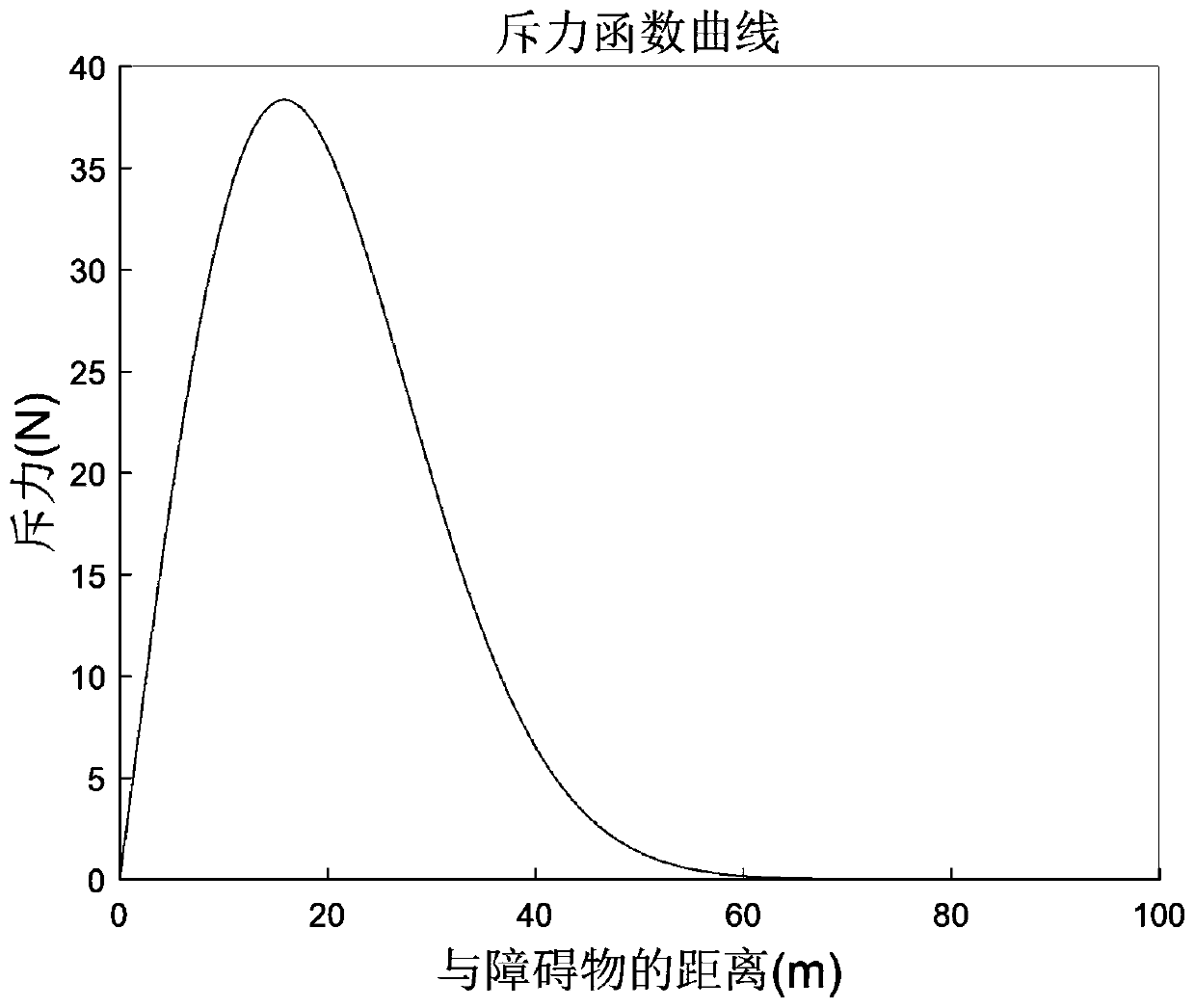
ActiveCN109870906ASimple structureFast operationVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlMassive gravitySimulation
The invention discloses a high-speed rotor aircraft path planning method based on a BBO optimized artificial potential field, and belongs to the field of aircraft intelligent task planning. The methodcomprises the following steps of establishing a body coordinate system and a local north-east ground coordinate system for a certain high-speed rotor aircraft, establishing a kinematic model and a kinetic model on the basis of two coordinate systems, and obtaining kinetic parameter boundary conditions of the aircraft through the physical characteristics of the high-speed rotor aircraft; computinga gravitational potential field and a repulsive potential field of the high-speed rotor aircraft by utilizing the kinematic model and the kinetic model; optimizing parameters of the gravitational potential field and the repulsive potential field through a BBO path planning algorithm in order to obtain a final planning path of the rotor aircraft. The algorithm disclosed by the invention is simplein structure and fast in operation speed, the requirements for on-line real-time computation can be well met, the path distance is reduced, the average speed of the aircraft is improved and is close to the limit design speed of the aircraft, and the route planning performance is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
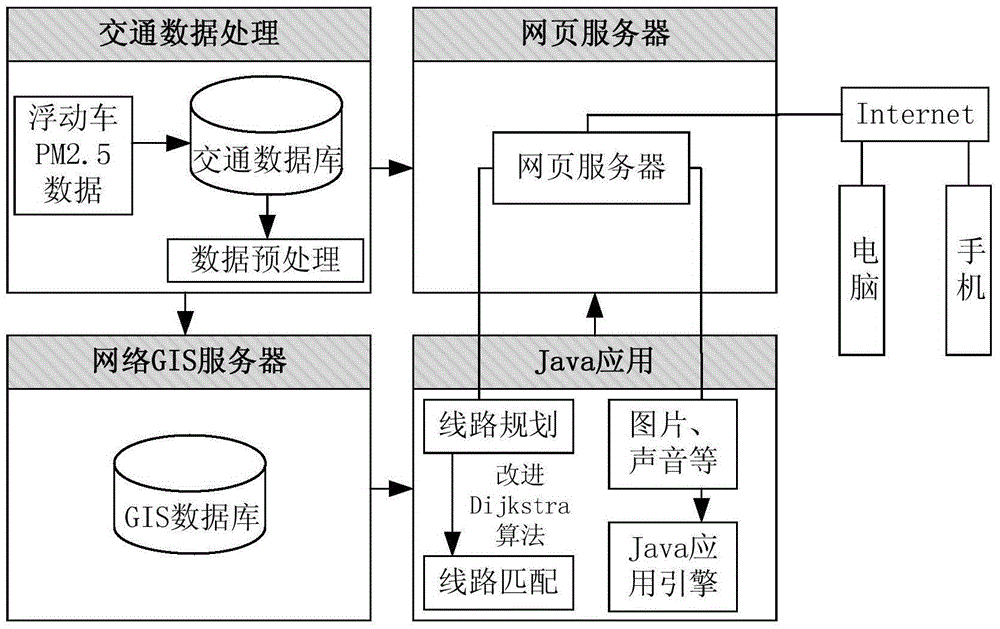
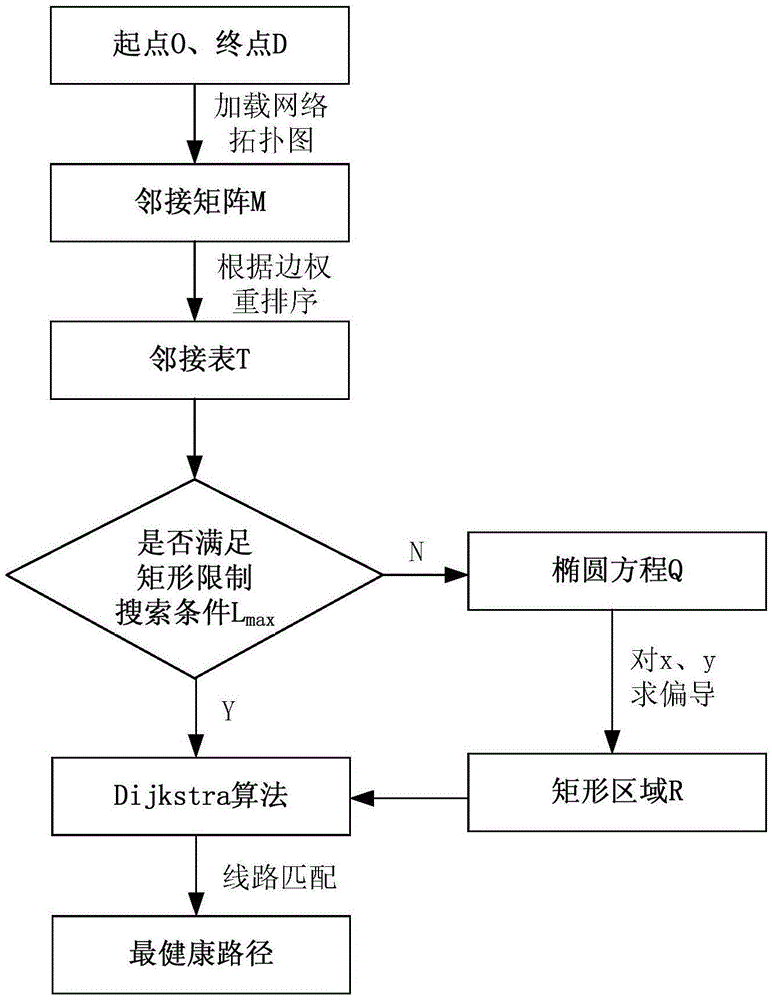
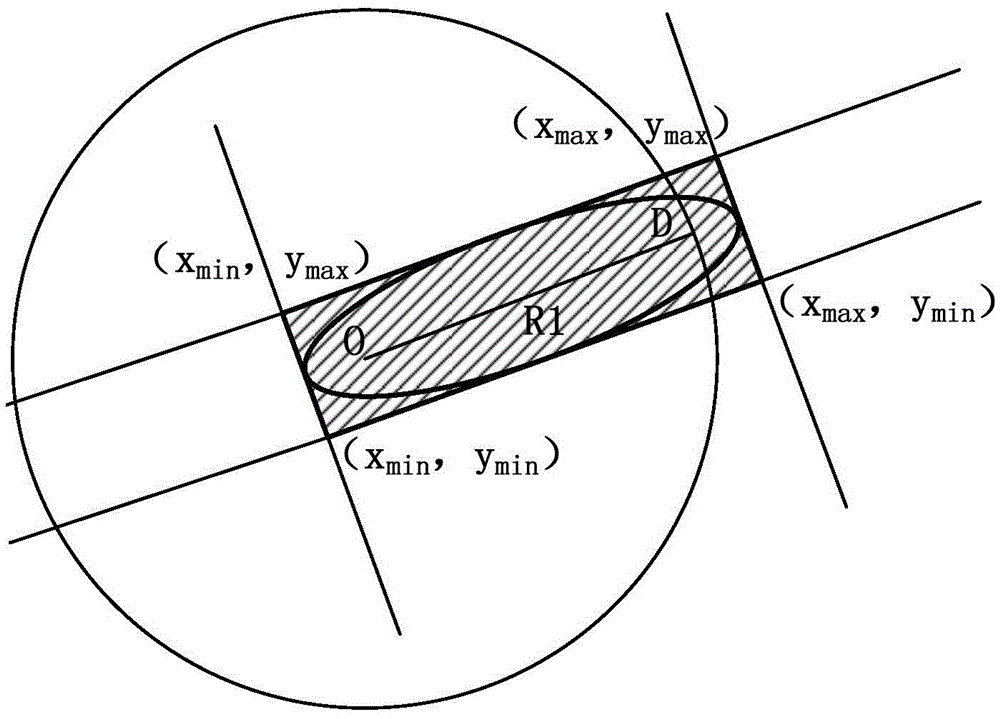
Apparatus and method for route planning based on PM2.5 healthy trip
ActiveCN105547310AEfficient planningNarrow down the search spaceInstruments for road network navigationInformation transmissionMobile device
The invention discloses an apparatus and method for route planning based on a PM2.5 healthy trip. The apparatus comprises three parts of a vehicle-mounted PM2.5 detector, an information transmission module, and a server terminal, wherein the information transmission module includes a GPS module and a GPRS module; the server terminal includes a route planning module; and the PM2.5 detector is mounted on a floating vehicle and is connected to the information transmission module, which is connected to the server terminal. A mobile device of a user can easily access data in the server terminal by means of a browser. According to the method, an improved Dijkstra algorithm is adopted, an integrated PM2.5 concentration is mainly taken as impedance, and a minimum total concentration is taken as a target. A healthy trip is planned according to an optimized function taking a PM2.5 optimal route as the target.
Owner:南京艾特斯科技有限公司
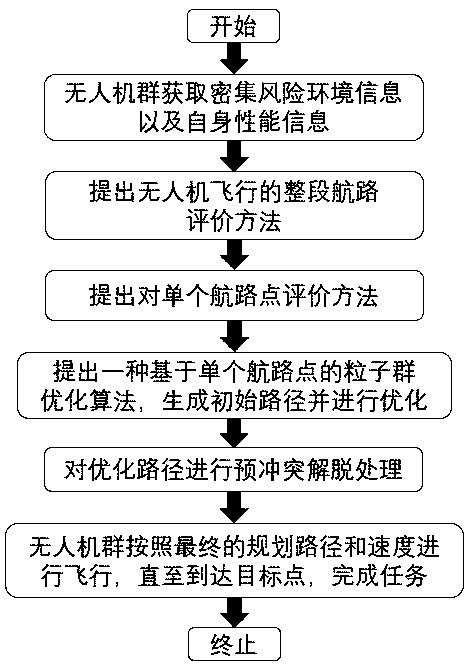
Unmanned aerial vehicle group path planning method
ActiveCN111256681AFly efficientlyReduce flight costsNavigational calculation instrumentsUncrewed vehicleTraffic system
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle group path planning method which comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring information of an unknown environment, including positions of a starting point and a target point, coordinates of an obstacle, possible radar and missile risks and the like; when the unmanned aerial vehicle group plans a path, needing to consider the performance ofthe unmanned aerial vehicle, such as a deflection angle, a pitch angle and a flight height; on the basis, enabling the unmanned aerial vehicle to select a path preferentially through calculation of aparticle swarm optimization algorithm, and achieving path planning of the whole unmanned aerial vehicle group. According to the invention, path planning of the unmanned aerial vehicle group in a denserisk environment can be realized, so that the unmanned aerial vehicle group can fly efficiently to cooperatively complete tasks. Based on the path planning of the unmanned aerial vehicle group, the research on the path planning method of the unmanned aerial vehicle group is carried out from the two aspects of improving the safety and high efficiency of the air traffic system, and the method has important significance in ensuring the flight safety of the unmanned aerial vehicle, reducing the flight cost, increasing the airspace capacity and improving the operation efficiency of the air trafficsystem.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Outdoor targeting robot
The invention discloses an outdoor targeting robot. The outdoor targeting robot comprises a chassis; a target body capable of rotating is mounted on the chassis; a skeleton, a base plate, a steering mechanism, a driving mechanism, a controller mounting plate, a wireless communication unit, a controller, a power supply body and an autonomous navigation device are mounted in the chassis; the drivingmechanism, the steering mechanism, the controller and the wireless communication unit are electrically connected with the power supply body; the controller is fixedly mounted on the controller mounting plate; the controller is in control connection with the autonomous navigation device, the steering mechanism and the driving mechanism; and the controller is in communication connection with an upper control center through the wireless communication unit. The outdoor targeting robot adopts an autonomous navigation technology to achieve such functions as path planning and autonomous obstacle avoidance, controls a robot driving mechanism and the steering mechanism to autonomously move from an initial point or a target point to a next target point or terminal according to specific scene conditions, realizes intelligent movement and control, and improves the training personification degree.
Owner:FUJIAN QUANZHOU HIT RES INSTIUTE OF ENG & TECH
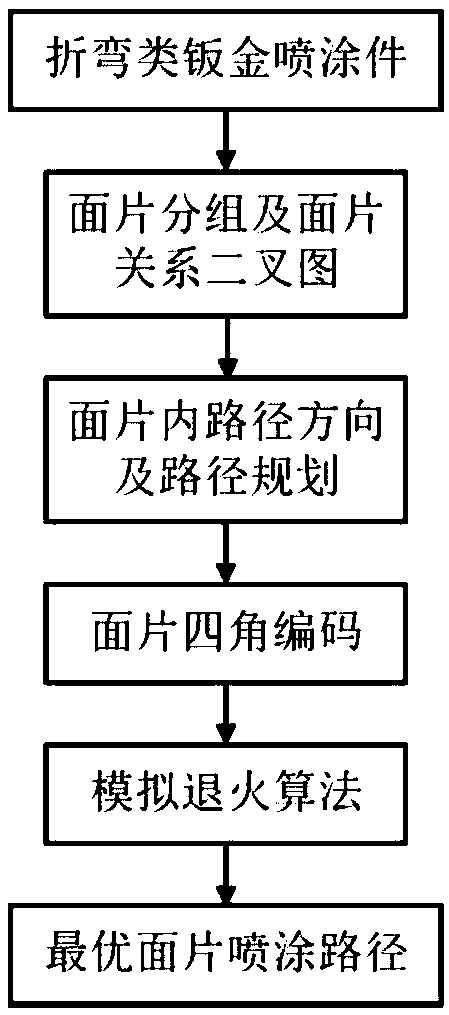
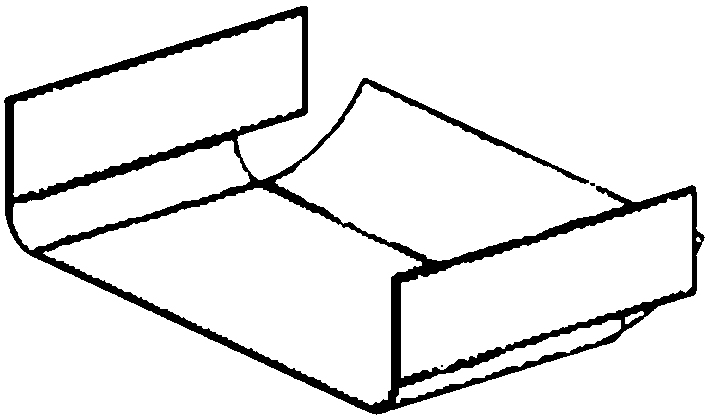
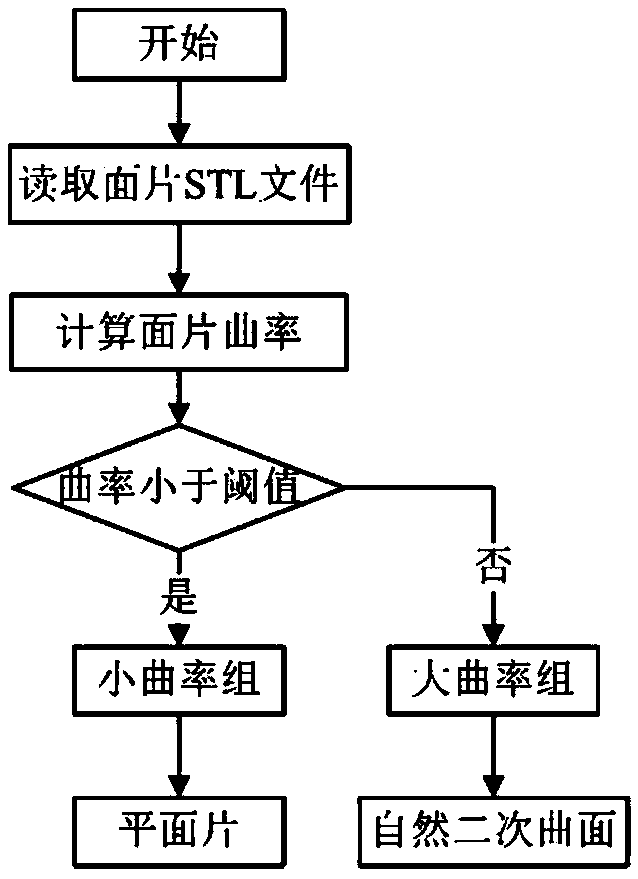
Spray path planning method for bending type sheet metal parts robot
The invention relates to a spray path planning method for a bending type sheet metal parts robot. The method comprises the following steps: 1) by using the relational binary tree method, dividing thebending type sheet metal parts to be sprayed into a plurality of dough pieces, sorting and numbering the dough pieces, determining the main direction of spraying and the spraying direction in each dough piece; 2) considering the spraying direction in the dough piece and the transition form between the dough piece, completing the S-shaped path plan of each dough piece reciprocating along the spraying direction in the dough piece, and performing four-corner coding for each dough piece; 3) using the improved simulated annealing algorithm, completing the path combination optimization between multi-dough pieces, obtaining the final optimal planning path. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of fast group numbering, simple calculation, improved efficiency, wide application field and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Cam experiment teaching aid
The invention discloses a cam experiment teaching aid which comprises a machine frame, a bidirectional cam set mechanism, a bidirectional push plate mechanism, a writing desk mechanism and a bottom transmission mechanism. The bidirectional cam set mechanism, the bidirectional push plate mechanism, the writing desk mechanism and the bottom transmission mechanism are arranged on the machine frame, and the bottom transmission mechanism controls the bidirectional cam set mechanism, the bidirectional push plate mechanism and the writing desk mechanism to move. The bidirectional cam set mechanism comprises an X-direction cam set, a Y-direction cam set, an X-direction cam shaft, a Y-direction cam shaft, an X-direction cam hoisting plate, a Y-direction cam hoisting plate, an X-direction pulley, a Y-direction pulley, an X-direction guide rod and a Y-direction guide rod. The writing desk mechanism comprises a work table, a flange linear bearing, a pen clamp, a pen rod, a hoisting cam and a hoisting ejector pin. The work table is fixedly arranged on the machine frame through the flange linear bearing, and the pen clamp is arranged on the work table. The variable combined cam mechanism is adopted and combined with a multi-level adjusting and controlling method, basic knowledge points of a cam, characters and drawings of complex figures can be demonstrated, and a concept of plane two-dimensional coding is adopted so that the complex figures can be projected to a matrix.
Owner:冠县民富物业管理有限公司
Mobile robot obstacle avoidance path planning method
PendingCN113296523AFlexible planning of obstacle avoidance pathsSolve environmental adaptabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesIn vehicleObstacle avoidance
The invention belongs to the field of local navigation of robots and intelligent vehicles. According to the specific technical scheme, the obstacle avoidance path planning method for the mobile robot comprises the following specific steps: 1, constructing a grid environment map based on working environment information acquired by a vehicle-mounted external sensor laser radar of the mobile robot; 2, calculating gravitation borne by the robot, an included angle between the gravitation and the horizontal direction, repulsive force and an included angle between the repulsive force and the horizontal direction by improving gravitation and repulsive force field functions; 3, calculating resultant force borne by the robot and an included angle between the resultant force and the horizontal direction; 4, calculating and storing the next position of the robot; 5, enabling the robot to move to the next position from the current position, and adding the corresponding step length every time the robot operates by one step; 6, judging whether the robot reaches a specified target point or not, and ending if the robot reaches the target point, if not, returning to the step 2. According to the method, the original potential field function is corrected to ensure that the robot reaches the specified target position, and robot path planning is realized.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Multi-AUV formation control method based on improved navigator virtual structure method
InactiveCN112731942AImprove stabilityIncrease flexibilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsObstacle avoidancePathPing
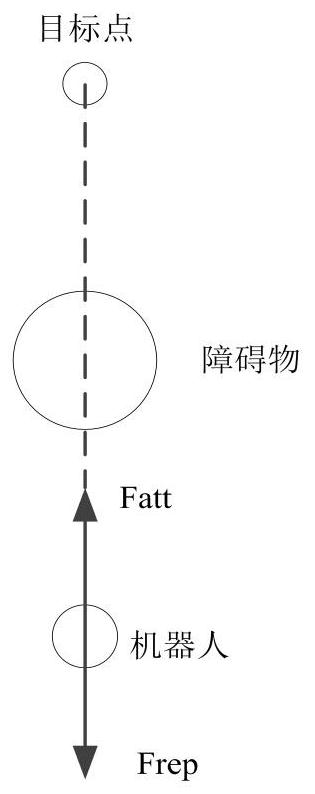
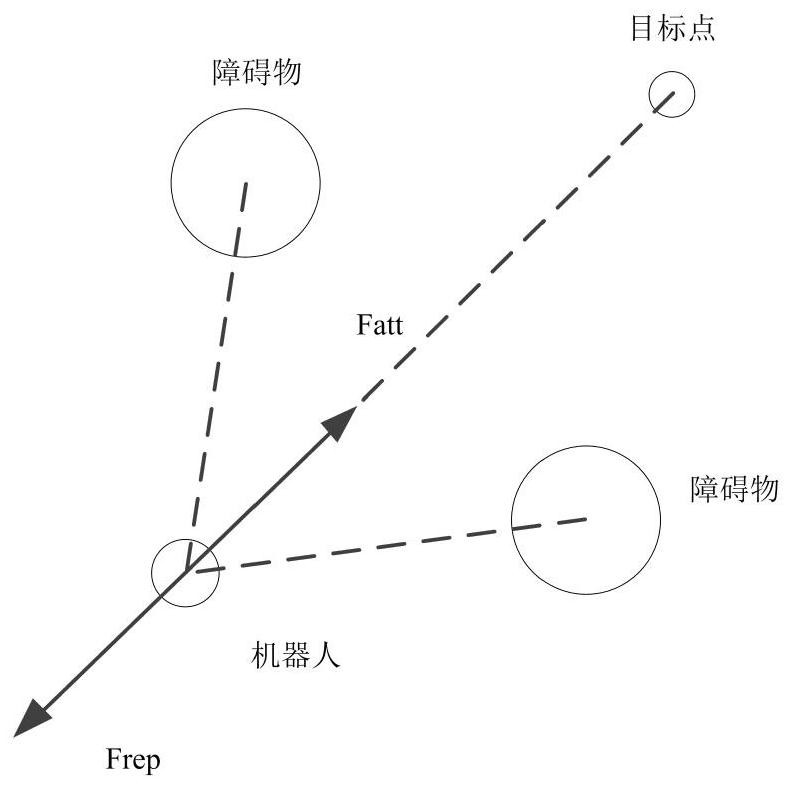
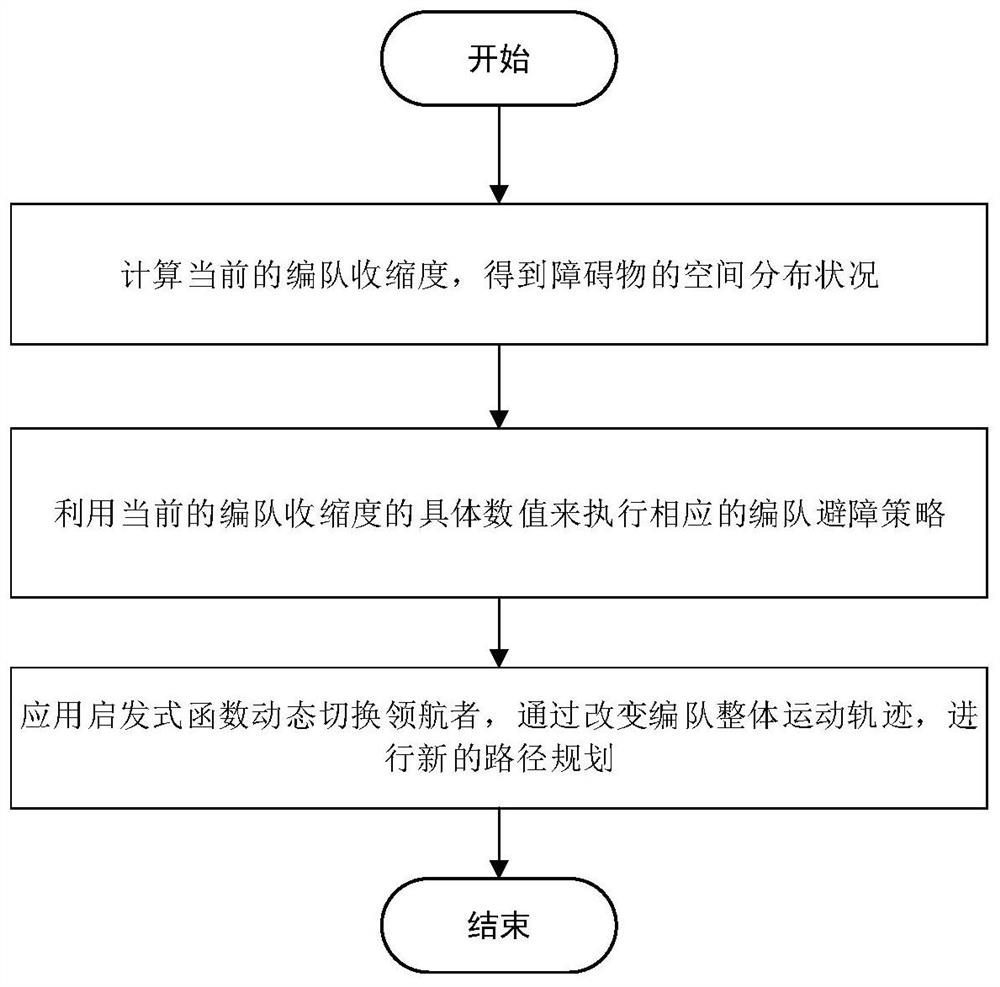
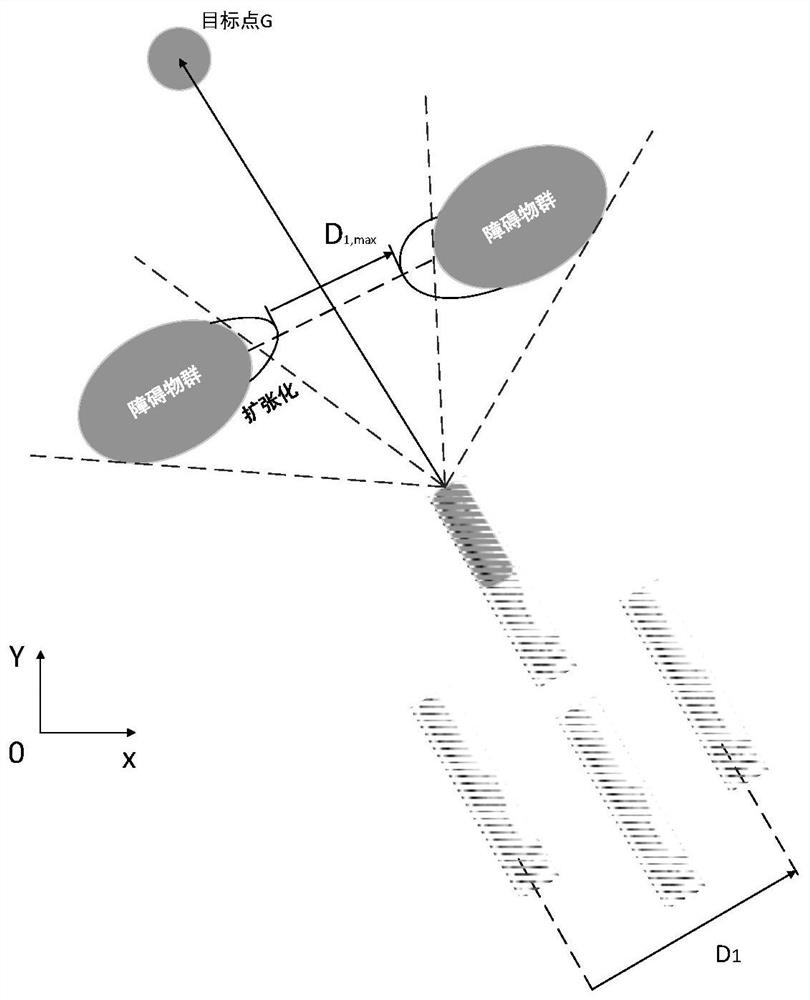
The invention belongs to the technical field of multi-AUV formation control, and particularly relates to a multi-AUV formation control method based on an improved navigator virtual structure method. According to the invention, path planning is effectively realized, and obstacles in the environment are effectively avoided. By improving the original navigator method and the virtual structure method, the problems that the formation obstacle avoidance flexibility of the virtual structure control method is poor and the centralized control of the traditional navigator method is insufficient are solved. According to the invention, efficient obstacle avoidance strategy selection is carried out according to the AUV formation shrinkage degree; the problem of poor obstacle avoidance flexibility of the virtual structure control method formation facing narrow space and other environments is solved by utilizing formation shrinkage; meanwhile, a dynamic navigator switching strategy is provided, and a heuristic evaluation function is introduced on the basis of a dynamic navigator switching method to serve as a judgment basis for selecting a new navigator. According to the method, efficient obstacle avoidance can be carried out while the formation stability and flexibility of the rigid structure are improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
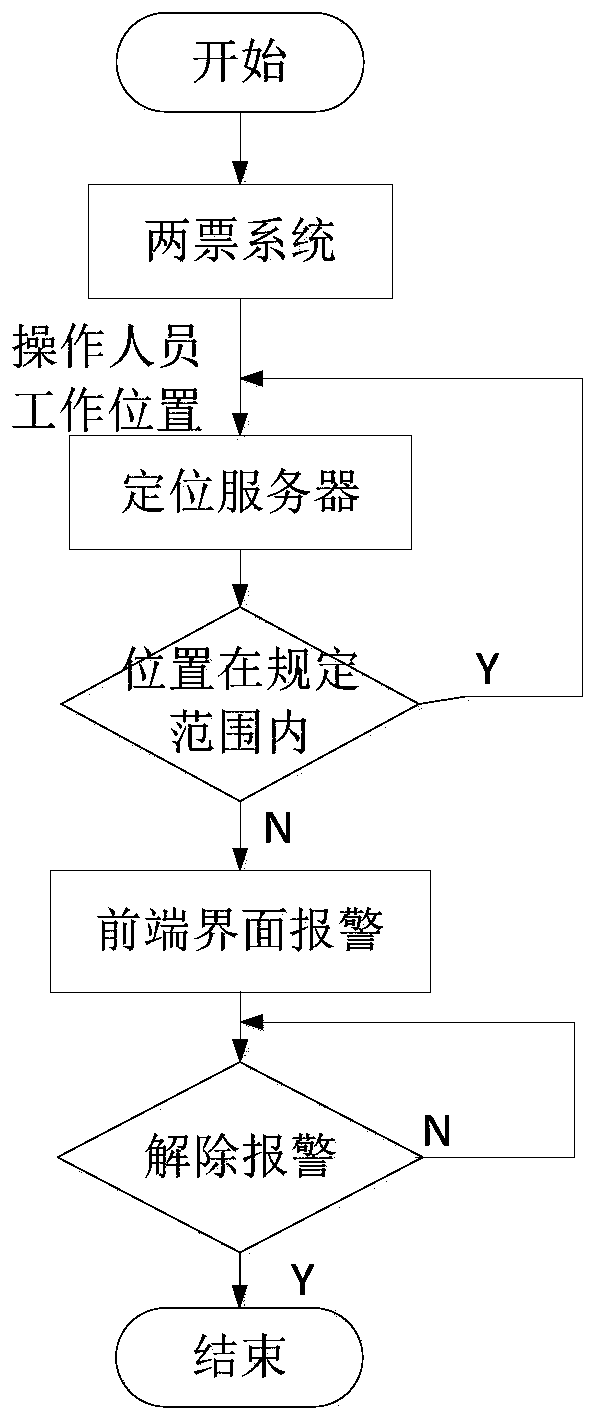
Substation operation personnel positioning system and method
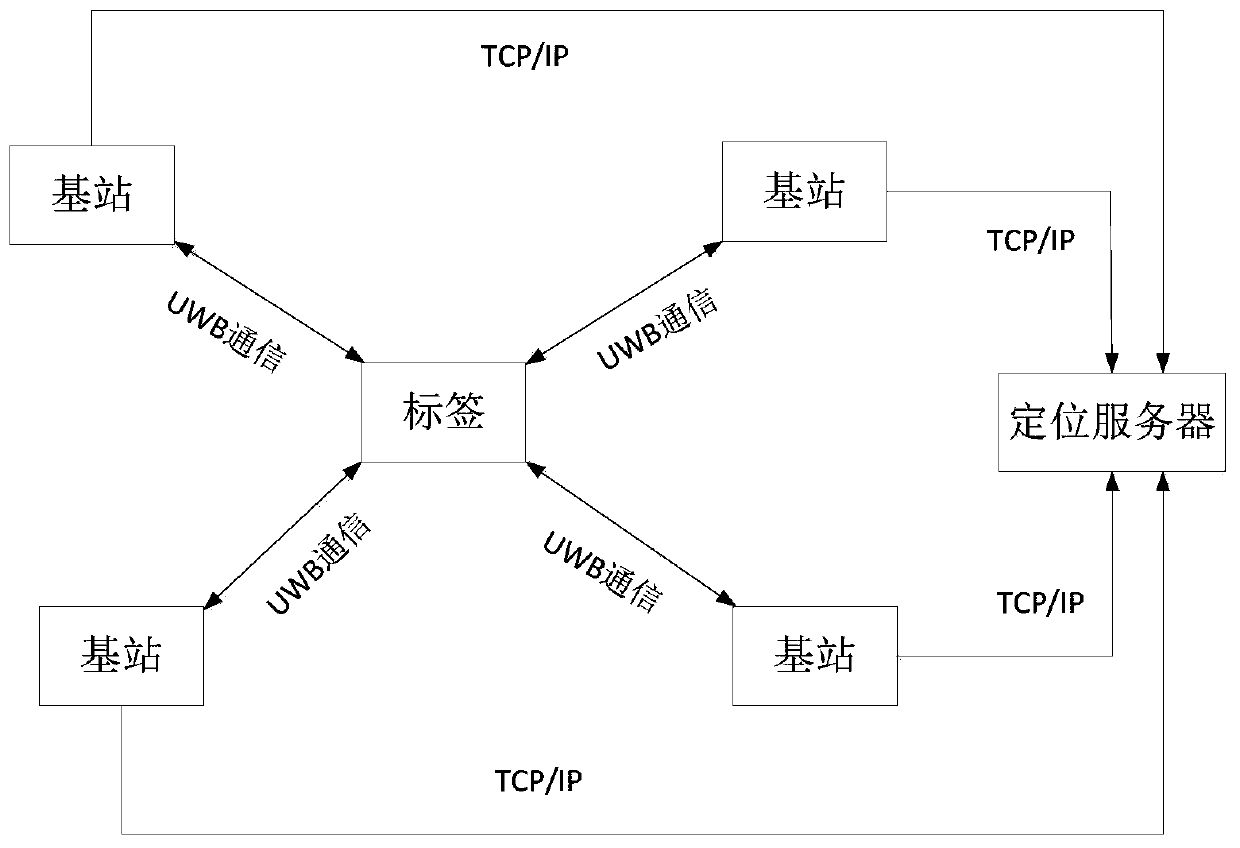
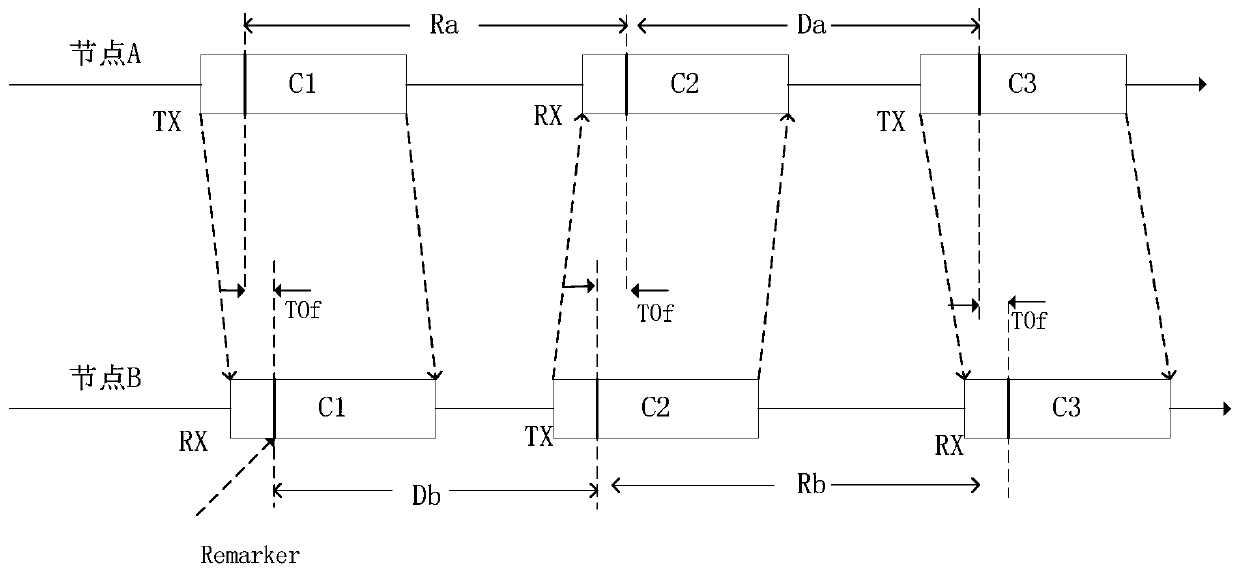
PendingCN109738865APrecise positioningHigh feasibilityPosition fixationLocation information based serviceUltra-widebandSleep state
The invention discloses a substation operation personnel positioning system and method. The system comprises a label, base stations and a positioning server. The label comprises a power management module, an acceleration sensor, a label processor and a distance measurement module based on an UWB (Ultra Wideband) technology. A power output end of the power management module is connected with powerinput ends of the acceleration sensor, the distance measurement module and the label processor. The distance measurement module realizes communication of the base stations and the label. According tothe system and the method, a DW1000 module is employed, and distance measurement precision of the DW1000 module reaches 15-30cm. Positioning is the positioning based on distance, so operation personnel locations can be positioned relatively accurately through improvement of the distance measurement precision, and system feasibility is improved. According to the system and the method, the acceleration sensor is added in the label, and when it is detected that an acceleration signal is smaller than a set threshold, the label enters a sleep state, so power consumption is reduced, and standby duration is extended.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +3
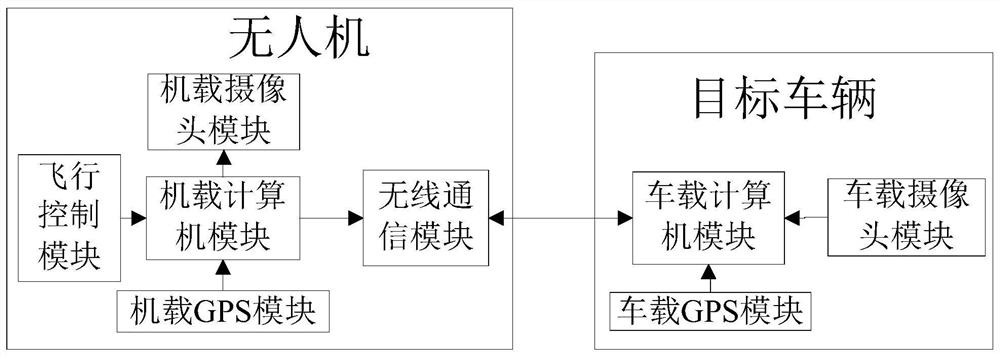
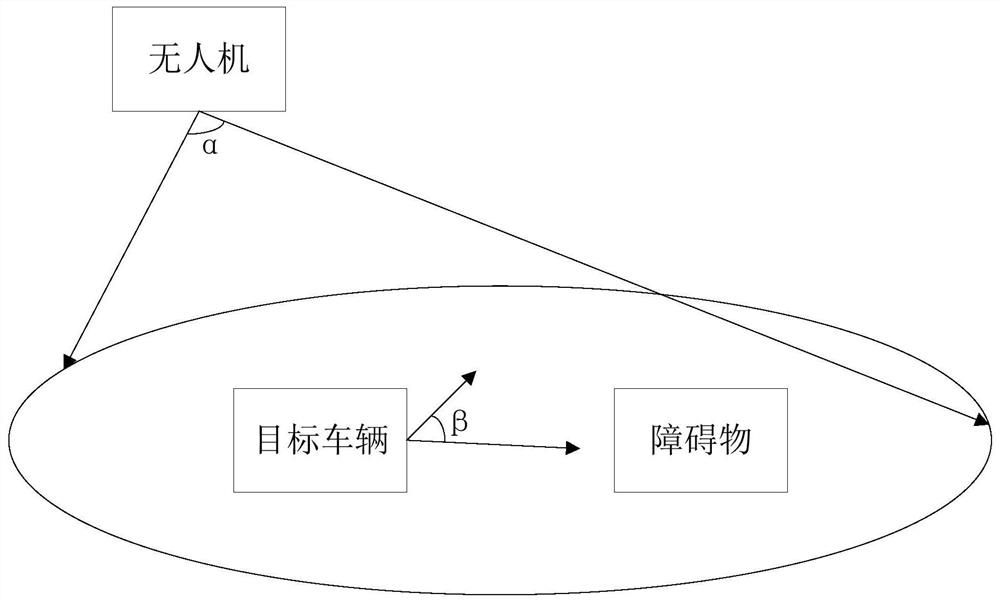
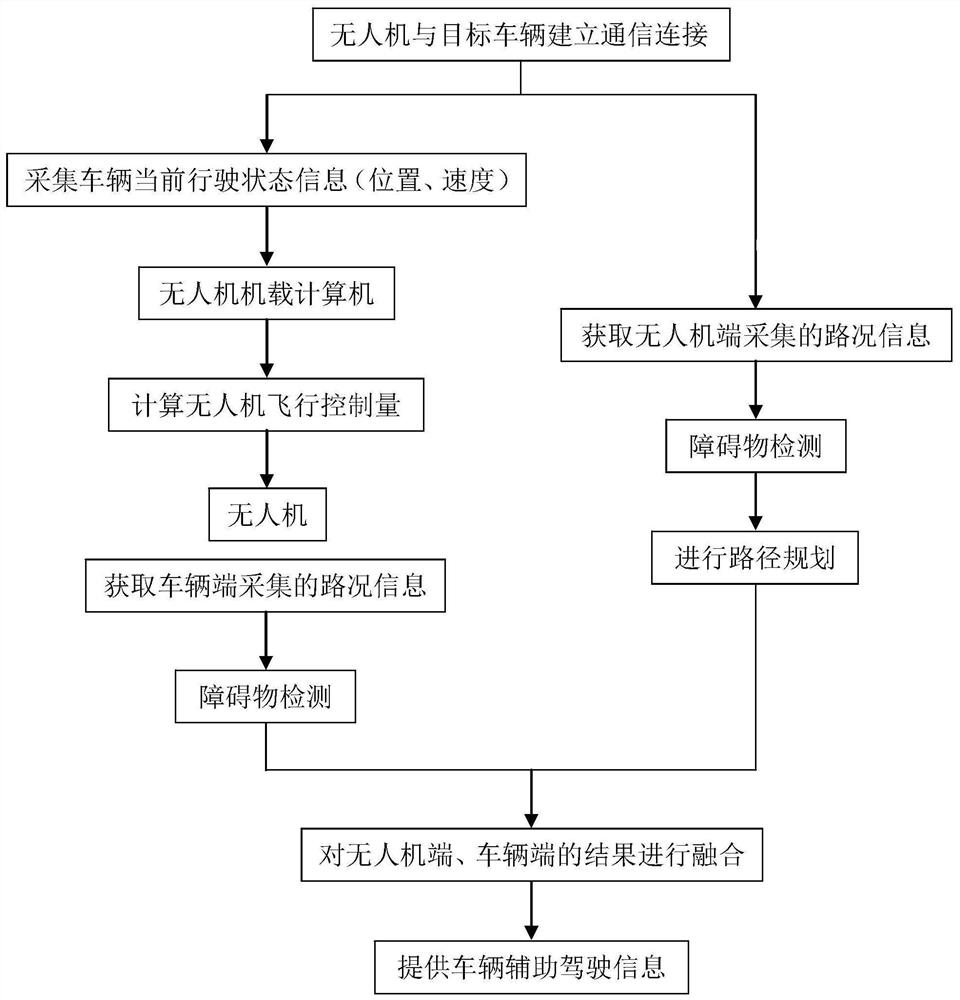
Vehicle auxiliary driving system and method based on unmanned aerial vehicle road perception
ActiveCN112817307AExpand coverageStrong Situational AwarenessPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesIn vehicleControl engineering
The invention discloses a vehicle auxiliary driving system and method based on unmanned aerial vehicle road perception. The vehicle auxiliary driving system is provided with an unmanned aerial vehicle and a target vehicle, wherein the unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a UAV-mounted controller, a UAV-mounted camera module, a UAV-mounted wireless communication module, a flight control module and a UAV-mounted GPS module; the target vehicle comprises a vehicle-mounted controller, a vehicle-mounted camera module, a vehicle-mounted wireless communication module and a vehicle-mounted GPS module; the UAV-mounted wireless communication module is wirelessly connected with the vehicle-mounted wireless communication module; the UAV-mounted camera module collects first road condition information in front of and around the target vehicle; the UAV-mounted GPS module locates a position of the unmanned aerial vehicle; the UAV-mounted controller calculates a position and a speed of the unmanned aerial vehicle; the vehicle-mounted camera module collects second road condition information in front of the target vehicle; the vehicle-mounted controller processes the first road condition information and the second road condition information; and the vehicle-mounted GPS module positions the position of a target vehicle. According to the vehicle auxiliary driving system and the method, the unmanned aerial vehicle is introduced into the vehicle auxiliary driving system for road perception, and the situation perception capability is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Mobile robot fusion path planning method for urban environment
InactiveCN113391633AReduce distanceRealize path planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesGlobal planningSimulation
The invention discloses a mobile robot fusion path planning method for the urban environment, and belongs to the technical field of mobile robot motion control. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a mobile robot judges whether global planning or local path planning is adopted according to obstacle information detected by a laser radar; 2, when the distance between the robot and the obstacle is greater than a set threshold value, an artificial potential field method is adopted to conduct a global path planning mode; and when the distance between the robot and the obstacle is smaller than a set threshold value, local obstacle avoidance is carried out by adopting a DDPG algorithm; and 3, the distance between the mobile robot and the target point is judged, and if the distance is smaller than a set threshold value, the task is completed; and if yes, repeating the first step and the second step until the target point is reached. According to the invention, the mobile robot can find a collision-free optimal path from the starting point to the terminal point.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com