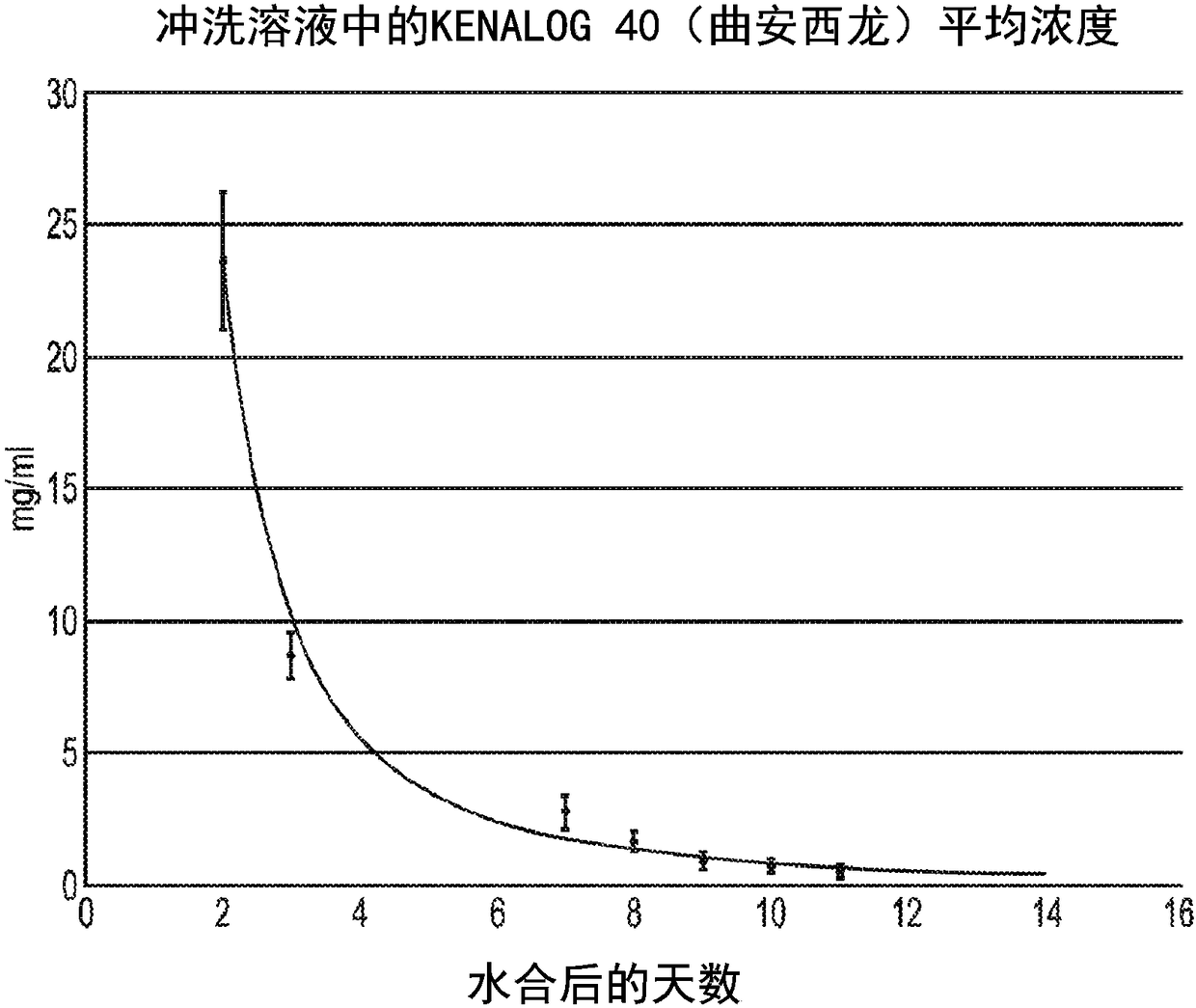
Dissolvable nasal sinus sponge
A sponge, solution technology, applied in extracellular fluid diseases, antibacterial drugs, drug combinations, etc., can solve problems such as infection, patient pain, and no therapeutic benefit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1: Formation of Dissolving Sponge
[0057] About 4.8 grams of hydroxyethylcellulose with a molecular weight of ~750k and 3.2 grams of hydroxyethylcellulose with a molecular weight of ~1.3M were placed in a beaker and mixed thoroughly. Then 350ml of water was added to the beaker with hydroxyethylcellulose. The mixture was then heated to a temperature of about 30-40° C. at about 100-150 RPM using a hot plate and an overhead mixer with a paddle link for 1.5-2 hours until the material was clear (not cloudy) and all lumps were complete dissolve. Then, the pH of the hydroxyethylcellulose solution was adjusted to 3 to 4 using hydrochloric acid. Separately, about 2 g of chitosan HCL was put into a beaker, and then about 50 ml of water was added. Mix the chitosan-HCl solution using a stirring plate with a stir bar until the chitosan-HCl is completely dissolved and the color is yellow. The chitosan solution was then added to the hydroxyethyl cellulose solution while s...
Embodiment 2-6
[0058] Example 2-6: Effect of Solution Viscosity on Sponge Formation
[0059] The initial solution with 2.5% solids prepared according to Example 1 was then diluted from 2.5% to 1.25% (50% dilution), 0.625%, 0, 3125%, 0.151%, 0.0756% to form Examples 2-6 . The solution was then formed into a sponge in the same manner as described in Example 1 above. A sponge having a solid content of 0.5% by weight or higher and a viscosity of 0.05 Pa·s or higher is formed. Viscosity, weight percent solids, and sponge mass are reported in Table 2. Examples 4, 5, 6 (Table 2) did not form solid sponges.
[0060] Table 2
[0061]
Embodiment 7-9
[0062] Examples 7-9: Adhesion test
[0063] The sponges produced according to the examples were cut in half and placed in separate trays (1 / 2 sponge) and hydrated with water (8ml). The sponge was then allowed to dry overnight at room temperature. The sponges were then tested for adhesion. The results, reported in Table 3, indicated that the hydrated sponges were mucoadhesive with an average adhesion force of 37 grams of force.
[0064] table 3
[0065] Example
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com