Motor stator and motor with same
A technology for motor stators and sub-stators, which is applied to electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the production efficiency of motor stators, easy axial dislocation of stator iron cores, and difficult assembly operations, and achieves guaranteed performance. , The effect of saving materials and convenient assembly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
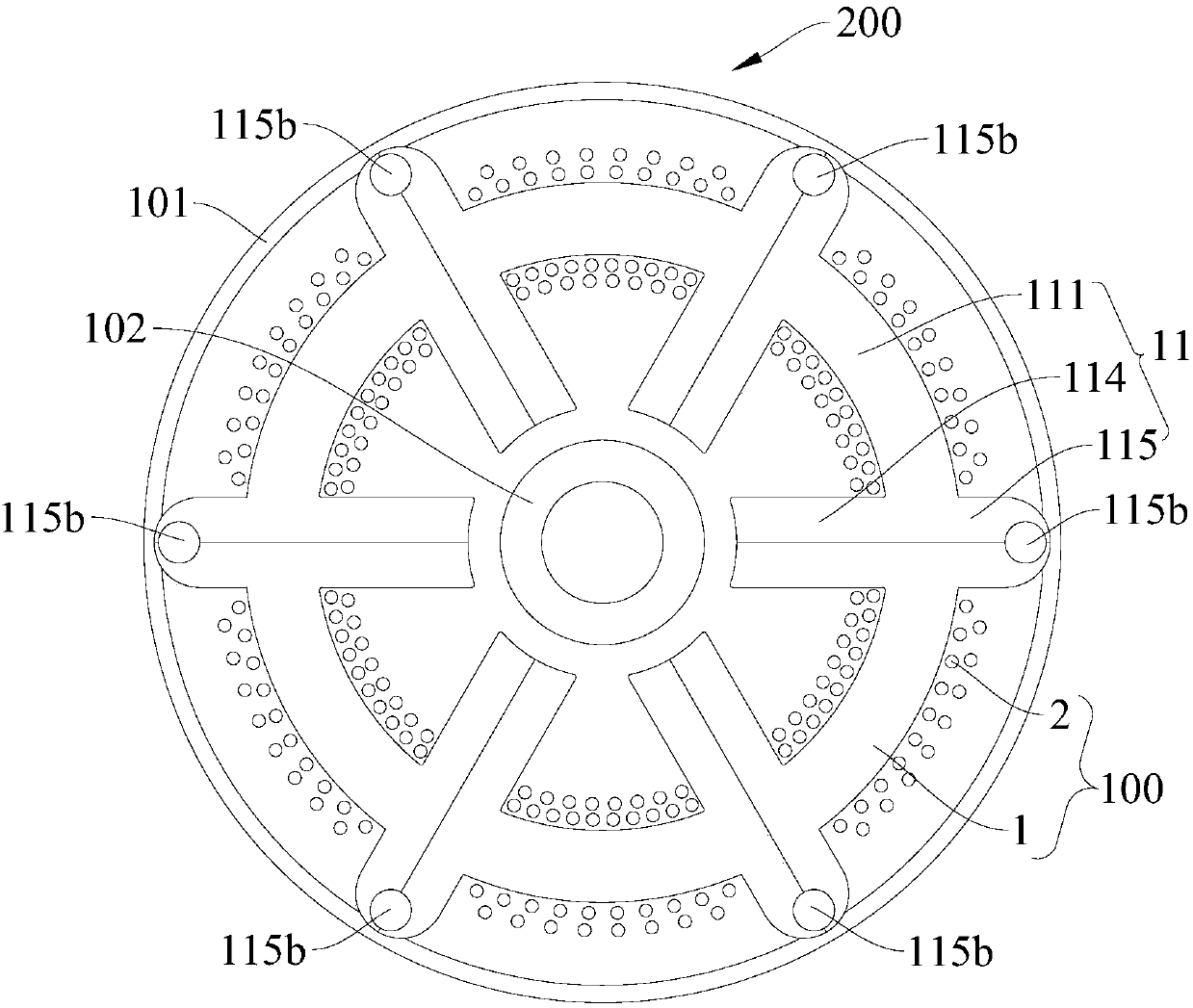
[0071] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, the motor 200 includes a casing 101, a motor stator 100 and a motor rotor 102, the casing 101 is roughly a cylindrical structure, six recesses 101a are formed on the inner wall of the casing 101, and the motor stator 100 is formed with six recesses 101a corresponds to the matching convex surface one by one, the motor rotor 102 is coaxially embedded in the motor stator 100, and the motor rotor 102 is a two-stage permanent magnet ring integrally formed.
[0072] The motor stator 100 includes a stator core and six stator windings 2. The stator core includes six stator cores 11 connected end to end along the circumferential direction. The six stator cores 11 have the same structure and each stator core 11 is composed of A plurality of punched sheets are stacked, and each stator core 11 includes a stator yoke 111, two stator teeth 114 and two connecting outer ends 115, and the stator teeth of two adjacent stator cores 11 are in contact ...
Embodiment 2
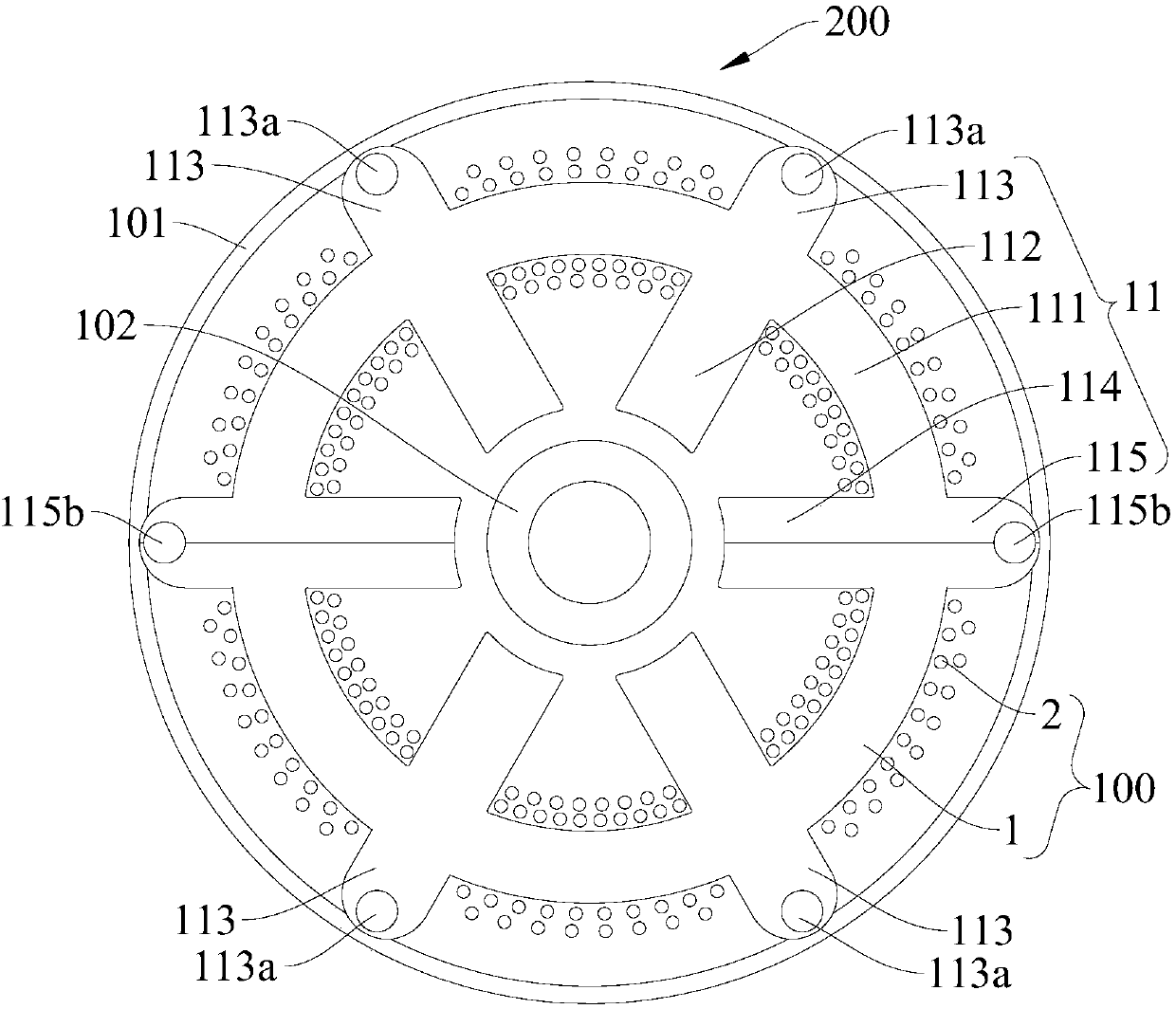
[0077] like figure 2 As shown, the structure of this embodiment is substantially the same as that of Embodiment 1, wherein the same components use the same reference numerals, and the difference is that the stator core includes two sub-stator cores 11 connected end-to-end along the circumferential direction, Each stator core 11 includes a stator yoke 111, two stator teeth 114, two stator teeth 112, two outer ends 113 and two connecting outer ends 115, the stator teeth 112 are connected with the complete stator teeth The structure is the same, the two stator teeth 112 are arranged on the inner side of the stator yoke 111 and in the circumferential direction of the stator yoke 111, the two stator teeth 112 are evenly spaced between the two stator teeth 114, and the two outer ends The part 113 is arranged on the outer side of the stator yoke part 111, and the two outer ends 113 are arranged radially opposite to the two stator tooth parts 112 respectively; each outer end part 113...
Embodiment 3
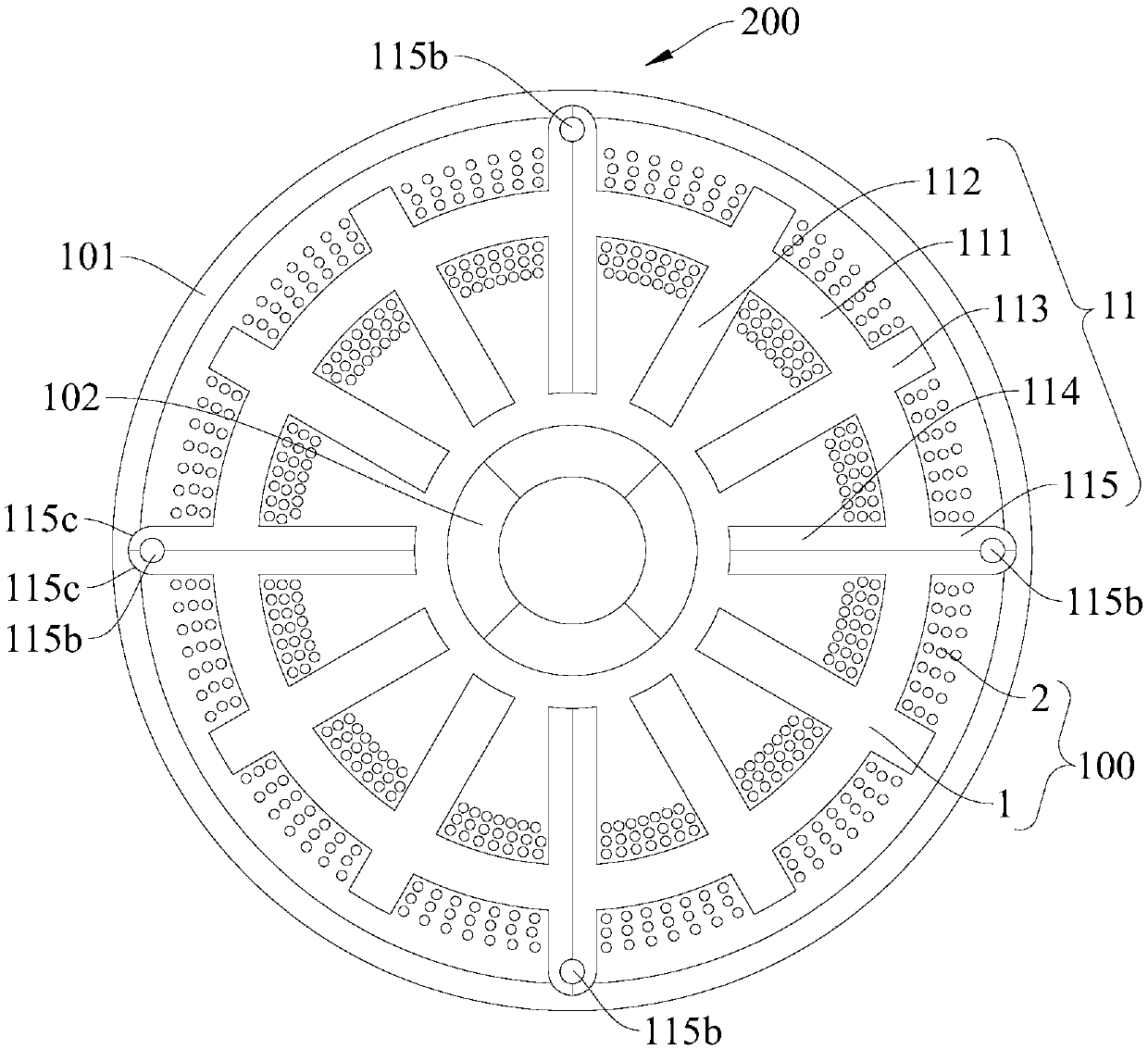
[0079] like Figure 3-Figure 6 As shown, the structure of this embodiment is substantially the same as that of Embodiment 2, wherein the same components use the same reference numerals, the difference is that: the motor rotor 102 is a four-stage permanent magnet ring; the inner wall of the casing 101 is formed with Four recesses 101a; the stator core includes four sub-stator cores 11 connected end-to-end along the circumferential direction, and each sub-stator core 11 includes a stator yoke 111, two sub-stator teeth 114, two stator teeth 112, Two outer ends 113 and two connecting outer ends 115, the stator teeth 112 have the same structure as the complete stator teeth; each outer end 113 is not formed with a positioning installation hole 113a, and the length of the outer ends 113 Less than the length of the connecting outer end 115, at this time the four concave and convex surfaces match.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com