Genetic evolution topological optimization improvement method
A technology of topology optimization and genetics, applied in the direction of genetic rules, genetic models, etc., to achieve the effects of improving stability, avoiding unit deletion by mistake, and avoiding inefficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
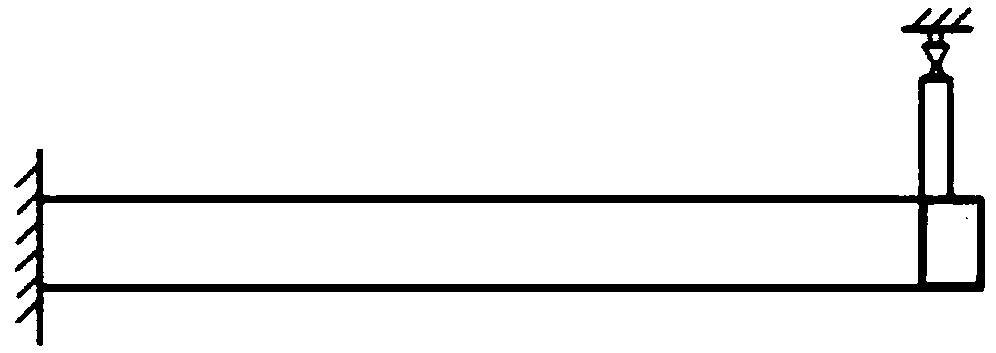
[0059] Embodiment 1: Take the famous "Zhou-Rozvany counterexample" as an example.
[0060] The present invention can be realized by using MATLAB to call ANSYS (finite element calculation) cyclically. The structure is as figure 2 As shown, the material is isotropic, the elastic modulus is 1, Poisson’s ratio is 0, the horizontal load intensity is 2, the vertical load intensity is 1, the volume constraint is 40%, the structure is divided into 100 elements, and the objective function Topology optimization for minimizing strain energy.
[0061] The specific implementation method is:
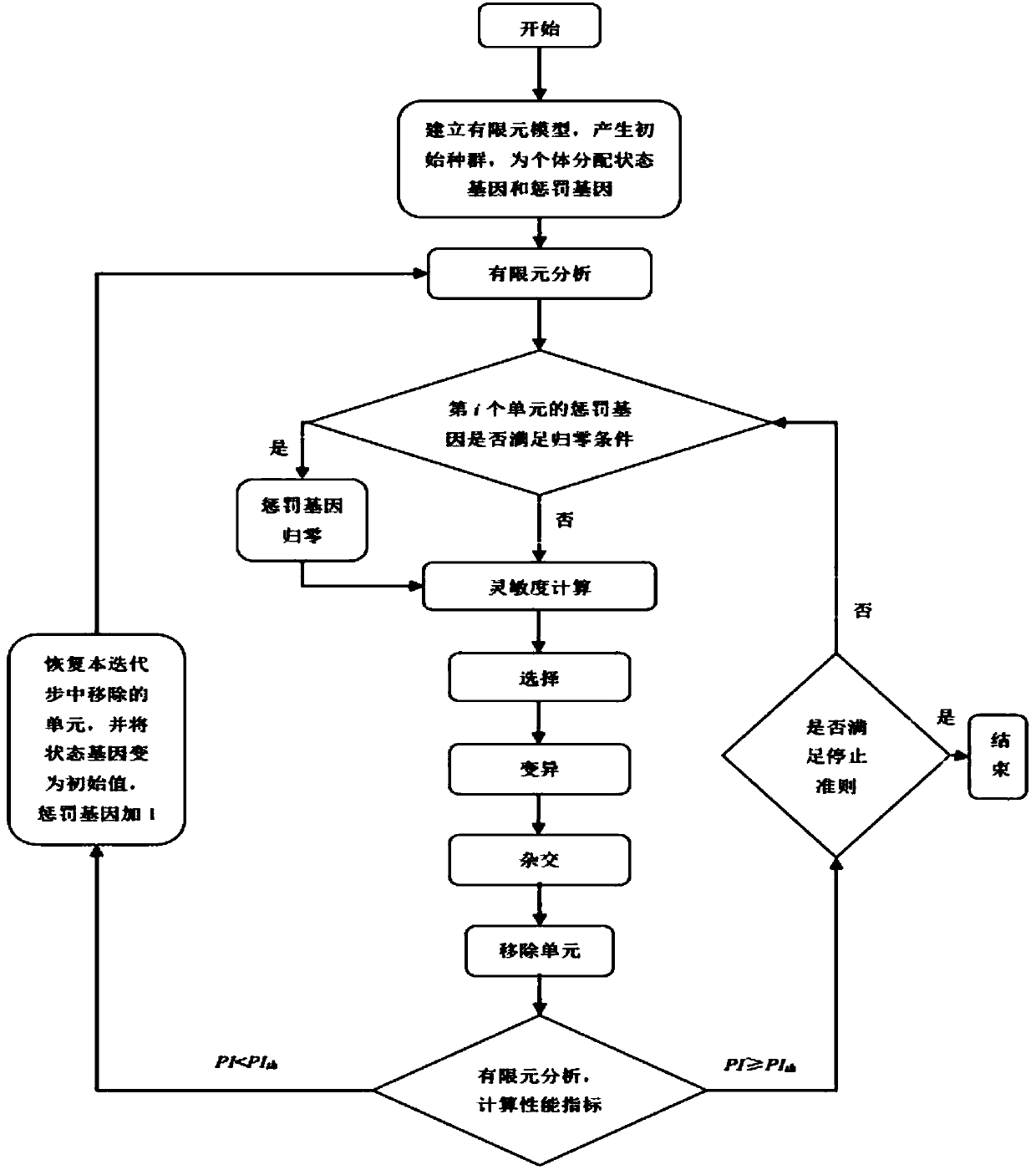
[0062] Step 1: According to the given boundary conditions and loads, define the initial design domain, and divide the finite element mesh discretization design domain.
[0063] Step 2: Set calculation parameters: PI th =0.347, penalty coefficient d=0.01, state gene string n=4, selection probability q=0.5, hybridization rate P c =0.1, variation rate P m =1.
[0064] Step 3: Perform finite eleme...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Embodiment 2: Take a simply supported beam bearing three points as an example.
[0074] For example Figure 4 The shown three-point loaded simply supported beam was subjected to topology optimization. The simply supported beam has a span of 200mm, a height of 100mm, and a thickness of 5mm. Three concentrated loads P=10kN act on 1 / 4, 1 / 2, and 3 / 4 of the beam span at the same time. The elastic modulus E=207Gpa, Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.3. Divide into 5000 units (2mm×2mm). P.I. th The value is set to 1 to ensure that the results after topology optimization are better than the initial design domain. Penalty coefficient d=0.01.
[0075] Reference 2 for other calculation parameters, set as: state gene string n=2, selection probability q=0.5, hybridization rate P c =0.2, variation rate P m = 0.8. When the volume removal rate is 85%, the GESO algorithm in Reference 2 has a non-optimized solution, and some important units are mistakenly deleted in a certain iteration, as sh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com