Energy-saving fresh air system
A technology of fresh air system and fresh air duct, applied in ventilation systems, heating and ventilation control systems, heating and ventilation safety systems, etc., can solve the problems of energy waste, no automatic adjustment of fresh air volume, etc., to avoid insufficient flow, stable and easy. Maintenance and energy consumption reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0032] At present, a small number of buildings solve the problem of fresh air energy consumption by adding intelligent control systems. The main method is to install sensors in the terminal room to obtain information such as PM2.5 and carbon dioxide content, control the opening of the terminal valve or tuyere, and control the inverter through the static pressure sensor installed on the fresh air main pipe to adjust the fan speed of the fresh air unit; When the terminal demand decreases, the static pressure on the main pipe increases, reducing the fan speed; thereby reducing the fan's energy consumption and cooling (heating) capacity. The main problems are: First, an automatic control system needs to be added, which is complex and expensive; second, because the system requires on-site installation and commissioning involving many related units, the probability of later problems is high and once the problems are found, they are prone to excuse each other. This method has not been...
no. 2 example
[0045] This embodiment provides an energy-saving fresh air system 10 whose basic structure, principle and technical effects are the same as those of the first embodiment. For a brief description, for parts not mentioned in this embodiment, please refer to the first embodiment Corresponding content.
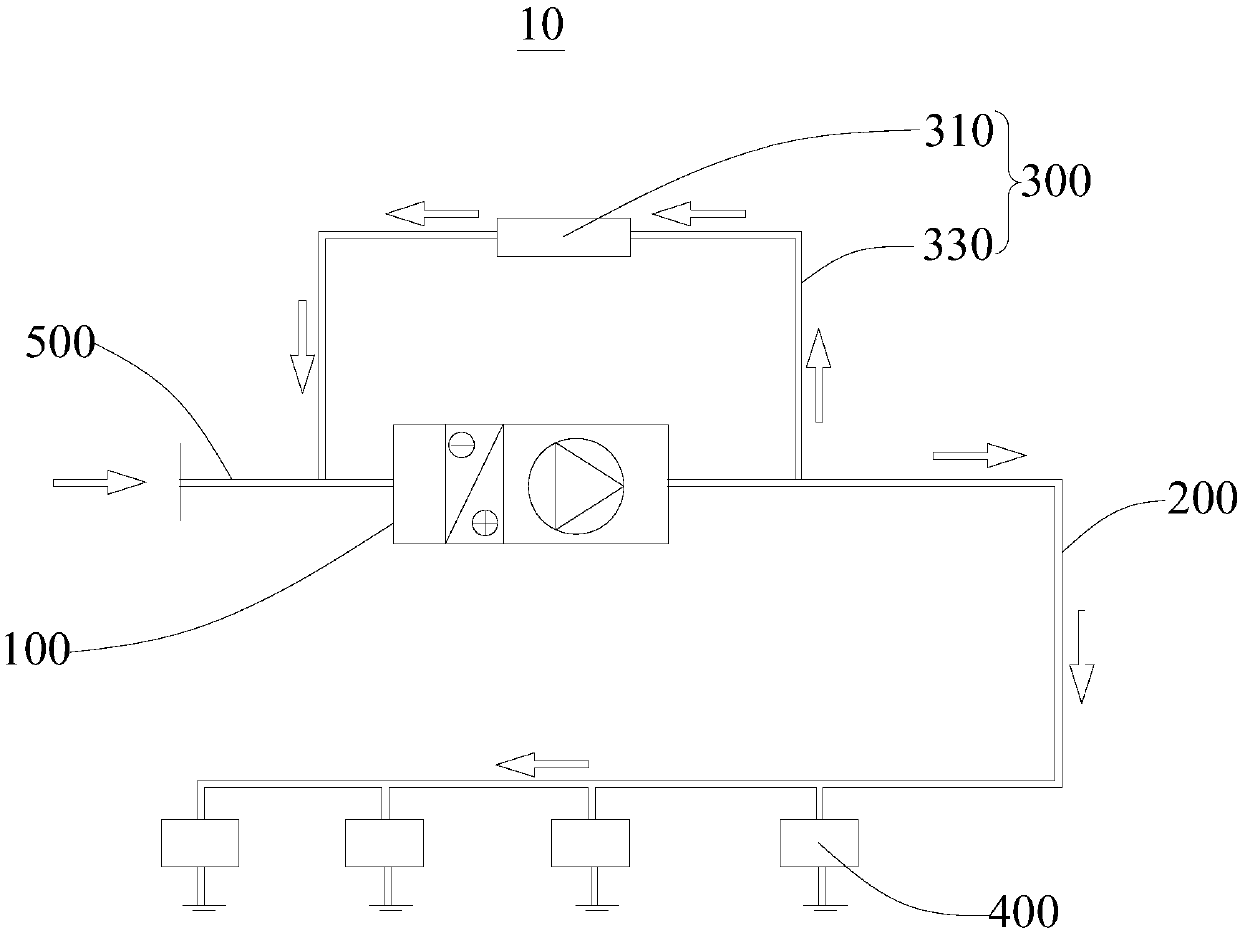
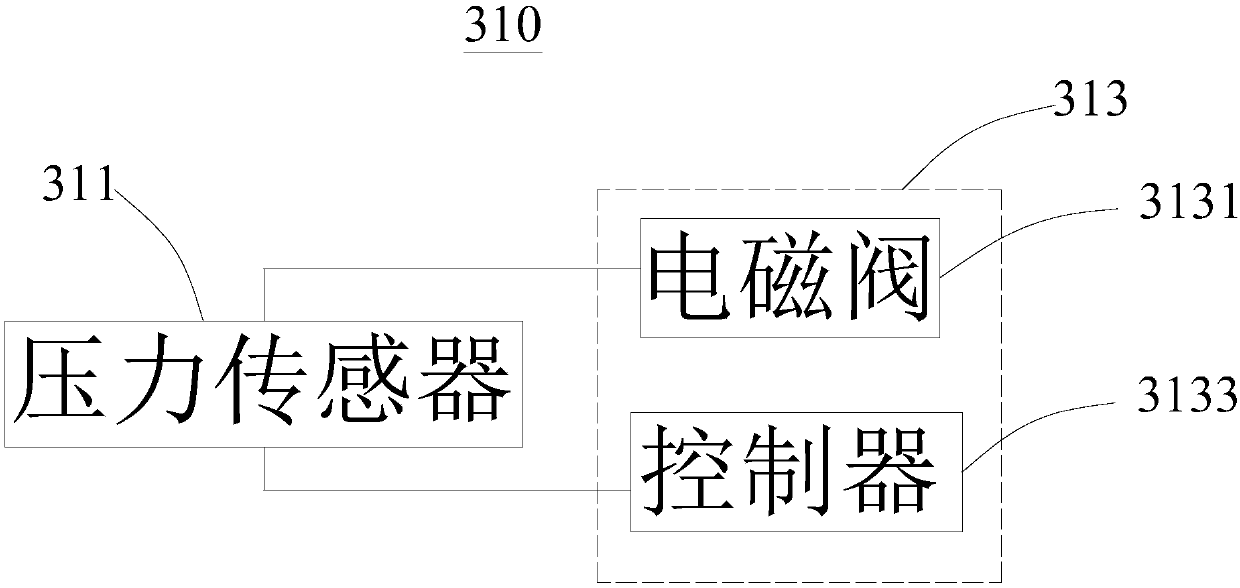
[0046] participate image 3 An energy-saving fresh air system 10 provided by this embodiment includes a fresh air unit 100, a fresh air duct 200, a bypass mechanism 300, a terminal opening and closing mechanism 400, and an air inlet duct 500. The fresh air unit 100 has an air inlet end and an air outlet end, One end of the fresh air duct 200 is connected to the outlet end, the other end is connected to the end opening and closing mechanism 400, one end of the bypass mechanism 300 is connected to the end of the fresh air duct 200 close to the fresh air unit 100, and the other end is connected to the inlet end for The static pressure value of the fresh air duct 200 selectively connects...
no. 3 example
[0052] This embodiment provides an energy-saving fresh air system 10 whose basic structure, principle and technical effects are the same as those of the first embodiment. For a brief description, for parts not mentioned in this embodiment, please refer to the first embodiment Corresponding content.
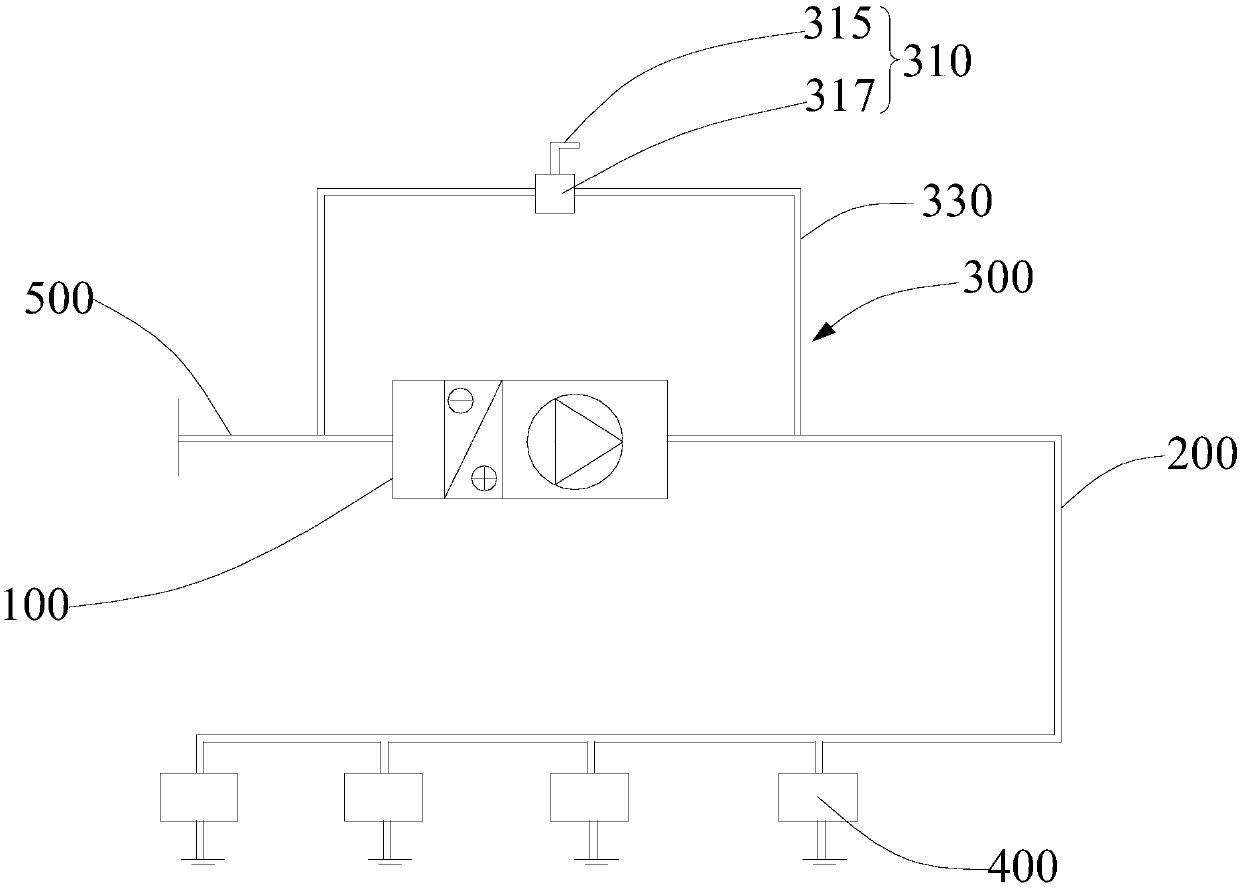
[0053] See Figure 4 (The arrow in the figure indicates the direction of airflow). The energy-saving fresh air system 10 provided by this embodiment includes a fresh air unit 100, a fresh air duct 200, a bypass mechanism 300, a terminal opening and closing mechanism 400, and a ventilation chamber 600. The fresh air unit 100 has At the inlet and outlet ends, one end of the fresh air duct 200 is connected to the outlet end, the other end is connected to the end opening and closing mechanism 400, the end opening and closing mechanism 400 extends into the air change chamber 600, and one end of the bypass mechanism 300 is connected to the fresh air The pipe 200 is close to one end of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com