Decoupled processor instruction window and operand buffer
An operand and buffer technology, applied in instruction analysis, concurrent instruction execution, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as low performance and high power consumption of processors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
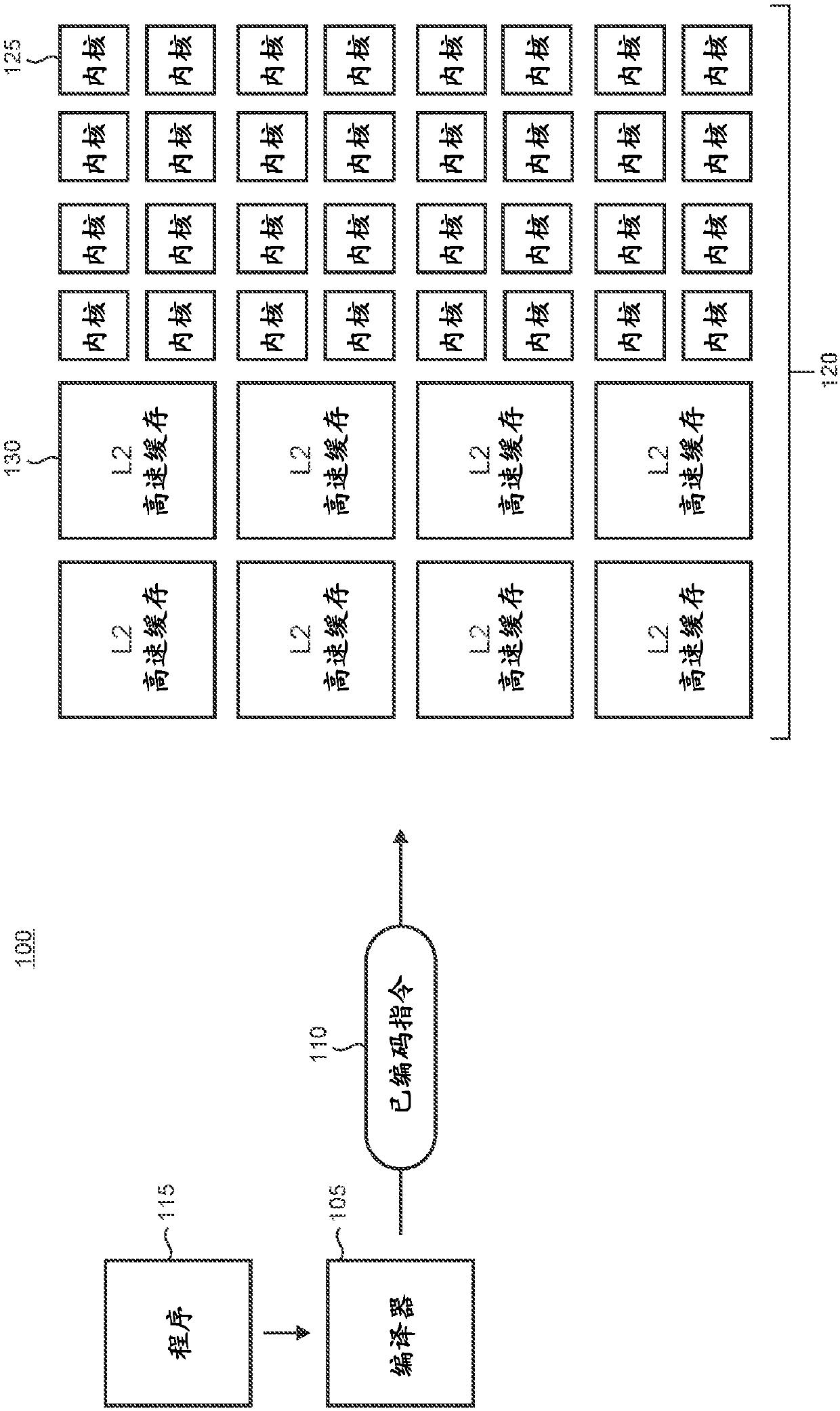
[0009] figure 1 An illustrative computing environment 100 is shown with which current age-based management of instruction blocks may be utilized. The environment includes a compiler 105 that can be used to generate encoded machine-executable instructions 110 from a program 115. The instructions 110 can be processed by a processor architecture 120 configured to process to 128 instructions) instruction blocks.
[0010] Processor architecture 120 generally includes a plurality of processor cores (representatively indicated by reference numeral 125 ) in a tiled configuration, interconnected by an on-chip network (not shown), and also communicated with one or more 2 A level (L2) cache (representatively indicated by reference numeral 130) operates interoperably. Although the number and configuration of cores and caches may vary by implementation, it should be noted that physical cores may be merged together into one or more larger Of the logical processors, larger logical process...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com