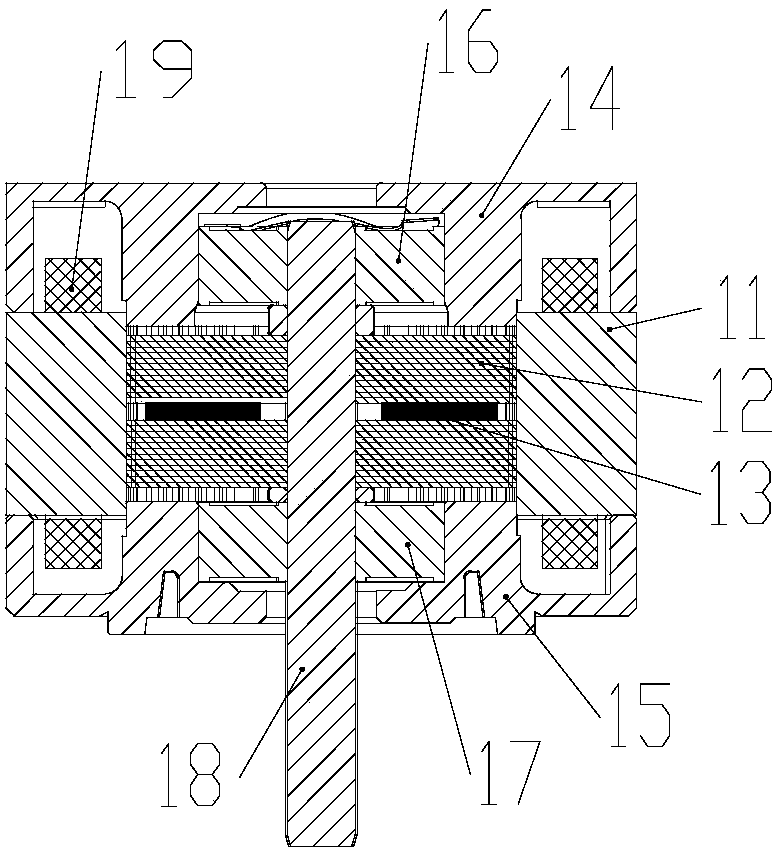
Stepping motor
A stepping motor and stator iron core technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc. Saturation and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving the magnetic density distribution, ensuring the slot area, and reducing the magnetic density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
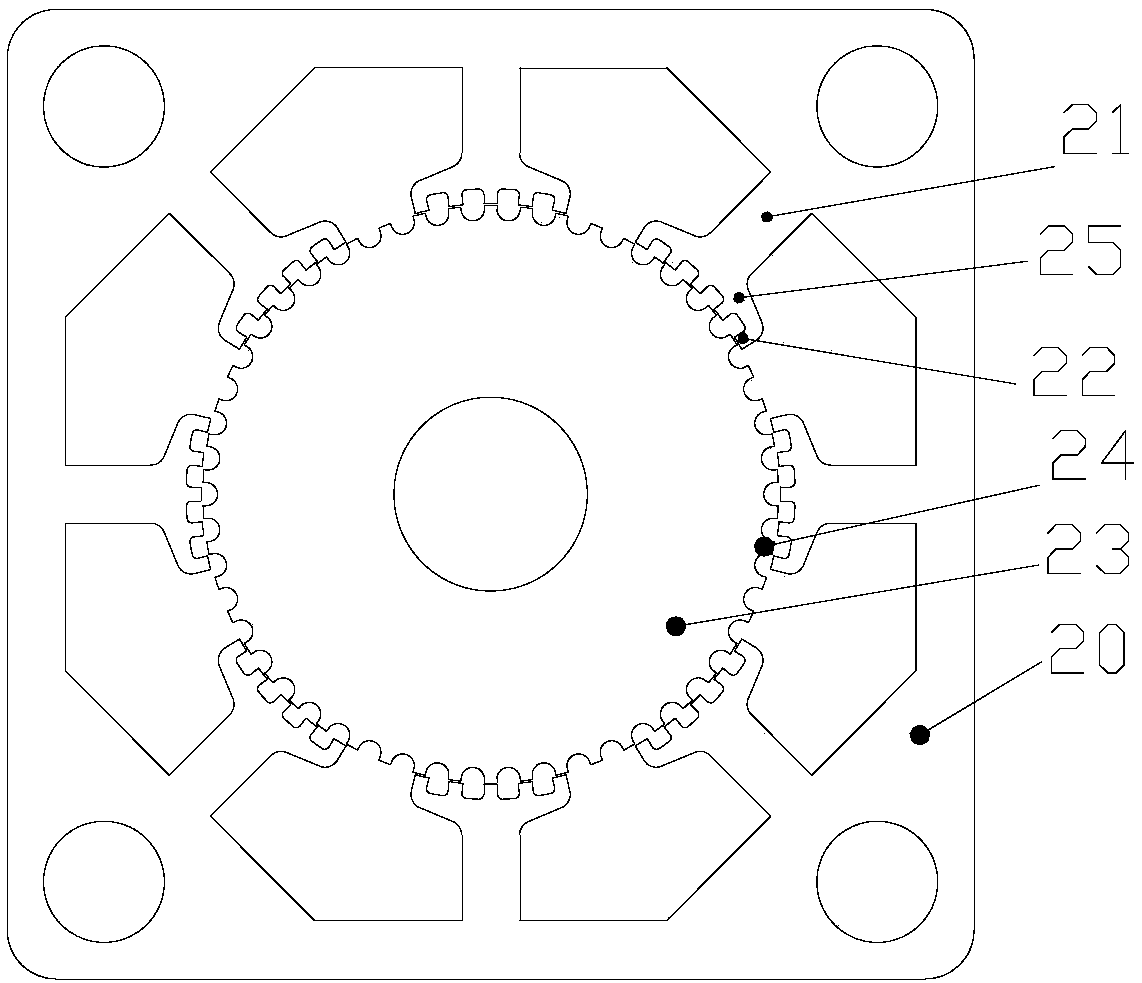
[0044] A stepper motor, including a stator core 11 and a rotor core 12, the stator core 11 includes a stator core body 20, and the stator core body 20 is evenly distributed with 8 stator main poles along the circumferential direction 21. The pole shoe 25 of each stator main pole 21 is provided with a plurality of evenly distributed stator small teeth 22, and the width of the stator main pole 21 gradually increases from outside to inside.
[0045] Such as Image 6 As shown, because the magnetic density in area A is relatively saturated, increase the width of the main pole in area A to Bp2; the magnetic density saturation in area C is low, reduce the width of the main pole in area C to Bp1, and the entire main pole changes from a rectangle to a trapezoid.
[0046] The stator main pole 21 has a trapezoidal structure, its small end is connected to the stator core yoke ( 26 ), and its large end is connected to the pole shoe 25 .
[0047] The specific size of the trapezoidal struct...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Such as Figure 7 As shown, because the magnetic density in area A is relatively saturated, increase the width of the main pole in area A to Bp2; the magnetic density saturation in area C is low, reduce the width of the main pole in area C to Bp1, and the entire main pole changes from a single rectangle to an edge The radial direction is composed of two rectangular main pole parts from large to small.
[0052] The main pole of the stator has a first-order boss structure.
[0053] The specific size of the first-order boss structure is as follows:
[0054] Bt*N*0.5≤Bp1
[0055] Among them, Bp1 is the width of the convex part of the small head, L1 is the length of the convex part of the small head, Bp2 is the width of the bottom of the big head, L2 is the length of the bottom of the big head, Bt is the width of the small teeth of the stator, and N is the stator on the main pole of a single stator Number of small teeth.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the entire main pole changes from a single rectangle to a combination of three rectangular main pole parts from large to small along the radial direction. The main pole of the stator has a second-order boss structure.
[0058] The specific size of the second-order boss structure is as follows:
[0059] Bt*N*0.5≤Bp1
[0060] Among them, Bp1 is the width of the convex part of the small head, L1 is the length of the convex part of the small head, Bp2 is the width of the middle step, L2 is the length of the middle step, Bp3 is the width of the bottom of the big head, L3 is the length of the bottom of the big head, and Bt is the stator The width of the small teeth, N is the number of stator small teeth on a single stator main pole.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com