Control method and device of feeding type inversion power supply
A technology of inverter power supply and control method, which is applied in the direction of single-network parallel feeding arrangement, etc., can solve problems such as affecting test efficiency, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and reducing operational complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
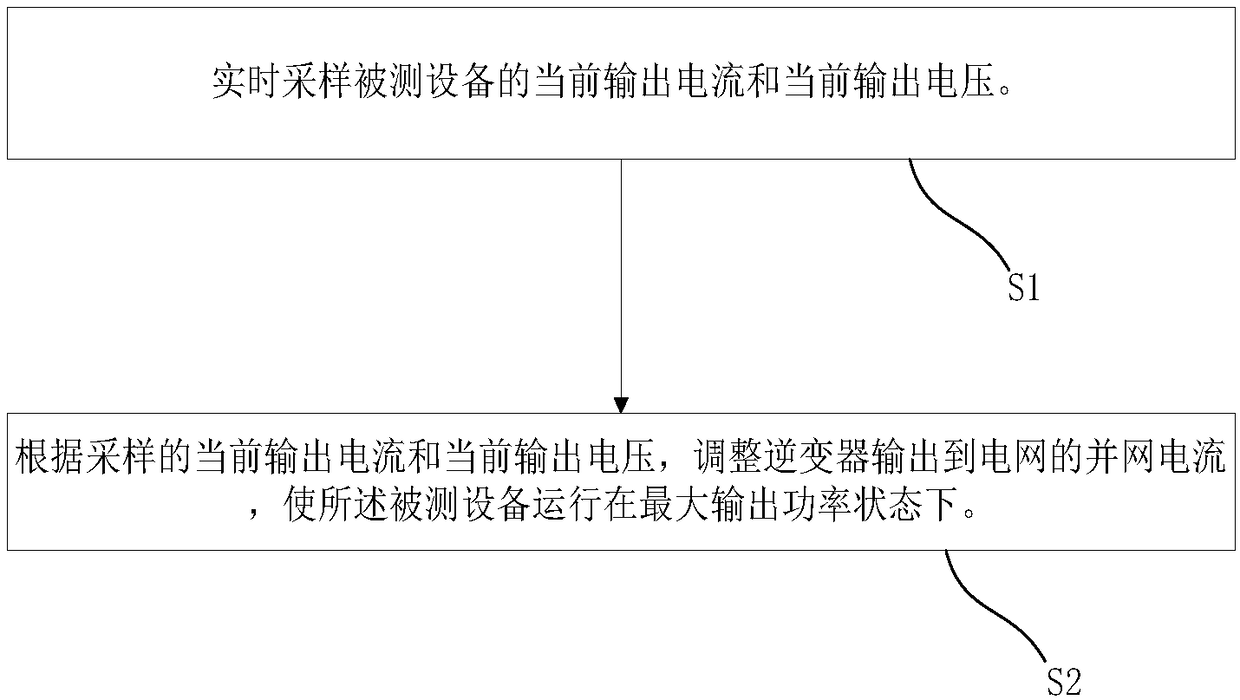
[0037] In one embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, a feed-in inverter power supply control method includes the following steps:
[0038] S1: Real-time sampling of the current output current and current output voltage of the device under test;
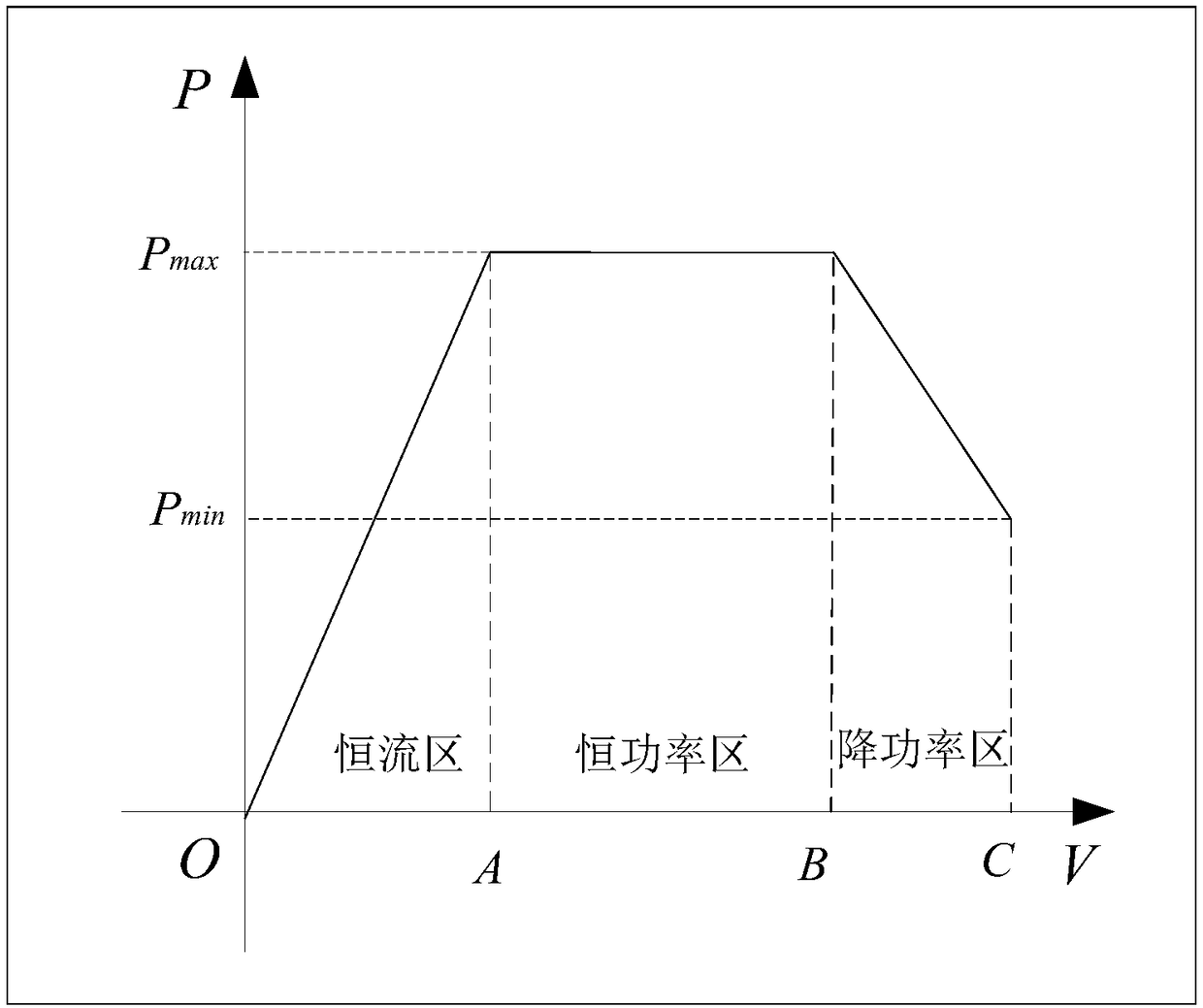
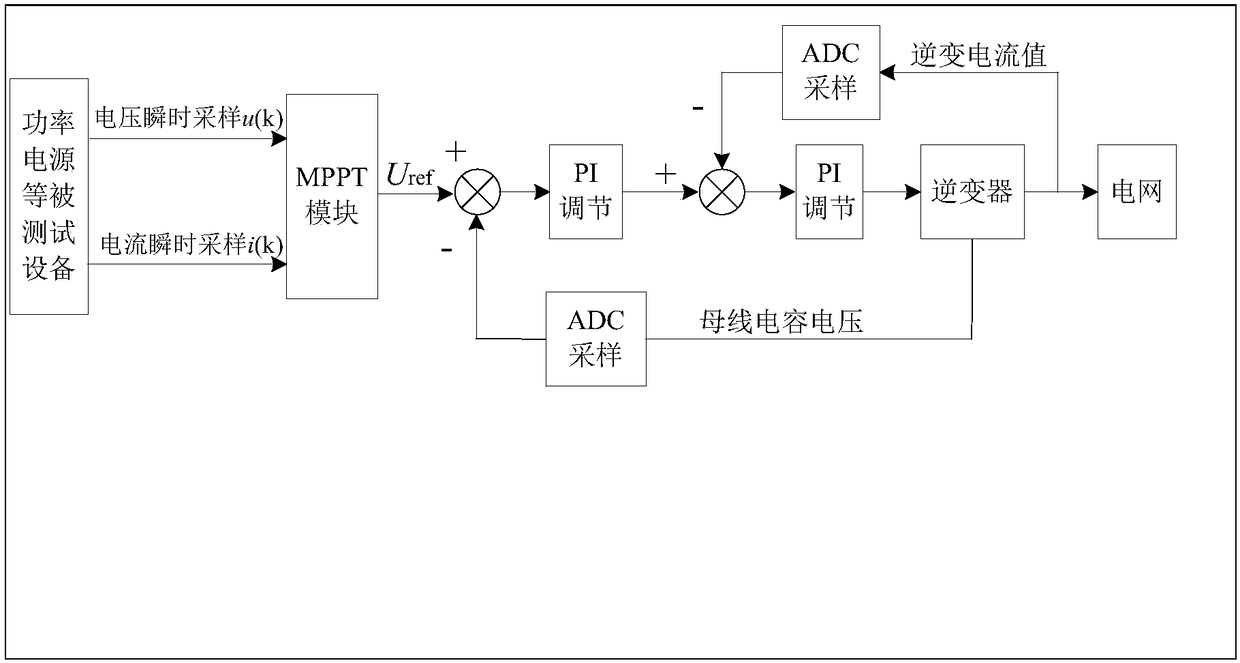
[0039] S2: Adjust the grid-connected current output from the inverter to the grid according to the sampled current output current and current output voltage, so that the device under test operates at a maximum output power state.
[0040] Further, the S1 step also includes the following steps:
[0041] S11: Calculate the current output power of the devi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com