Methods and apparatuses for monitoring the functionality of redundantly interconnected contacts
A contact and function technology, applied in measuring devices, instruments, detailed information of electromagnetic relays, etc., can solve problems such as expansion of installation space, load or functional danger, restrictions, etc., to achieve the effect of high monitoring flexibility and high flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
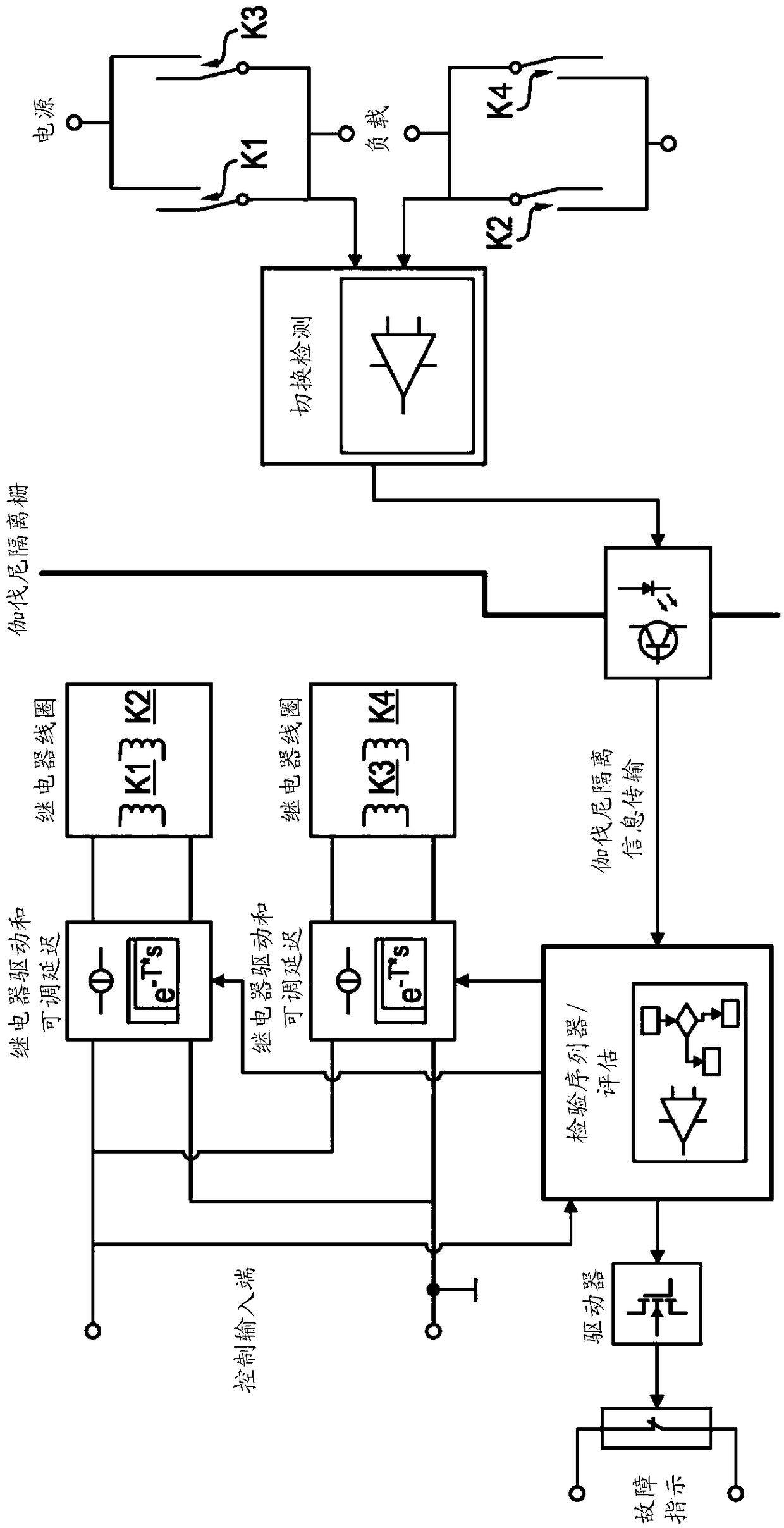
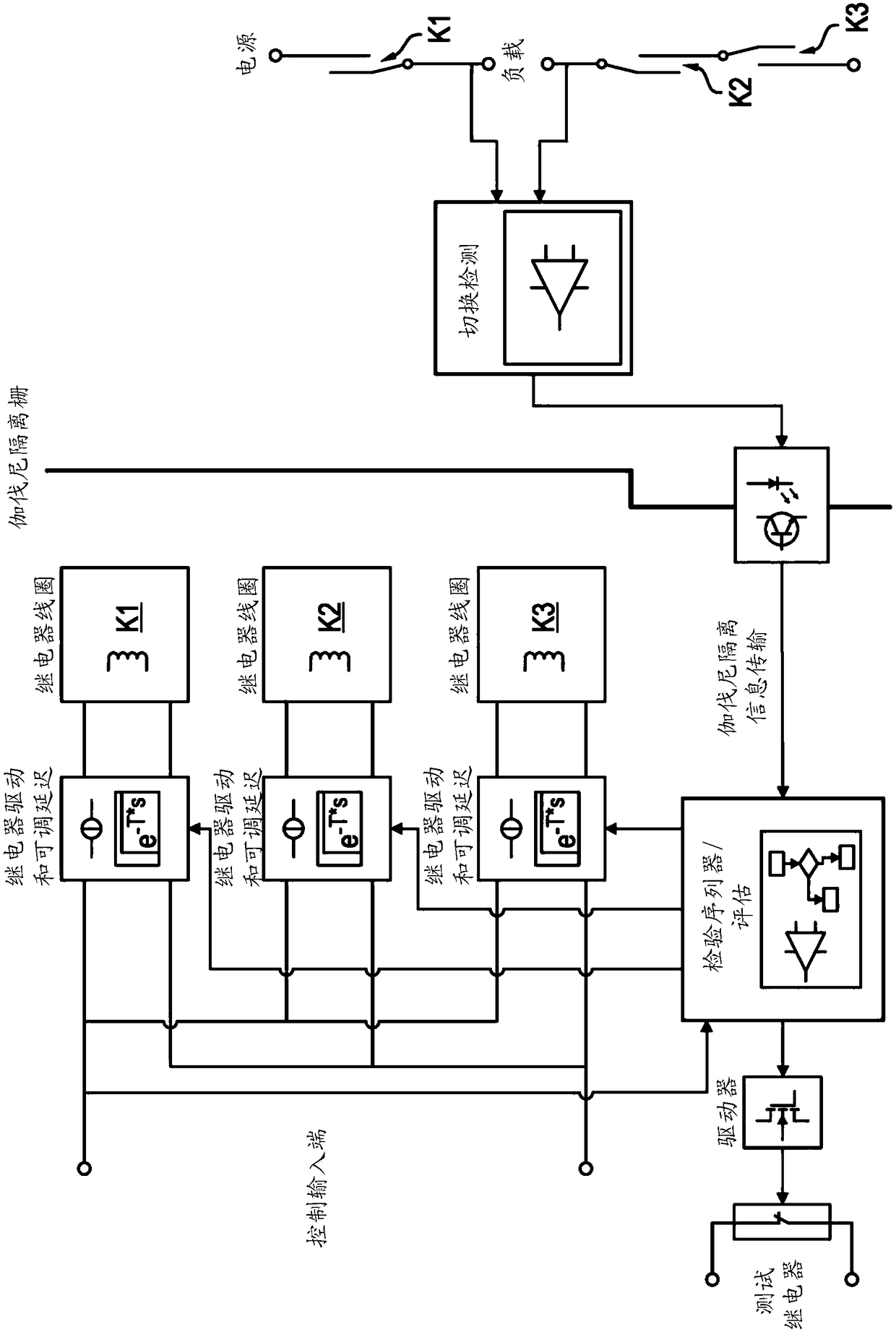
[0047] figure 1 Illustrations of methods and / or apparatuses according to embodiments of the invention are shown within block diagrams. In this embodiment, n=2 redundant channels are realized for the all-pole switching process, wherein channel CH1 is realized by switch K1 and switch K2, and switch K1 and switch K2 are realized by switches K1 and switch K2 to activate the relay coil. Channel CH2 is implemented by switches K3 and K4, which are energized by relay coils for these switches K3 and K4. The relay coils for activating switches K1, K2, K3 and K4 are in figure 1 The middle part of is shown.
[0048] figure 1 The layout of the left part and figure 1 The arrangement of the right part is isolated by Galvani. Control inputs include relay drivers with adjustable delays for switching or energizing relay coils. Switches K1, K2, K3 and K4 are provided for providing electrical connection between the power source and the load.
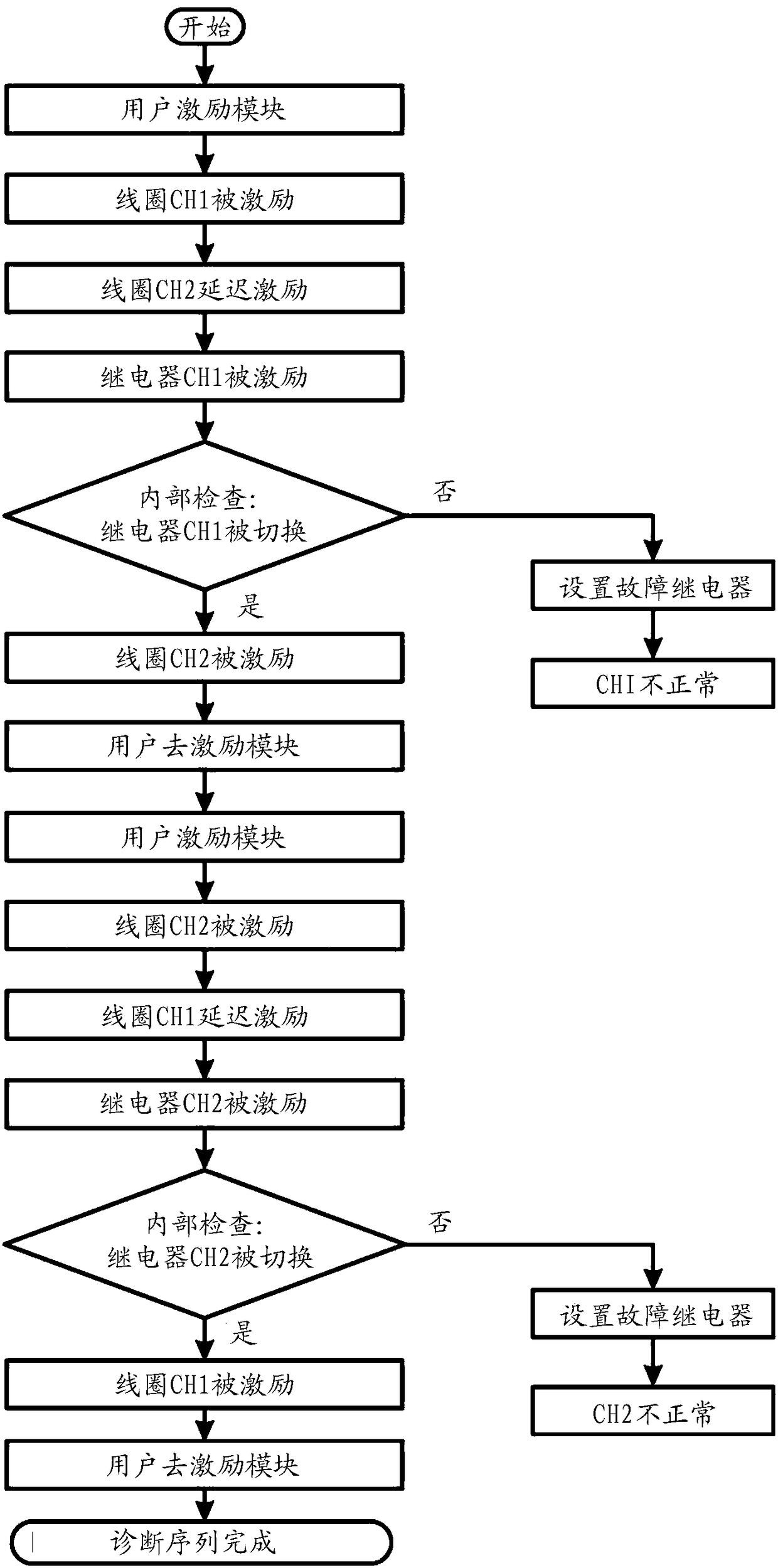
[0049] Switching detection circuits are provi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com