Secure two-party collaboration SM2 signature method
A safe and signature-generating technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as difficulty in preventing man-in-the-middle attacks, lack of identity authentication mechanism for both parties in communication, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
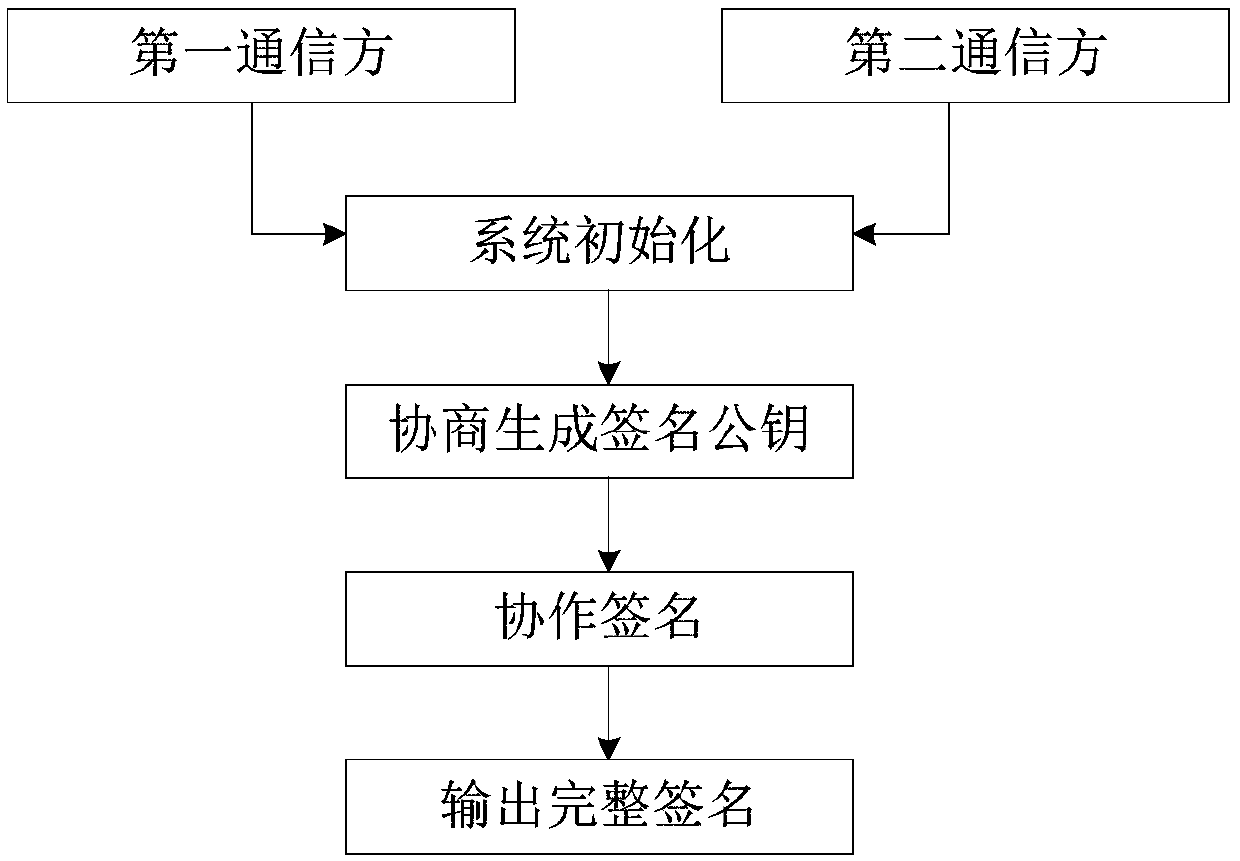
[0054] exist figure 1 Among them, the secure two-party cooperative SM2 signature method in this embodiment consists of the following steps.
[0055] (1) System initialization
[0056] The first communication party and the second communication party share the elliptic curve parameter E(F of the SM2 algorithm p ), G and n, E(F p ) represents the finite field F p All rational points of the upper elliptic curve E, including the point O at infinity, are a collection, and G represents the base point of the upper order of the elliptic curve E being n, and n is a finite positive integer. The elliptic curve parameter E(F of the present embodiment p ), the specific values of G and n are the same as those of the parameters in Appendix A.2 of GB / T32918.2-2016. The cryptographic hash method hash that the communication parties agree to use is the cryptographic hash method given in GB / T 32905-2016, that is, the SM3 algorithm; the commitment protocol com is the commitment defined in Fig...
Embodiment 2
[0096] (1) System initialization
[0097] The homomorphic encryption method Enc in this step adopts the Benaloh homomorphic encryption method with additive homomorphism proposed by J. Benaloh in "Dense probabilistic encryption" in 1994. Other steps in this step are the same as in Example 1.
[0098] (2) Negotiation to generate signature public key
[0099] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0100] (3) Collaborative signature
[0101] Step 1) to step 6) are the same as in Example 1.
[0102] 7) The two parties in the communication cooperate to sign
[0103] The homomorphic encryption method Enc in this embodiment adopts the Benaloh homomorphic encryption method. The second communication party consists of k 2 [*]Q 1 The result is obtained as a point (x 1 ,y 1 ), by x 1 The result obtained by +emodn is used as a partial signature r, where mod represents a modulo operation; a position in [1,n is generated 2 ], according to the encryption operation Benaloh in the B...
Embodiment 3
[0109] (1) System initialization
[0110] The homomorphic encryption method Enc in this step adopts the NS homomorphic encryption method with additive homomorphism proposed by D.Naccache and J.Stern in "A new publickey cryptosystem based on higher residues" in 1998. Other steps in this step are the same as in Example 1.
[0111] (2) Negotiation to generate signature public key
[0112] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0113] (3) Collaborative signature
[0114] Step 1) to step 6) are the same as in Example 1.
[0115] 7) The two parties in the communication cooperate to sign
[0116] The homomorphic encryption method Enc in this embodiment adopts the NS homomorphic encryption method. The second communication party consists of k 2 [*]Q 1 The result is obtained as a point (x 1 ,y 1 ), by x 1 The result obtained by +emodn is used as a partial signature r, where mod represents a modulo operation; a position in [1,n is generated 2 ], according to the encryption o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com