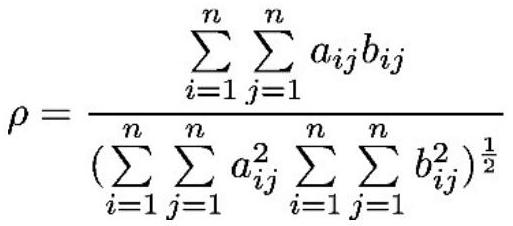Solving method of fpga operation circuit and Spearman's order correlation coefficient
A technology for computing circuits and computing results, applied in electrical digital data processing, computing, digital data processing components and other directions, can solve problems such as time-consuming, complex circuit structure, time-consuming calculation and solving, etc., to achieve rapid solutions and simplify FPGA operations Hardware circuit, the effect of speeding up operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] The generalized relative coefficient explains the internal relationship among PPMCC, KT and SR. make Represents n pairs of independent and identically distributed data pairs generated by the binary continuous distribution parent; the data pair sequence according to Arranged in ascending order, a new set of data pair sequences can be obtained where X 1 n is an ordinal statistic about X, and the corresponding Y [i] call it X (i) accompaniment; assuming X j in sequence The kth position in , then define the number k as X j rank of , denoted as P j ; Similarly put Y j The rank of is defined as Q j . The generalized correlation coefficient is defined as follows:
[0059]
[0060] when a ij =P j -P i and b ij =Q j -Q i The Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient can be derived γ s , which is the Spearman rank correlation coefficient derived from the generalized correlation coefficient using the original method. After research, the inventor found...
Embodiment 2
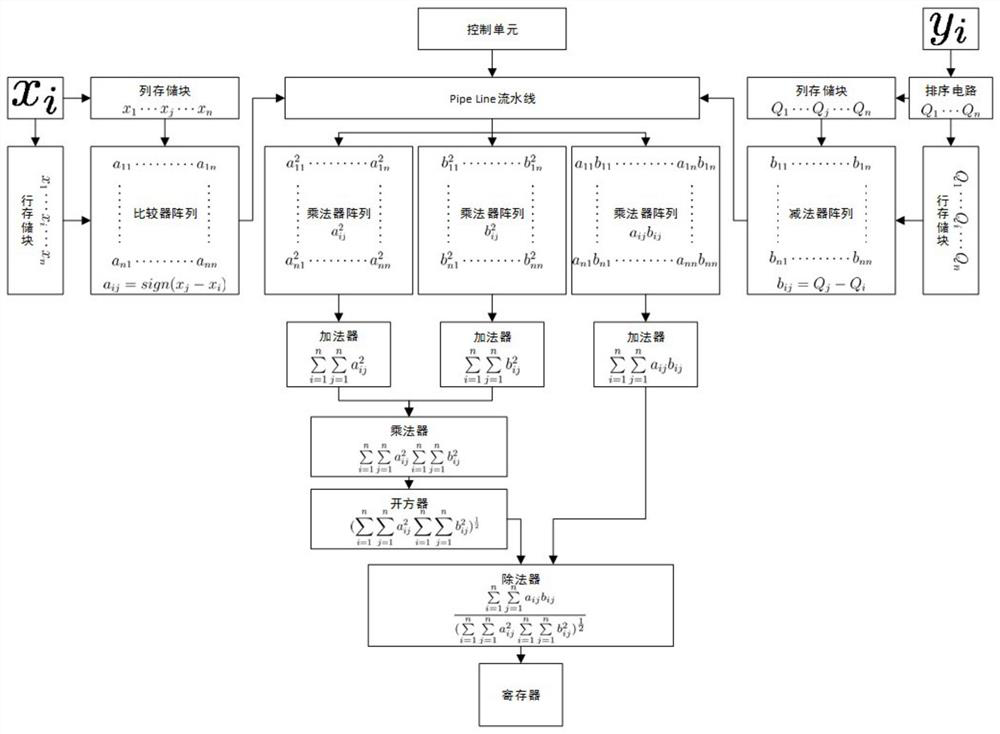
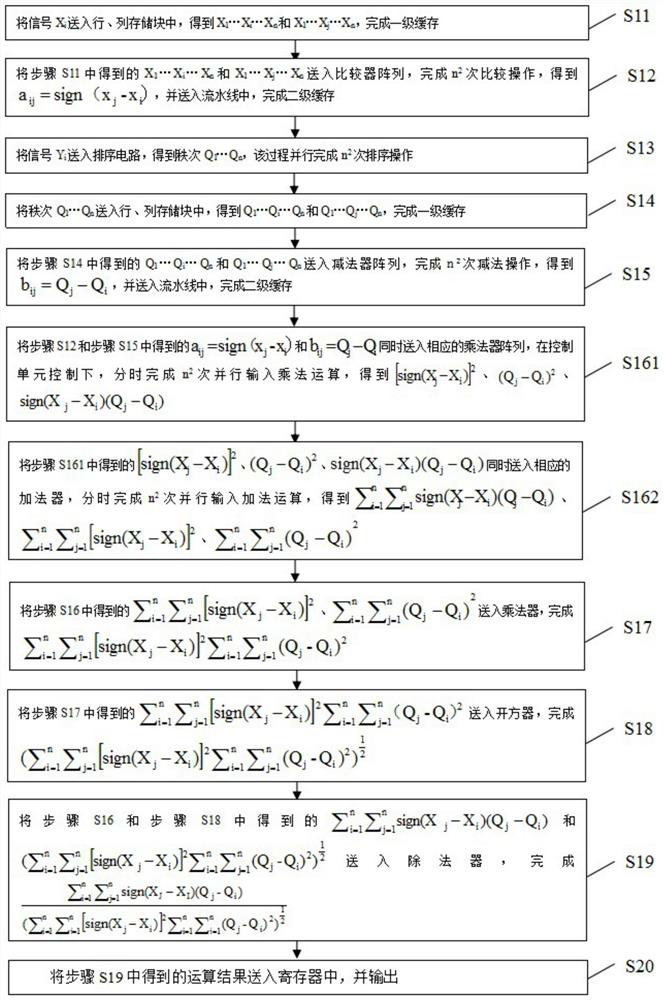
[0100] see figure 2 , is a schematic flowchart of a method for solving the Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The method is performed by the FPGA computing circuit provided by the embodiment of the present invention, and the steps are as follows:
[0101] S11. Signal X i Send it to the row and column storage block to get X 1 …X i …X n and x 1 …X j …X n , to complete the first-level cache;
[0102] S12, the X obtained in step S11 1 …X i …X n and x 1 …X j …X n into the comparator array to complete the n 2 comparison operation to get a ij =sign(x j -x i ), and sent to the pipeline to complete the secondary cache;
[0103] S13. Signal Y i Send it to the sorting circuit to get the rank Q 1 …Q n , the process is done in parallel n 2 second sorting operation;
[0104] S14. Rank Q 1 …Q n Send it to the row and column storage block to get Q 1 …Q i …Q n and Q 1 …Q j …Q n , to complete the first-l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com