A low-frequency low-noise balanced zero-beat detector
A low-noise, detector technology, used in photometry, instruments, measuring devices, etc. using electrical radiation detectors, can solve problems such as imperfect circuit design, low classical noise in the radio frequency band, etc., and achieve a high common mode rejection ratio , the effect of high gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
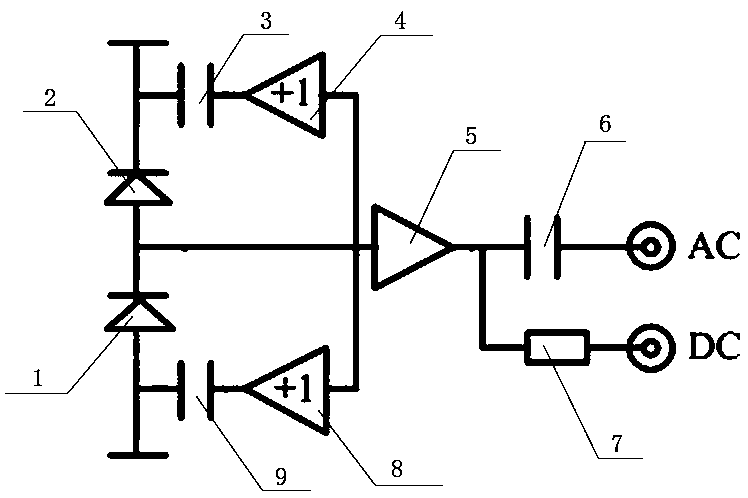
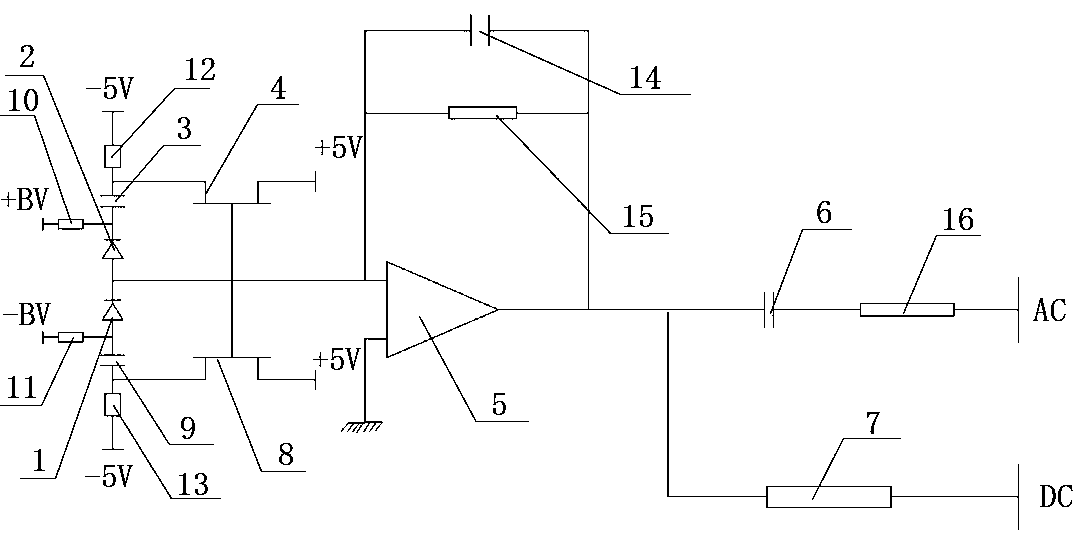
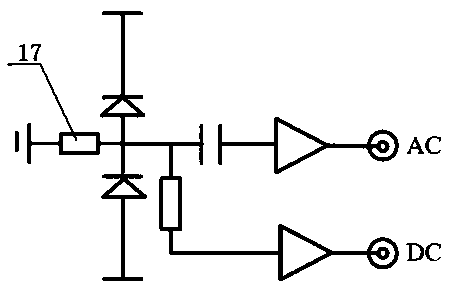
[0013] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a low-frequency low-noise balanced zero-beat detector can be used to detect and analyze the quantum noise spectrum of the squeezed light field frequency between 20Hz-200kHz, and can also monitor whether the incident light power of the two photodiodes is equal. The photocurrent difference signal generated by the two photodiodes is converted into a corresponding voltage signal through a bootstrap current-voltage converter composed of a buffer and a transimpedance operational amplifier, and the AC part of the voltage signal is output to the AC terminal through the first capacitor , used to measure the electronic noise of the detector and the quantum noise of the light field; the DC part is output to the DC terminal through the first resistor to detect whether the incident light power of the two photodiodes is equal. The device of the present invention comprises a differential circuit composed of a first photodiode PhD1 and a second ph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com