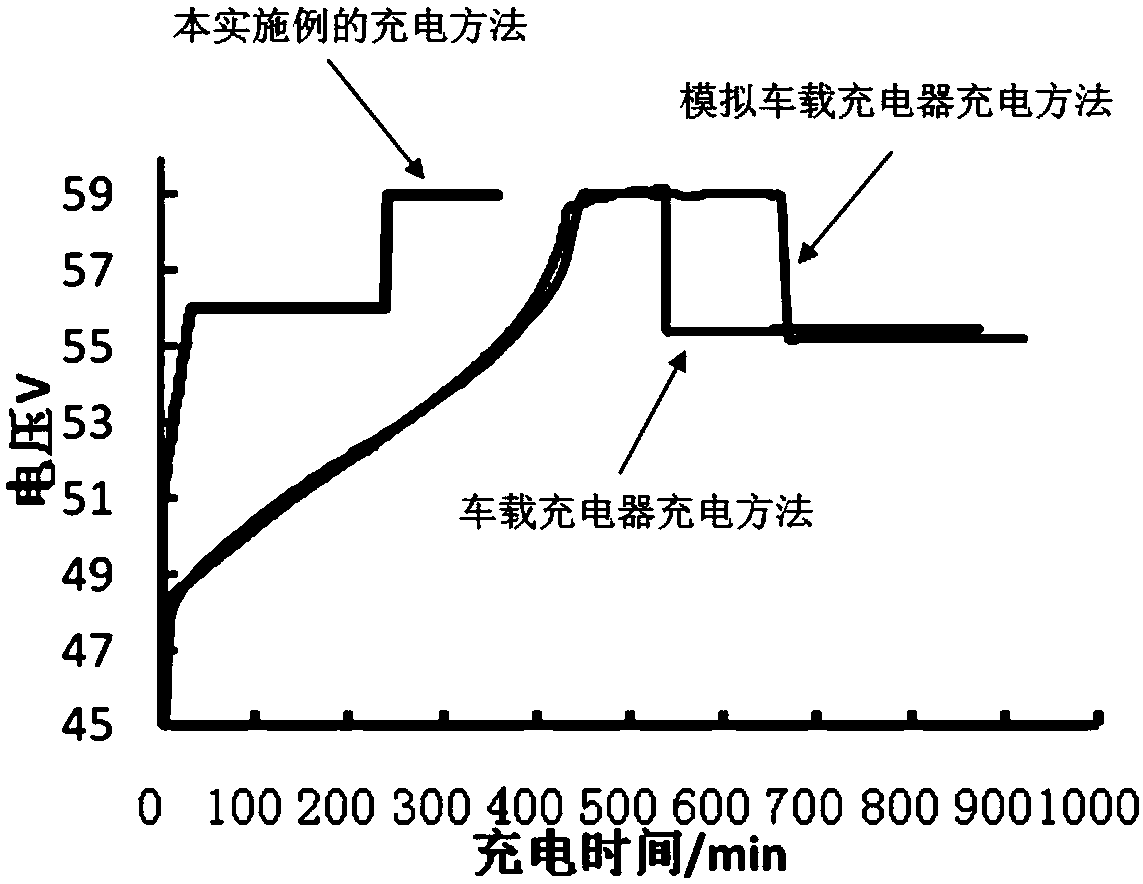
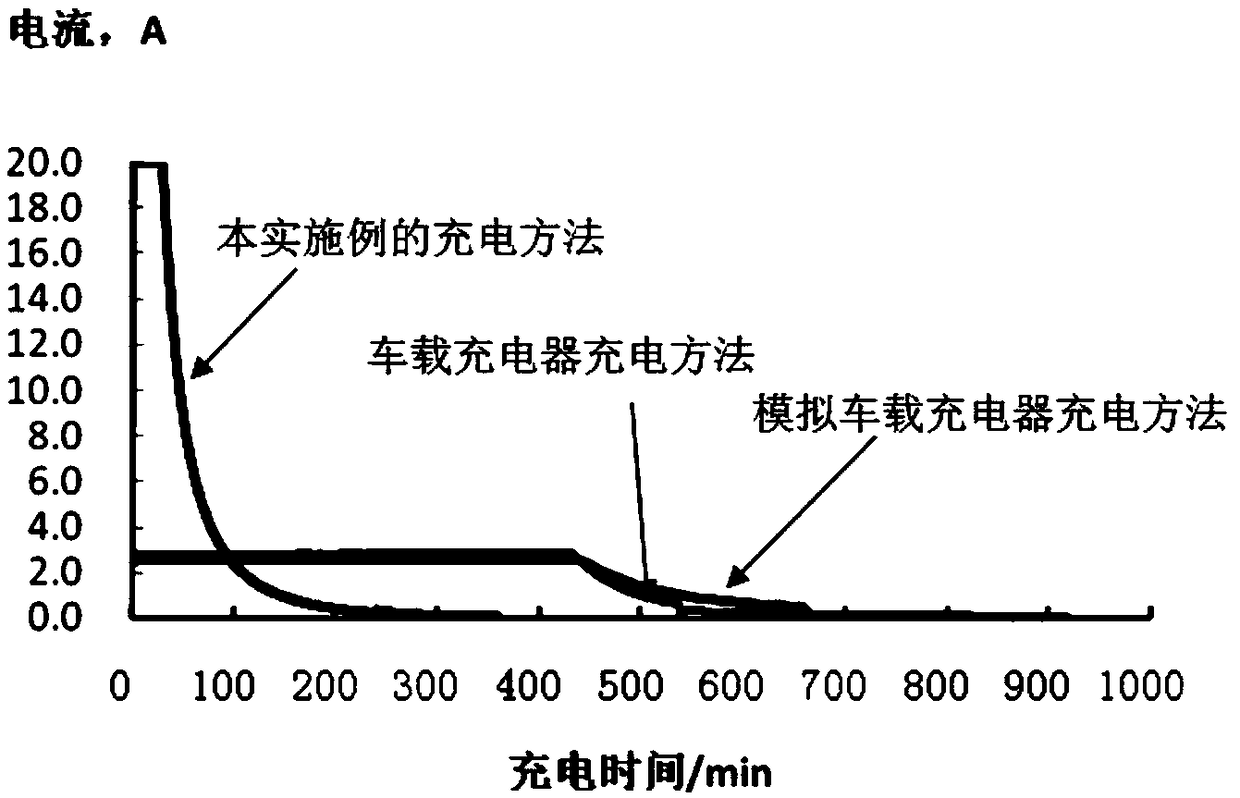
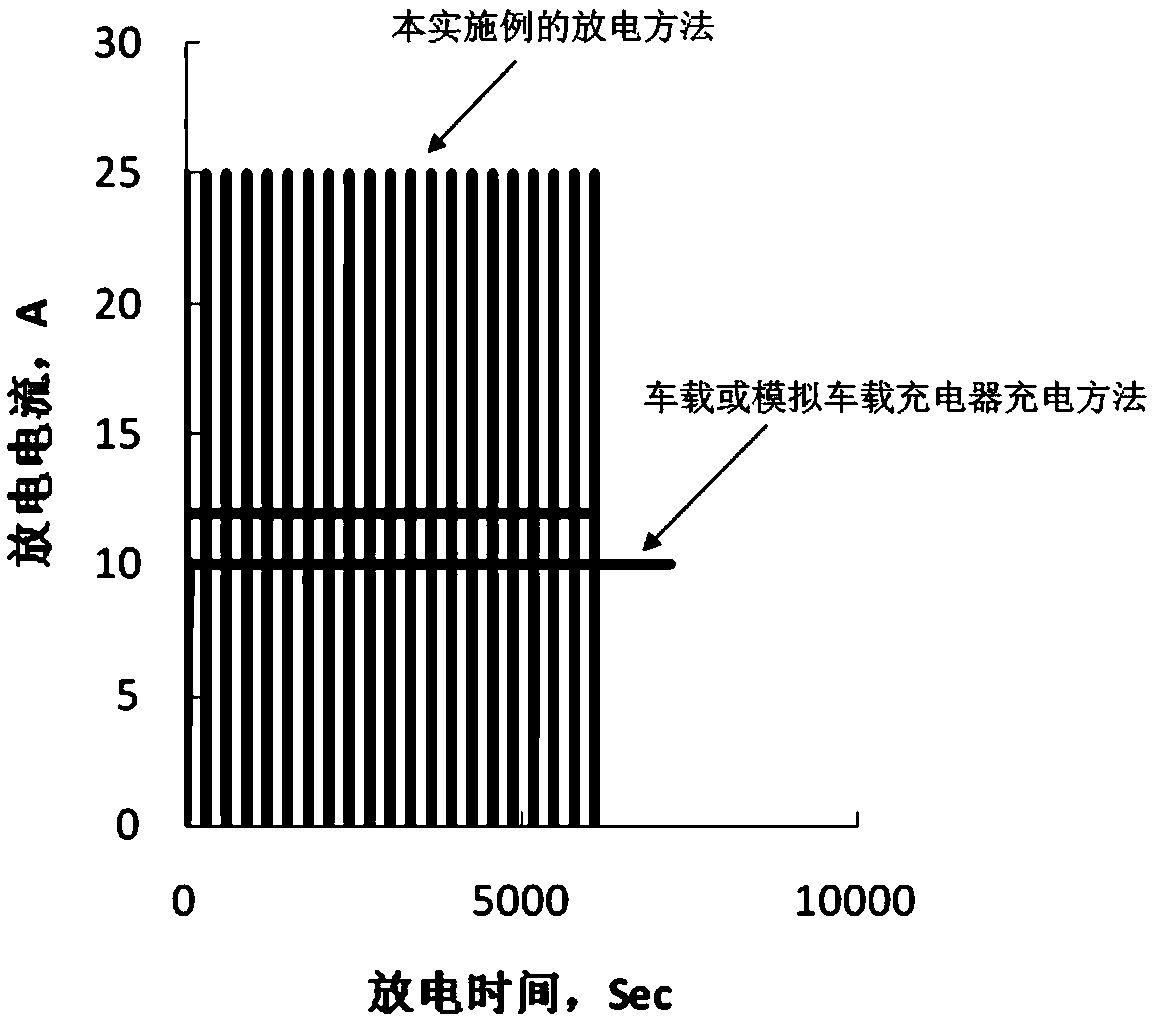
Lead-acid storage battery cycle life detection method
A lead-acid battery, cycle life technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems of long cycle, service life error, affecting battery life, etc., to avoid water loss, accurate cycle life, Battery Cycle Life Accurate Results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The detection method of the cycle life of the lead-acid battery of the present embodiment is applied to the detection of the lead-acid battery of the 6-DZM-20 model, and the rated capacity C of the lead-acid battery of the 6-DZM-20 model is 2 It is 20AH, the standard voltage is 12V, and the number of single cells is 6.
[0032] The detection method comprises the following steps:
[0033] 1) Charge the lead-acid battery
[0034] The two-stage constant current and constant voltage charging method is adopted, and the charging voltage and charging time of the two stages are different; 2 A and voltage 2.34±0.1V / single cell for constant current and constant voltage charging, after charging for the first preset time T1, then with current I 2 A and voltage 2.45±0.1V / single cell are charged with constant current and constant voltage until the charging is completed. Specifically, including:
[0035] The first stage of constant current and constant voltage charging: the first ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The difference between the detection method of the cycle life of the lead-acid battery of the present embodiment and the first embodiment is that in the first embodiment, the actual capacity of 2hr is detected once every 49 large cycles, that is, the detection cycle of the actual capacity of the battery is 49 large cycles ; For lead-acid batteries, as the large cycle continues, the battery capacity is getting closer and closer to 75% of the battery's rated capacity. If the actual capacity of 2hr is detected every 49 large cycles, it is easy to cause the obtained battery cycle. Lifespan is not accurate. Therefore, in this embodiment, the detection cycle of the actual capacity of the battery, that is, the preset maximum number of cycles, is reduced as the accumulated maximum cycle number increases, so that the obtained cycle life of the battery is more accurate. For example, for the first 100 large cycles, the actual capacity of the battery is detected with 50 large cycle...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The difference between the detection method of the cycle life of the lead-acid battery in this embodiment and the first embodiment lies in that the types of batteries tested are different.
[0056] Specifically, the detection method of the cycle life of the lead-acid battery in this embodiment is applied to the detection of the lead-acid battery of the 6-DZM-12 model, and the rated capacity C of the lead-acid battery of the 6-DZM-12 model is 2 It is 12AH, and the number of single cells is 6. The corresponding charging currents I1 and I2 are changed from 10A to 6A, the discharging currents I3 and I4 are respectively 15A and 8A, and other parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
[0057] For other steps in this embodiment, reference may be made to Embodiment 1.
[0058] As a preferred embodiment, the sum of the third preset time T3 and the fourth preset time T4 can also be 8 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, etc., which can be adjusted accordingly accordi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com