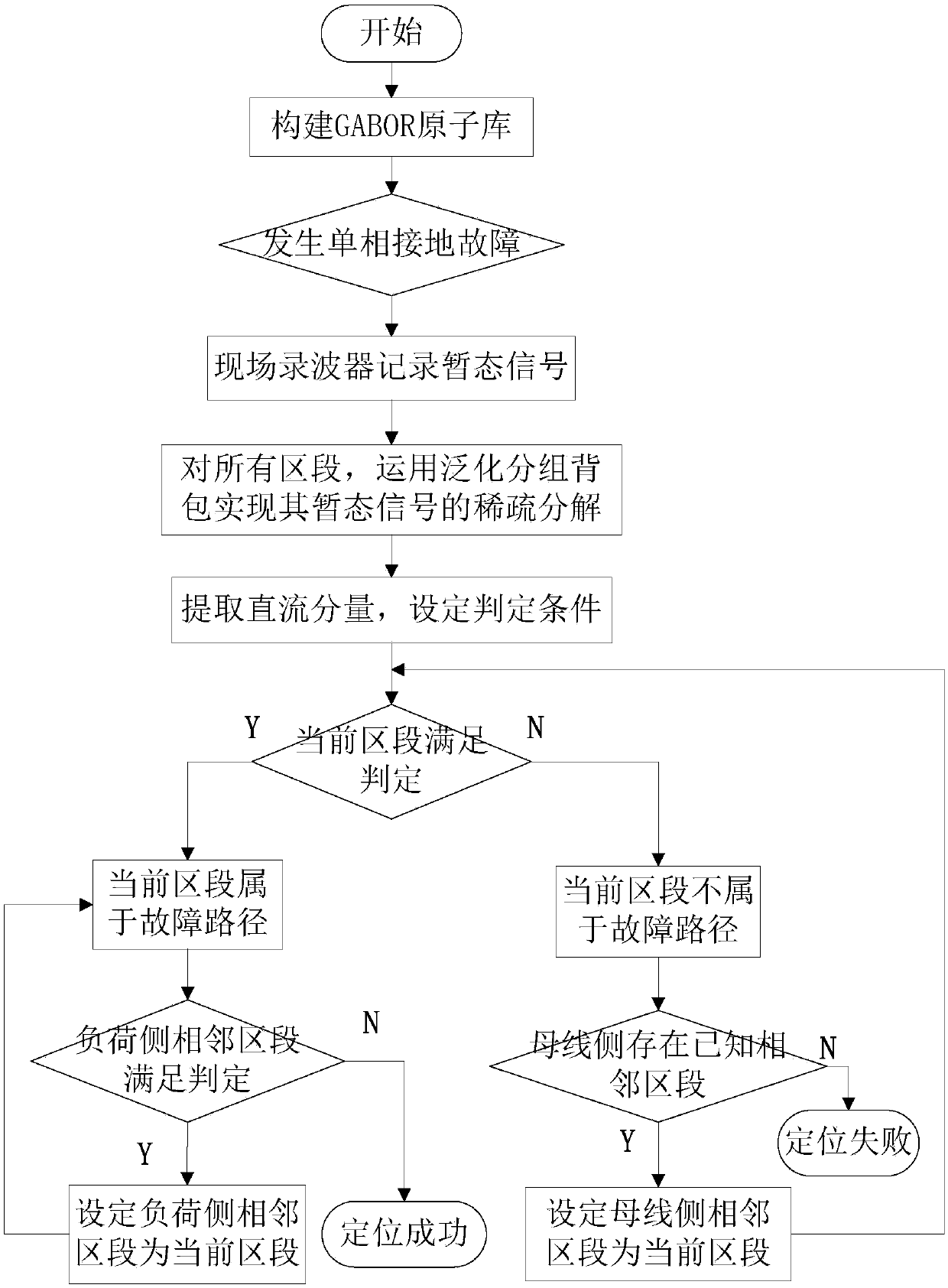
Power distribution network single-phase grounding fault section positioning method based on generalized group knapsack
A technology of single-phase ground fault and positioning method, which is applied in the direction of fault location, fault detection according to conductor type, and electrical measurement. The effect of improving the speed of fault location and improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
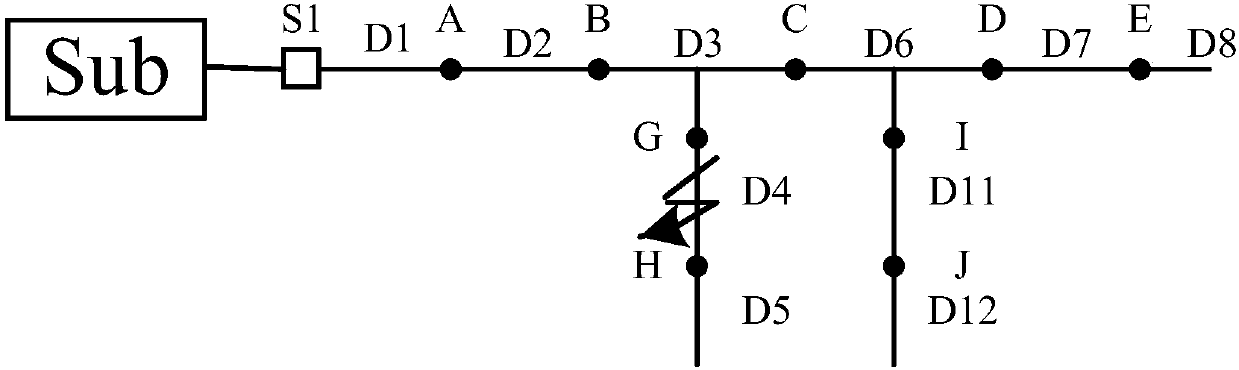
[0039] Example 1: if figure 2 As shown, a single-phase ground fault occurs in the D2 section of the distribution network, and a method for locating the single-phase ground fault section of the distribution network based on a generalized grouping backpack disclosed by the present invention is used, as shown in the attached figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
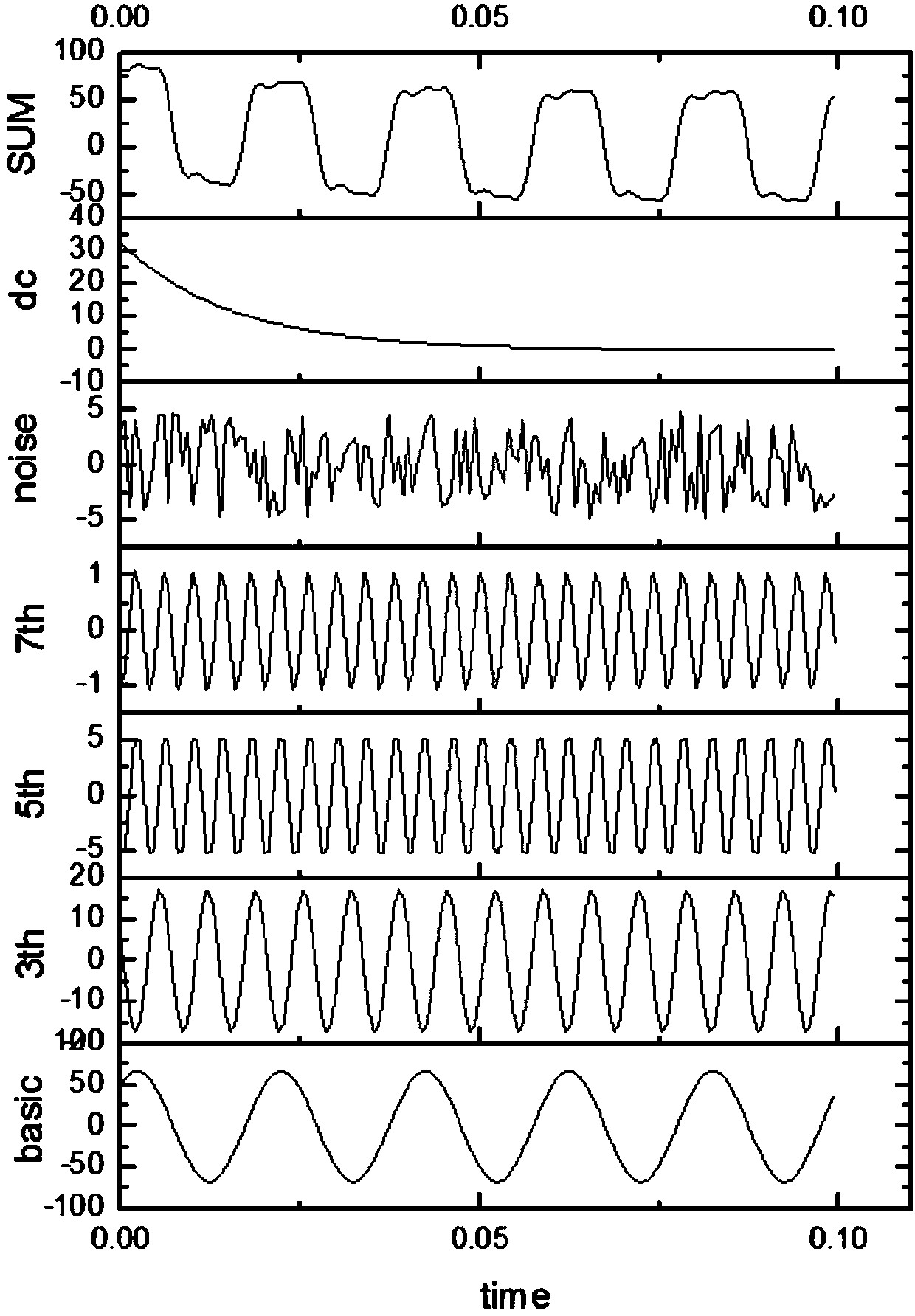
[0040] Step 1: Construct an atomic library by self-learning according to the characteristics of the collected power system transient signal. The atomic library includes the attenuated DC component, fundamental frequency component, whole harmonic component and fractional harmonic component of the system transient signal. groups:
[0041] In this application, an atom is a sub-signal with a length of l, different types of atoms form the above four groups, and the four groups form an atom library. Enumerate through the amplitude A and the decay time constant t within reason,
[0042] Form a collection {Ae -t},...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com