Near-infrared-spectrum-based tobacco leaf part feature extraction and discrimination method
A technology of near-infrared spectroscopy and feature extraction, applied in the field of feature extraction and discrimination of tobacco leaf parts based on near-infrared spectroscopy, can solve problems such as poor prediction, inability to meet the requirements of online identification of tobacco leaf parts, and detection accuracy, and achieve the goal of improving product quality Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
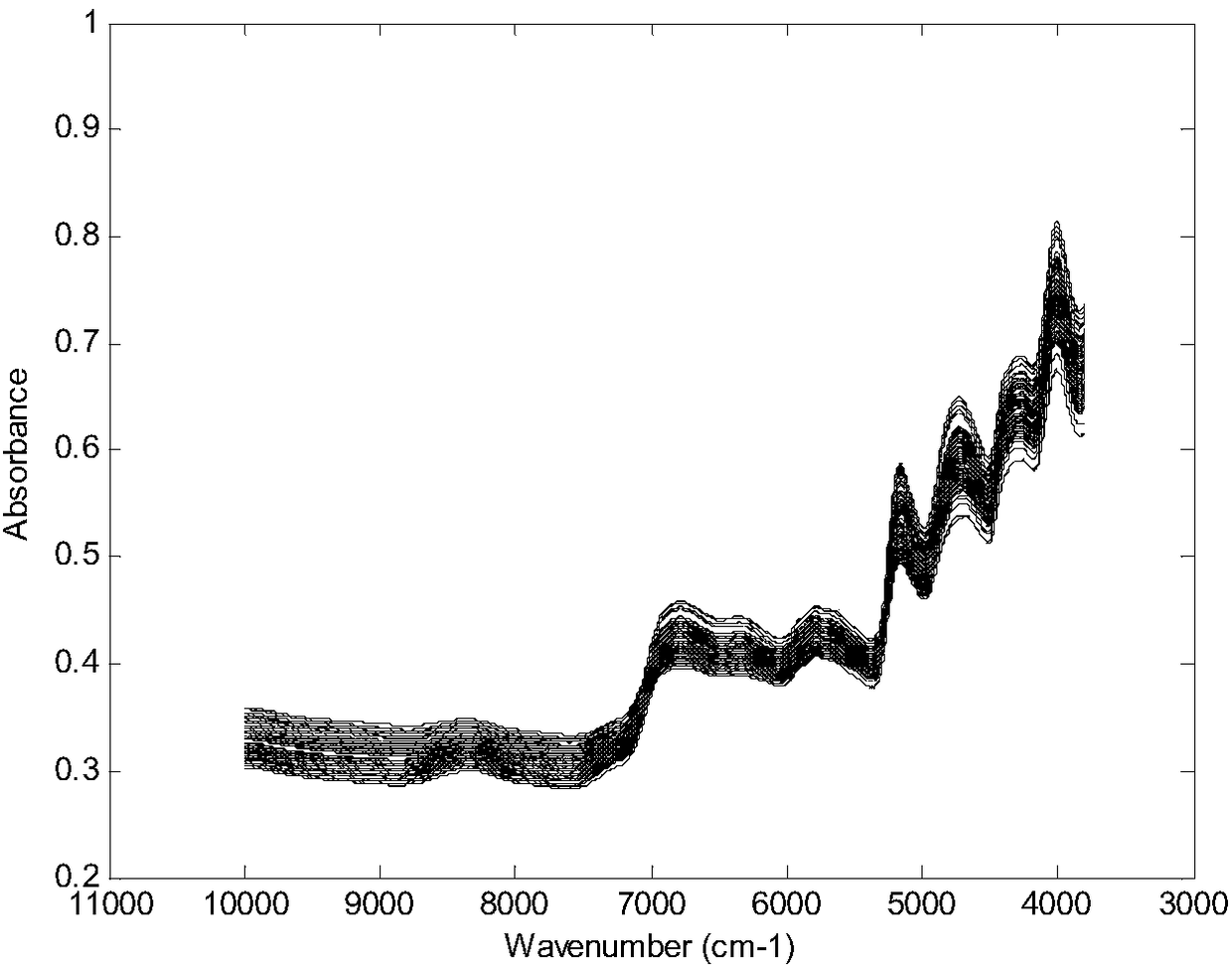
[0039] (1) Select 452 raw tobacco samples of various grades in Fujian production areas from 2015 to 2016. After sampling, the sample was prepared into a powder sample according to the tobacco industry standard "YC / T 31-1996 Tobacco and Tobacco Product Sample Preparation and Moisture Determination Oven Method" (tobacco leaves were placed in an oven, dried at 40°C for 4 hours, and then dried with a cyclone mill. (FOSS) ground through a 40-mesh sieve), sealed and balanced for 1d, and carried out spectral measurement, the sample spectrum of the training set is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0040] (2) Perform standard normal correction processing on the spectrum obtained in step (1).
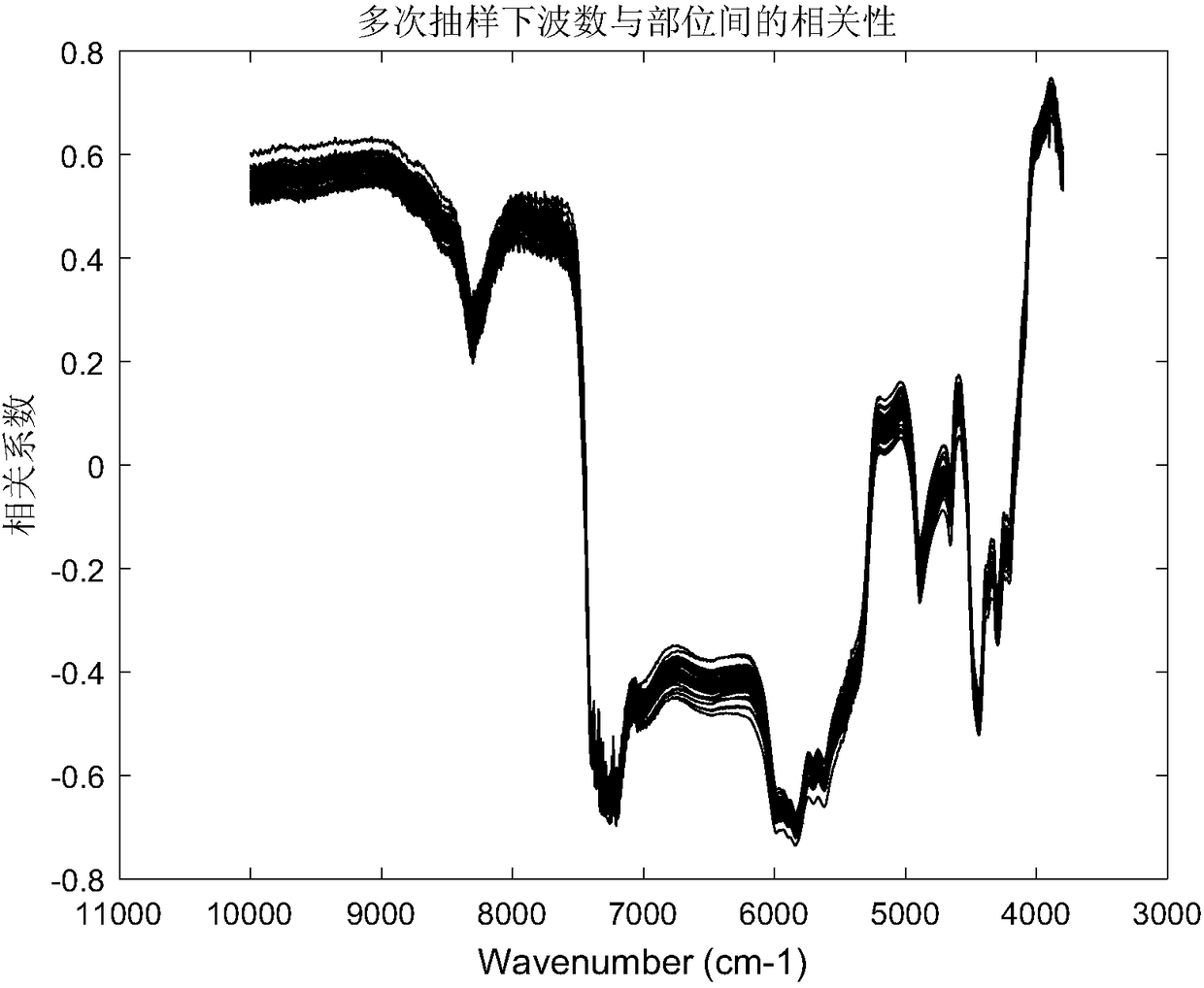
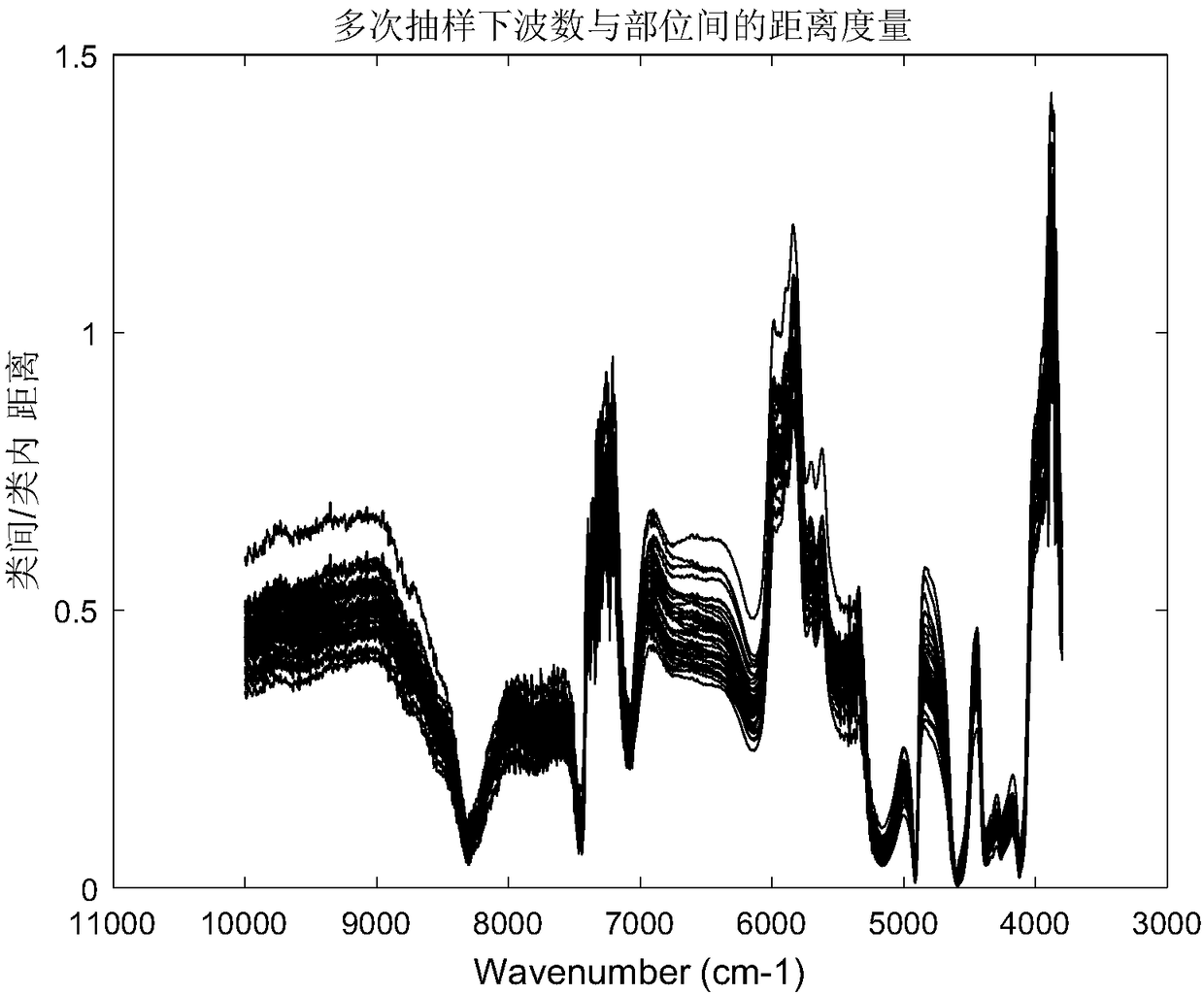
[0041](3) Perform 500 samplings, randomly select 316 (70%) of the 452 samples each time, and ensure that the proportion of parts in the sample is consistent with the original sample set during each sampling. Calculate the correlation p between each wavenumber point and the site in the extracted samp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com