State prediction method and state prediction device for submodules of modular multilevel converter
A modular multi-level, multi-level converter technology, applied in the direction of circuit devices, output power conversion devices, power transmission AC networks, etc., can solve problems such as different failure rates of sub-modules and changes in capacitance values. To achieve the effect of improving pertinence and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
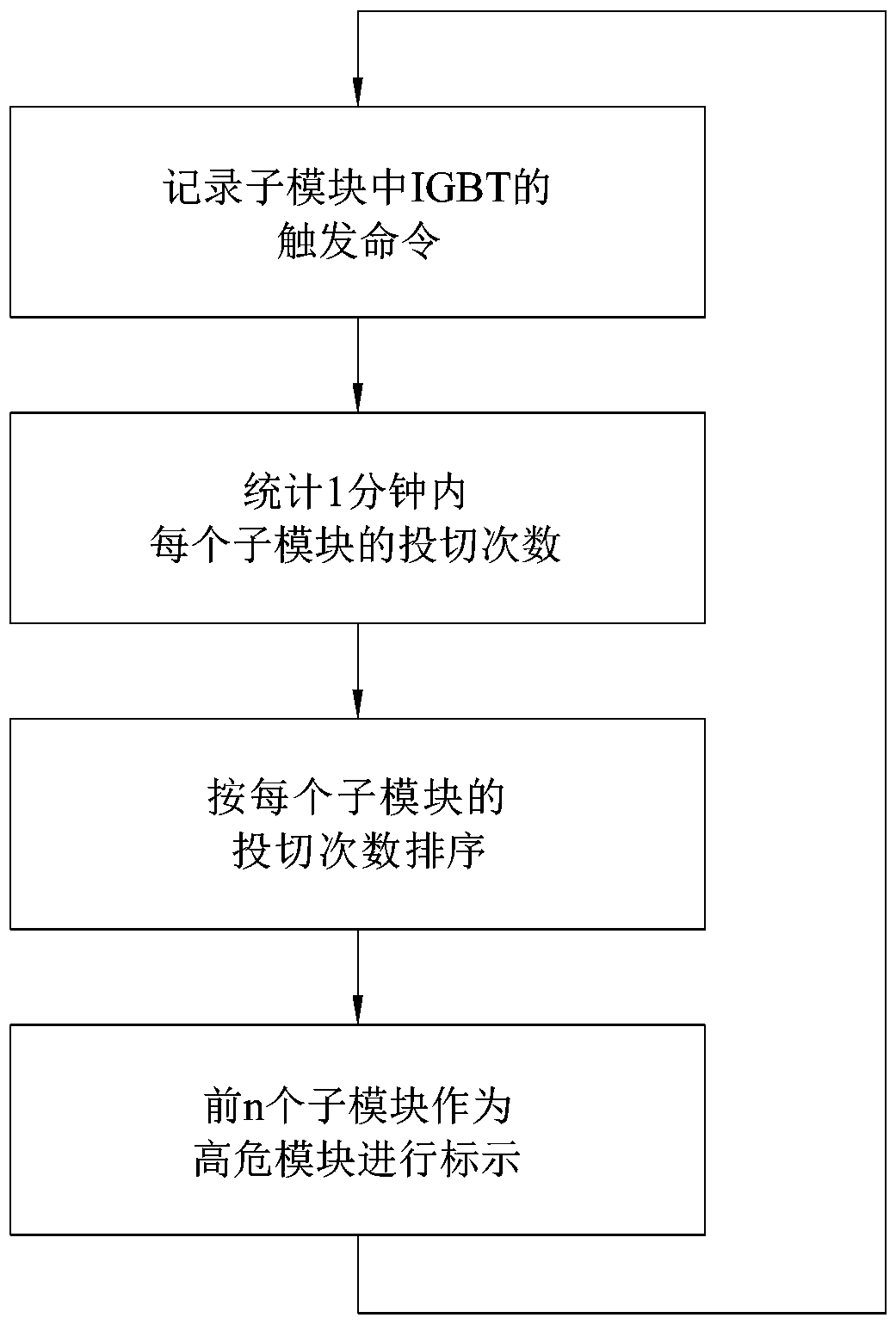
[0022] Embodiment one: as attached figure 1 As shown, the modular multilevel converter includes multiple sub-modules. Aiming at the prediction of the possibility of failure of the multiple sub-modules in the modular multilevel converter, a modular multilevel converter is adopted The sub-module state prediction method is: predict the fault state according to the switching times of each sub-module within a period of time (for example, 1min), and the failure possibility of the sub-module increases with the increase of the switching times.
[0023] In this process, it is first necessary to record the trigger command of each sub-module, the trigger command is the trigger command of the IGBT device in the sub-module, and then record the switching times of each sub-module according to the recorded trigger command.
[0024] After recording the switching times of each sub-module, the sub-modules are sorted according to the switching times from high to low, so as to obtain the order of ...
Embodiment 2
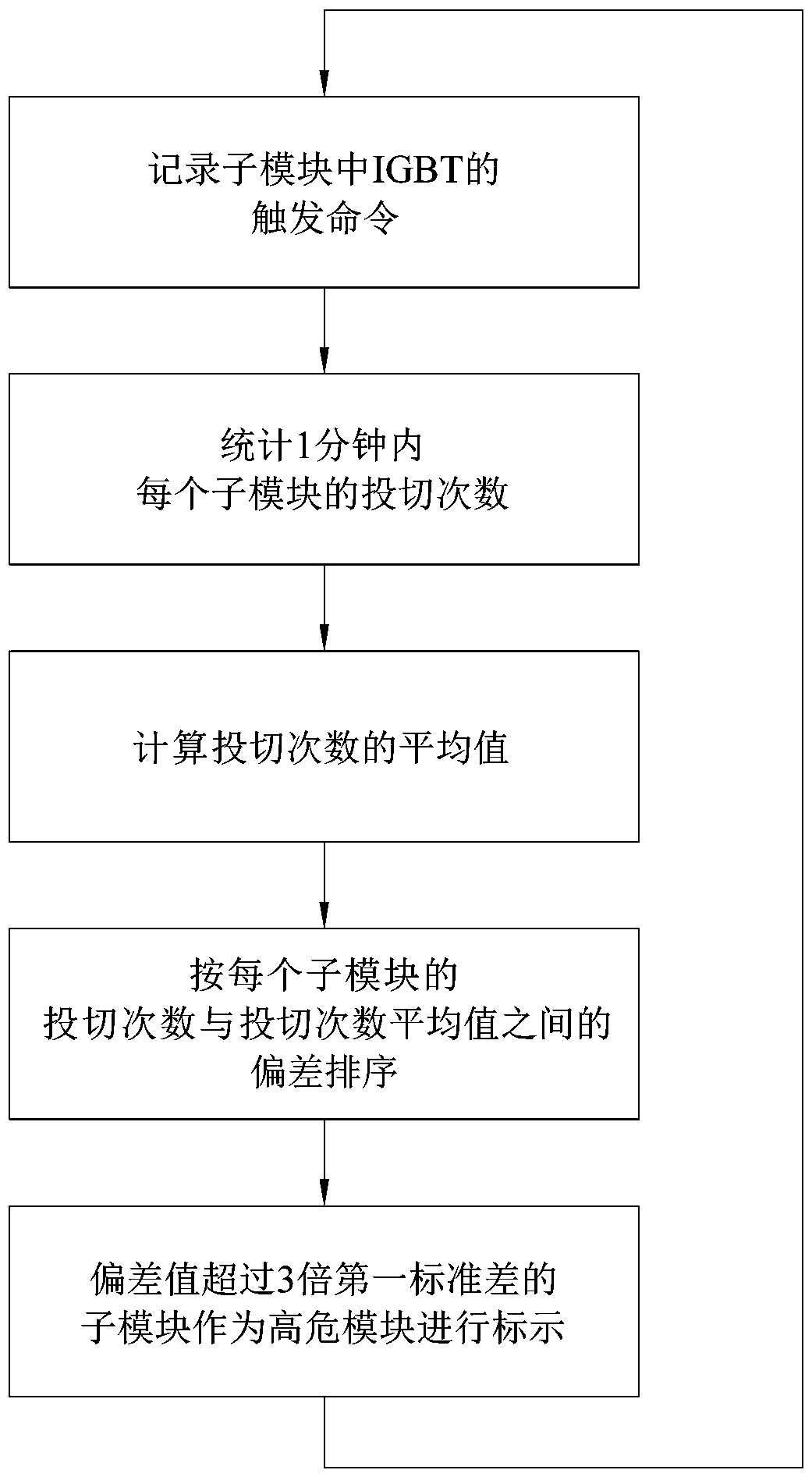
[0026] Embodiment two: as attached figure 2 As shown, the difference between the sub-module state prediction method of the modular multilevel converter in this embodiment and the first embodiment is that: after recording the switching times of each sub-module, the average value of the switching times of each sub-module is calculated, That is, the average number of switching times, the sub-modules are sorted from high to low according to the difference between the number of switching times and the average number of switching times, so as to obtain the order of the failure possibility of each sub-module.
[0027] The first standard deviation can be preset, and the difference between the number of switching times and the average number of switching times in the ranking of sub-module failure possibilities exceeds m 1 times the first standard deviation for sub-modules, m 1 Any value in the range [2, 4], such as m 1 =3. The sub-module with a larger deviation between the number o...
Embodiment 3
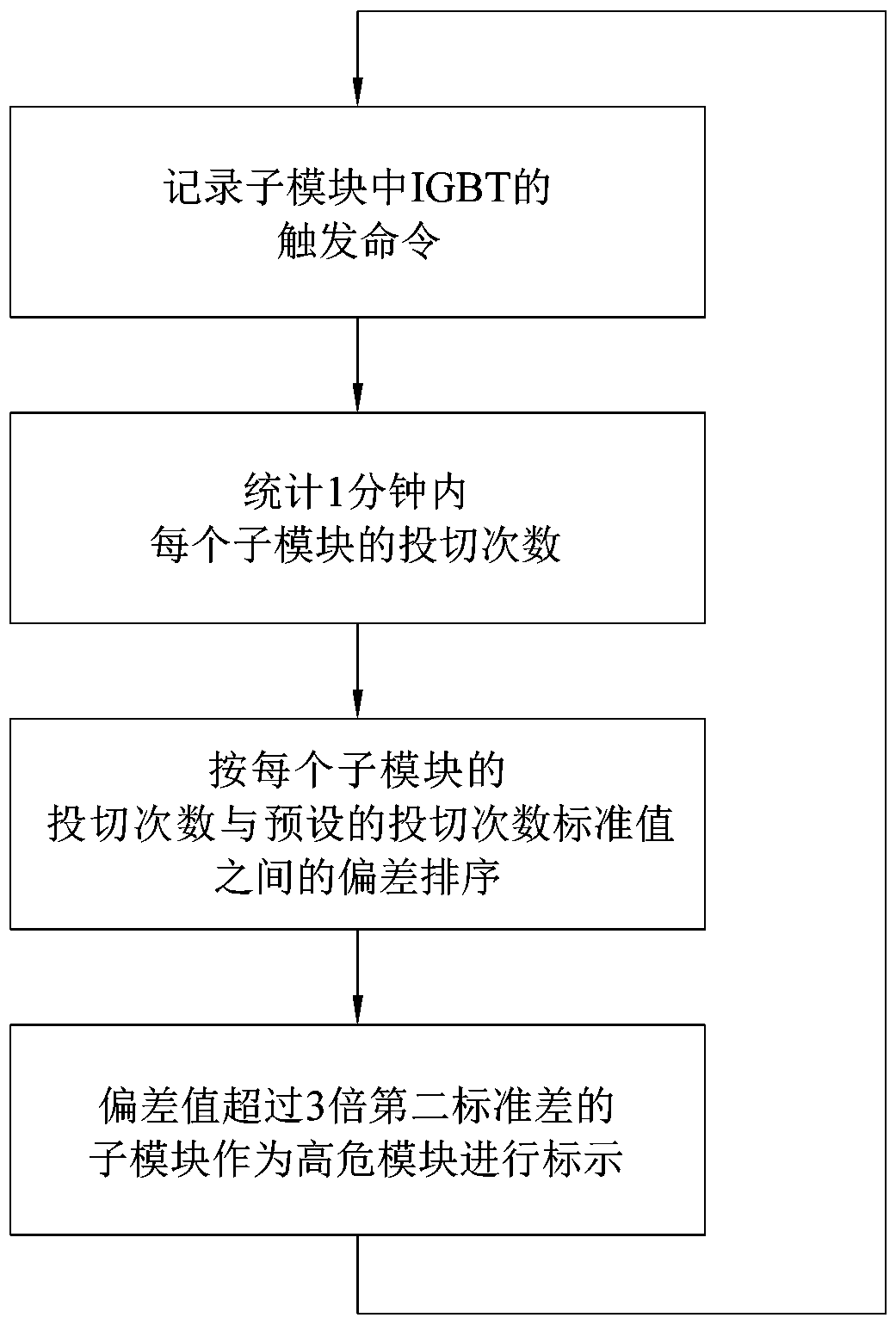
[0028] Embodiment three: as attached image 3 As shown, the difference between the sub-module state prediction method of the modular multilevel converter of this embodiment and the first embodiment is that: the standard value of switching times is preset, and after recording the switching times of each sub-module, each sub-module The modules are sorted from high to low according to the difference between their switching times and the standard value of switching times, so as to obtain the ranking of the fault possibility of each sub-module.
[0029] The second standard deviation can also be preset, and the difference between the number of switching times and the standard value of the number of switching times in the fault possibility ranking of sub-modules exceeds m 2 times the second standard deviation for sub-modules, m 2 Any value in the range [2, 4], such as m 2 =3. The sub-module with a larger deviation between the number of switching times and the second standard devia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com