A Method and Device for Channel Estimation and Pilot Optimization Based on Compressed Sensing
A technology of channel estimation and compressed sensing, which is applied in the field of channel estimation and pilot optimization based on compressed sensing, can solve the problems of poor optimization performance and large demand for pilots, reduce the block correlation value, accelerate the convergence speed, and reduce the The effect of frequency demand
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
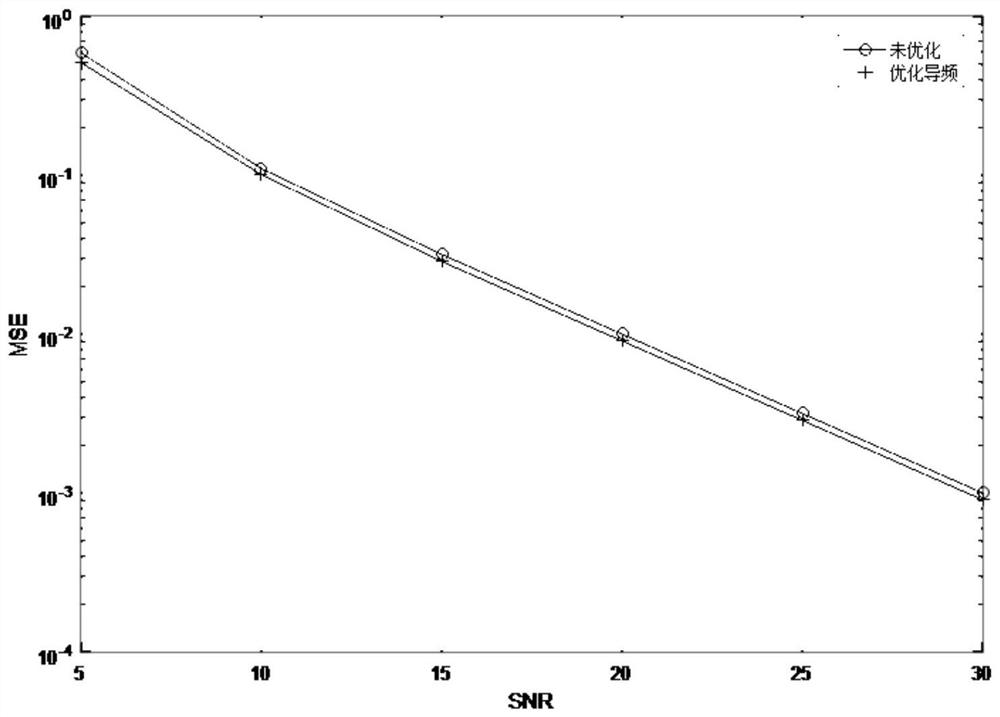
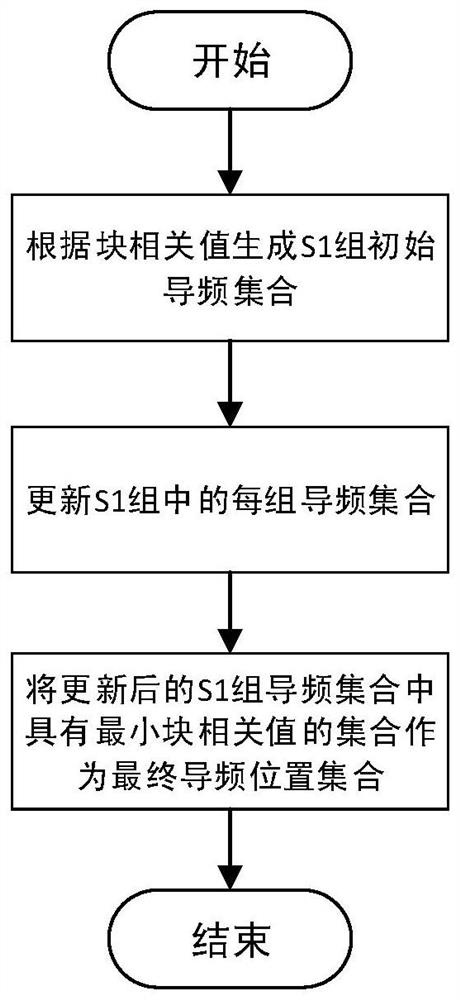
[0056] When the compressed sensing channel estimation method using the sparse characteristics of the massive MIMO channel estimates the channel state information, the pilot position needs to be optimized, and the following methods are used:
[0057] 1) According to the fact that the pilot signals sent by all antennas have the same pilot position and pilot power, the block correlation value of the known measurement matrix is simplified, and the objective function of pilot optimization with the minimum block correlation value is established.
[0058] The simplification process includes the following steps:
[0059] Step 1, consider a massive MIMO system, the base station has M antennas serving multiple single-antenna users. Then the channel impulse response from the mth antenna of the base station to a certain user is h m =[h m (0), h m (1),...,h m (L-1)] T , where L is the channel length, since the channel is sparse, so h m There are only K non-zero taps in , and Kp sub...
Embodiment 2
[0120] The optimization problem of the pilot position can be expressed by the objective function with the smallest block correlation value:
[0121]
[0122]Where, r=l-k, the formation process of the above objective function belongs to the prior art, and the specific journal name is "Pilot Allocation for MIMO-OFDM Systems: A Structured Compressive Sensing Perspective".
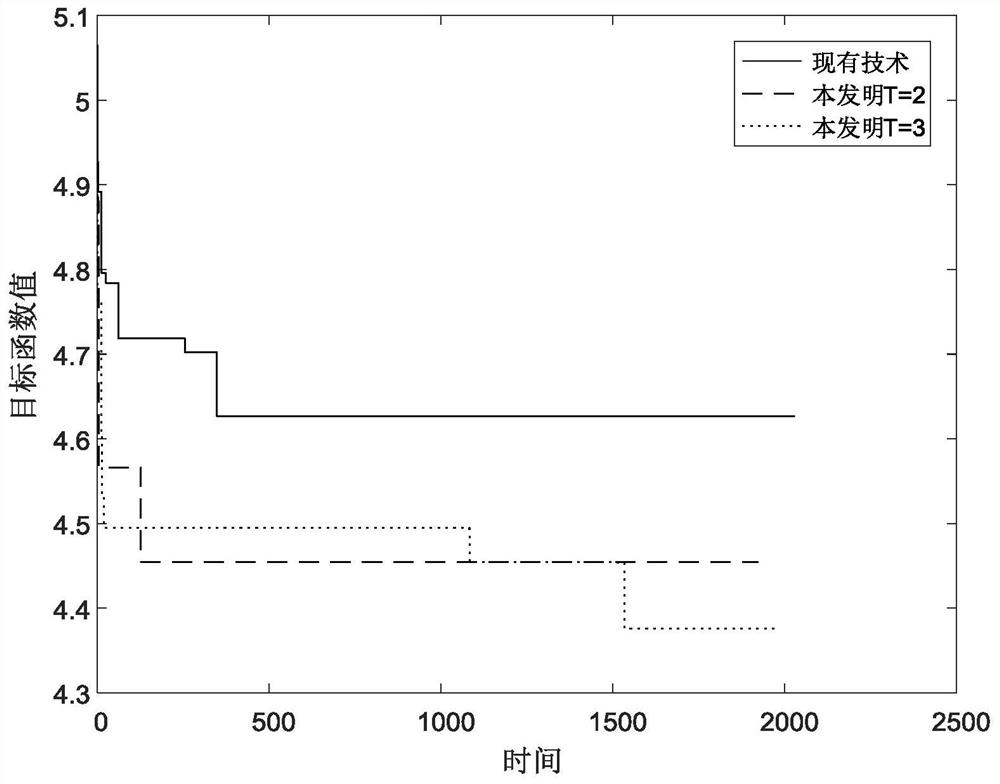
[0123] Pilot optimization using an iterative approach:
[0124] First, set the number of outer loops M 1 and the number of inner loops M 2 .
[0125] In each outer loop, randomly generate T (1≤T≤N P ) pilot positions, and then add a pilot position in each iteration according to the principle of minimum block correlation value until N P Pilot positions stop iterating, and set the obtained pilot positions as the initial value of the inner loop.
[0126] In each inner loop, it is assumed that the pilot position set generated by the latest iteration is p, for k=1,...,N P , select the element with the sm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com