Lactobacillus plantarum, compound probiotic wolfberry product and preparation method thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lycium barbarum, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, methods based on microorganisms, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems that the nutrition of Lycium barbarum can not be fully utilized, loss of nutrients, inconvenient to eat, etc., to achieve easy Carrying and eating, reducing the loss of active ingredients, and the effect of bright red color
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
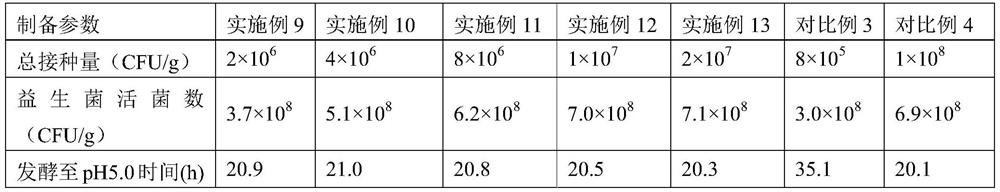
Embodiment 1
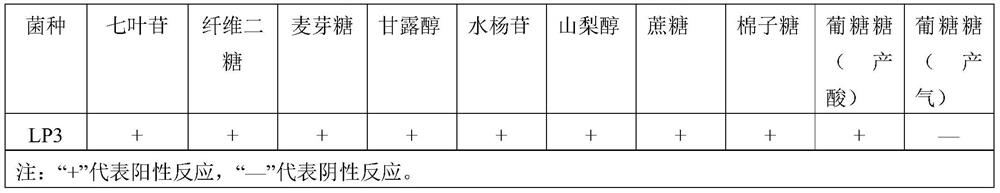
[0100] Example 1 Isolation, screening and identification of plant lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum) LP3
[0101] 1. Materials and methods
[0102] 1.1 Source, isolation and identification of strains
[0103] Naturally fermented kimchi samples were collected from households in Sichuan Province, 10 g of the sample was weighed and diluted with 90 g of sterile saline, 0.1 mL was spread on selective MRS solid medium, and incubated anaerobically at 37 °C for 72 h. Pick typical colonies for Gram-staining microscopic examination, select Gram-positive strains and streak them on MRS solid medium for 2-3 times to obtain pure colonies. The morphology of this strain is Gram-like bacteria observed under the microscope, which is straight rod-shaped, single, sometimes in pairs or in chains; the diameter of colonies on MRS solid medium is 1-3mm, milky white, raised, round, The surface is smooth and has no kinematic properties.
[0104] Physiological and biochemical identification and...
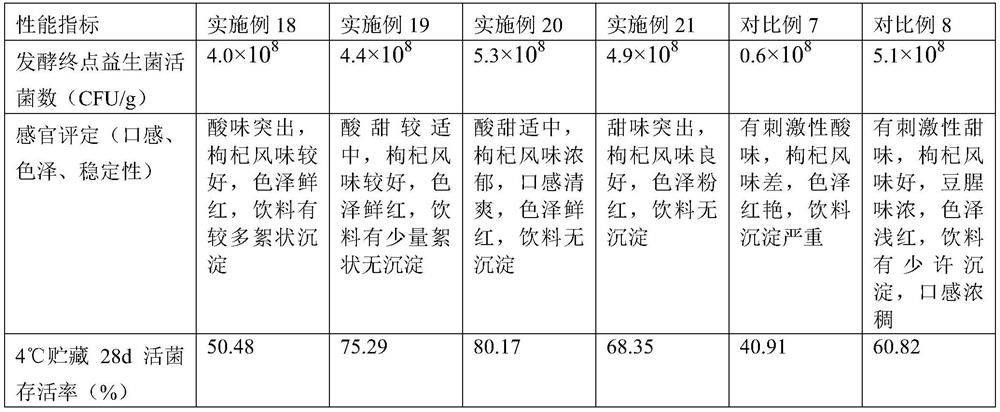
Embodiment 2
[0107] The antibacterial performance of embodiment 2 plant lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum LP3)
[0108] Clinically isolated pathogenic strains were used as indicator bacteria, which were: Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria unicellulare, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus parasitica, Loudi Penicillium; Lactobacillus plantarum LP3 was used as a bacteriostatic agent to determine the antibacterial performance of Lactobacillus plantarum LP3.
[0109] 1. Bacteriostasis test method: centrifuge the MRS medium fermentation broth of Lactobacillus plantarum LP3 at 3600r / min for 10min, take its fermentation supernatant, and use a 0.22μm microporous membrane to remove bacteria to obtain a cell-free extract , stored at -20°C until use. Dilute the indicator bacteria suspension to 1.0×10 6 Add CFU / mL to sterilized MRS solid medium cooled to 45°C, shake well and quantitatively (20mL) into a sterile plate. After cooling ...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Protease and gastrointestinal fluid tolerance of embodiment 3 plant lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum) LP3
[0114] 1. Gastrointestinal fluid tolerance test method:
[0115] 1.1. Add 3.5 g / L pepsin to sterilized PBS at pH 2.5 (adjusted with 1 mol / L HCl), filter and sterilize with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to prepare simulated gastric juice.
[0116] 1.2. Select the strains that have been screened for acid resistance for cultivation. Centrifuge and wash the bacteria twice after two generations as described in 2.2.1. Collect the bacteria, add the same amount of pH 2.5 simulated gastric juice as the culture medium, and keep at 37°C Cultivate for 3 hours, and measure the number of viable bacteria by MRS agar medium pouring method at 0 and 3 hours.
[0117] 1.3. In sterilized PBS with pH 8.0 (adjusted with 0.1 mol / L NaOH), add 0.1% trypsin and 1.8% ox bile salt and filter with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to prepare simulated intestinal fluid.
[0118] 1.4. C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com