Method for dynamic correction during SLAM (simultaneous localization and map building) of mobile robot
A mobile robot and map creation technology, applied in the direction of navigation calculation tools, etc., can solve the problem of deviation between positioning and map influence, achieve the effect of improving accuracy and stability, and improving the path planning of mobile robots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
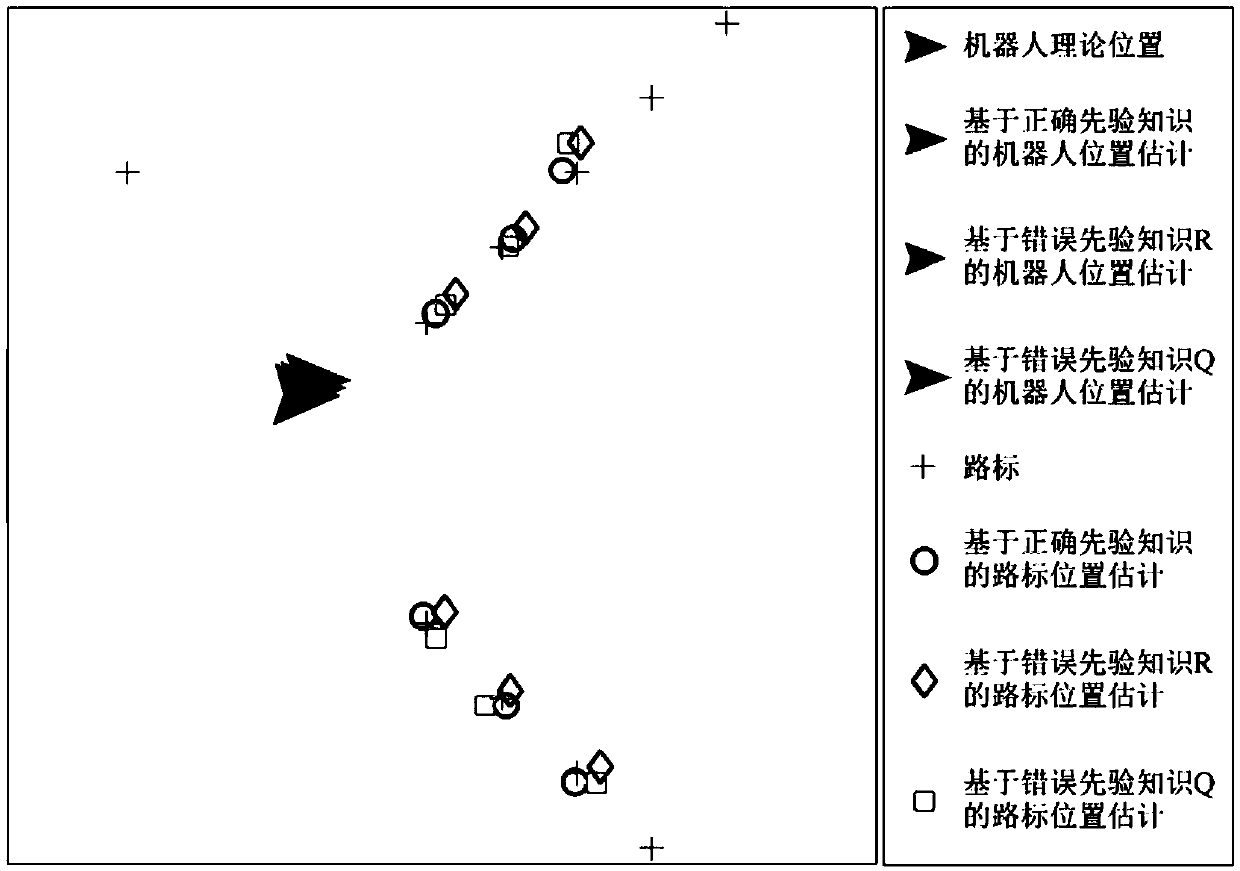
[0059] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, the present embodiment provides a dynamic correction method for simultaneous localization and map creation of a mobile robot, comprising the following steps:
[0060] Step1: Data collection and verification,
[0061] Analyze and sort out the deviation factors caused by the real-time positioning and map construction of historical message records;
[0062] Step2: Adjust revision parameters,
[0063] First, initialize the mobile robot, the default starting position is zero,
[0064] Then, according to the pose information of the mobile robot at time t-1, that is, the posterior probability density function of t-1, the state of the current moment is predicted through the existing prior knowledge, and the prior density function at time t is obtained. Probability density function is used to generate and collect particle sets, N particles are collected, and the weights of particles are initialized to 1 / N;
[0065] Then set the fitness function, t...
Embodiment 2
[0112] This embodiment provides a deduction process of a dynamic correction method for simultaneous positioning and map creation of a mobile robot. Each particle records the current position, speed and the optimal position that has been visited, which represents a solution of the algorithm. During the iterative update process, each particle moves towards the global optimum and the direction where it has reached the optimal position:
[0113]
[0114] x i (k)=X i (k)+V i (k+1)
[0115] x i (k) represents the position of the i-th particle in the k-th iteration, and the particle is based on V i (k+1) velocity from position X i (k) fly to X i (k+1) position, V i The speed of (k+1) consists of three parts: inertia, cognition and society. The inertia part simulates the last trajectory of the bird. ω is the inertia weight, which represents the influence of the previous trajectory on the current new trajectory. c 1 and c 2 is the acceleration coefficient of cognitive part ...
Embodiment 3
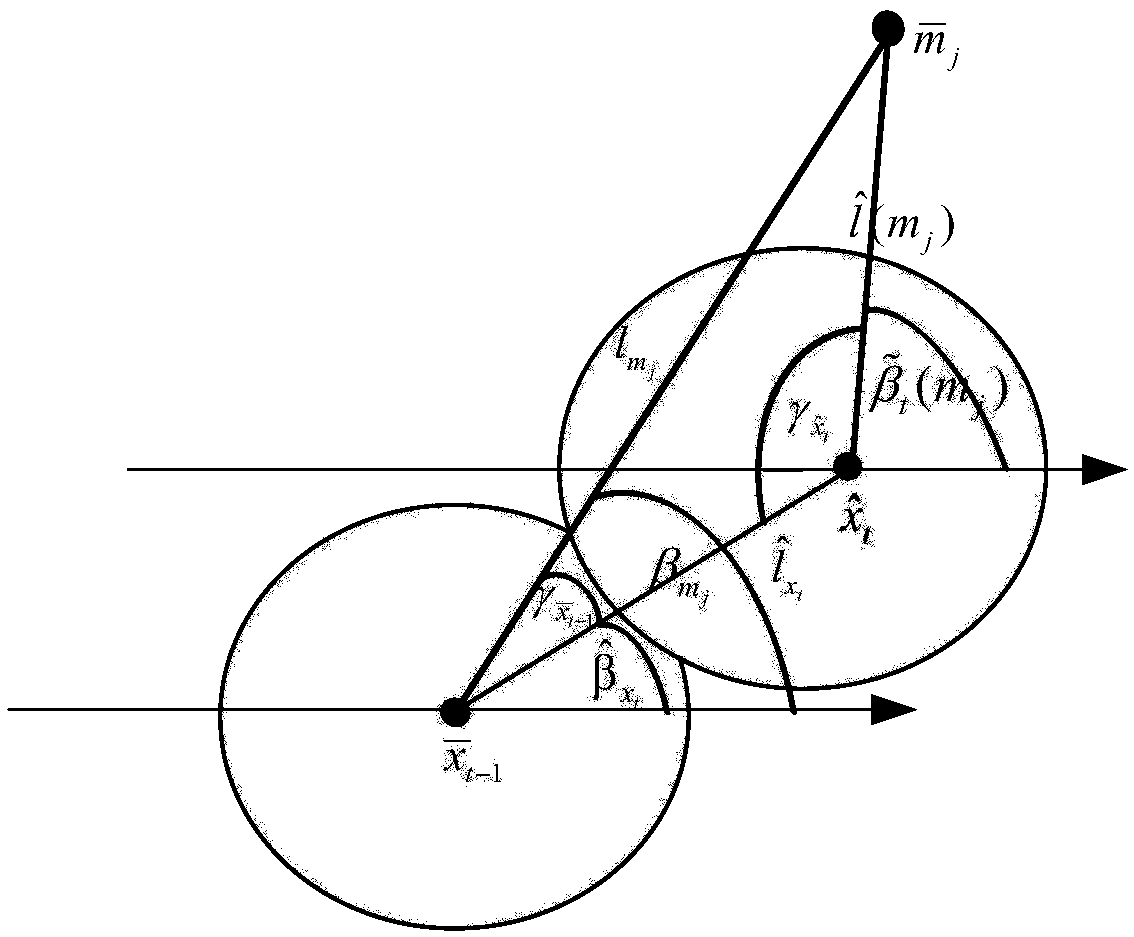
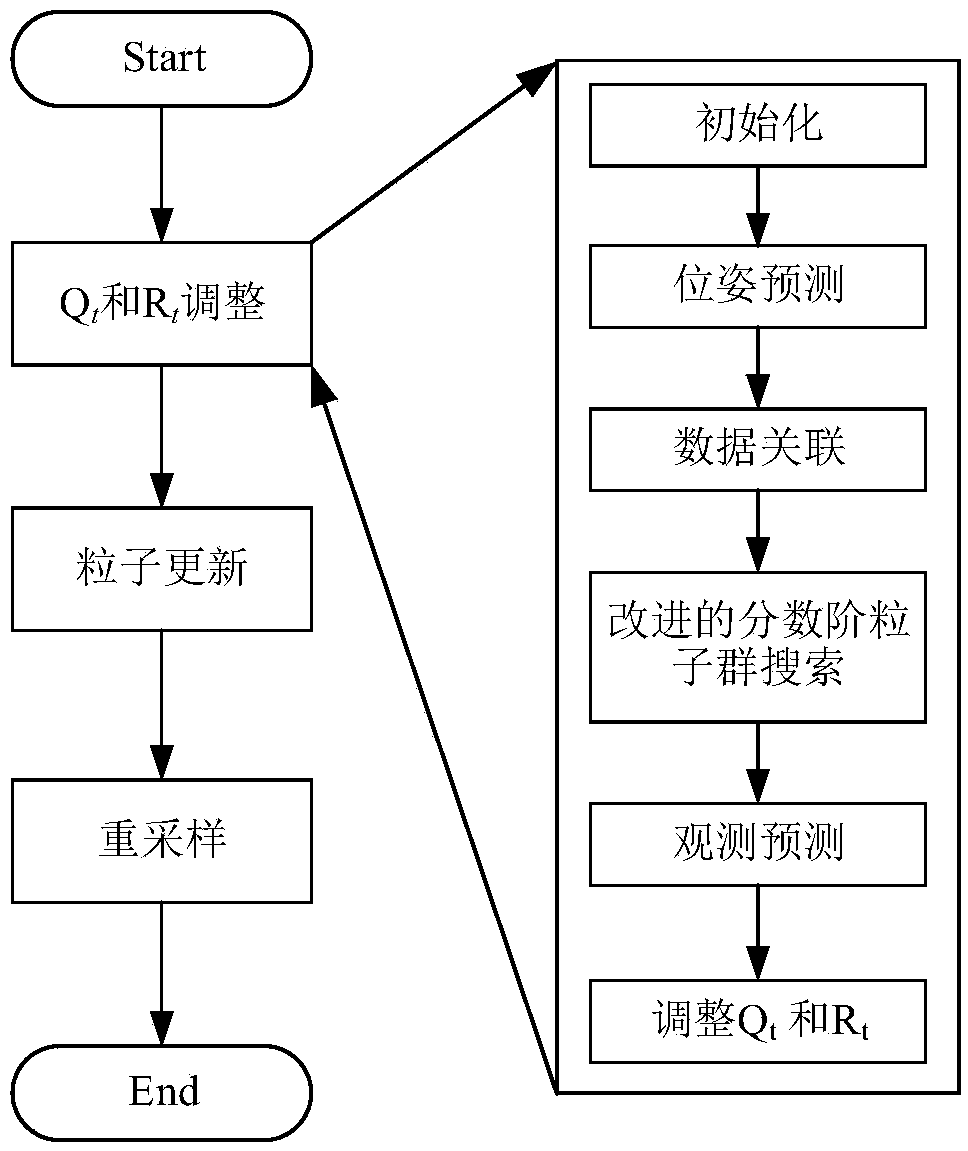
[0154] This embodiment provides a dynamic correction method for simultaneous positioning and map creation of a mobile robot, including the following steps:
[0155] Build motion and observation models for Qt and Rt tuning particles;
[0156] The proposed prior knowledge correction FastSLAM algorithm adds Q before the particle update t and R t In the process of adjustment, the method of updating and resampling of each particle still adopts the algorithm of FastSLAM2.0; due to Q t and R t The adjustment process is similar to the update process of FastSLAM2.0 particles, and the adjustment process is used to adjust Q t and R t The pose and environment information of the mobile robot (based on different coordinate systems and origin positions) as a special particle X [ex] Look, Q t and R t The adjustment process is as follows:
[0157] 1) Initialization: If the number of landmarks observed this time or last time is too small, it is impossible to determine the corresponding ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com