A Loose Detection Method for Rail Fastener Nuts Based on Height Comparison
A technology of track fasteners and detection methods, which is applied to tracks, track maintenance, roads, etc., can solve problems such as changes and inability to automatically identify, and achieve the effects of eliminating potential safety hazards, flexible use methods, and a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
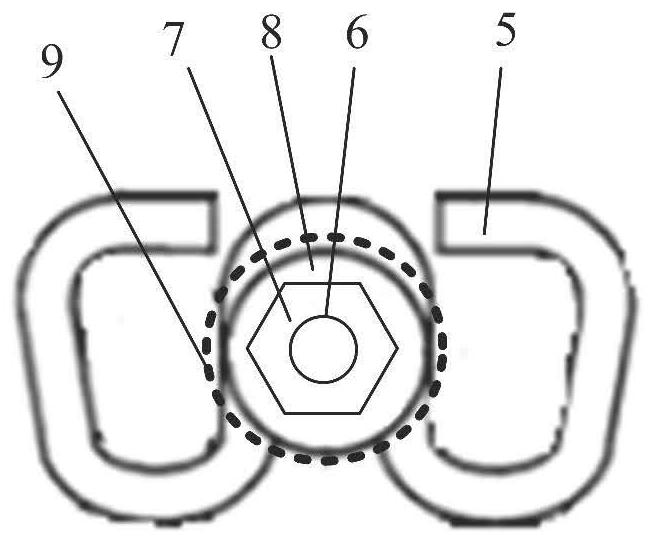
[0054] use image 3 The W-shaped fastener shown is illustrative of this embodiment.
[0055] Step 1: Use a 3D imaging system to obtain 3D shape data of rail fasteners;
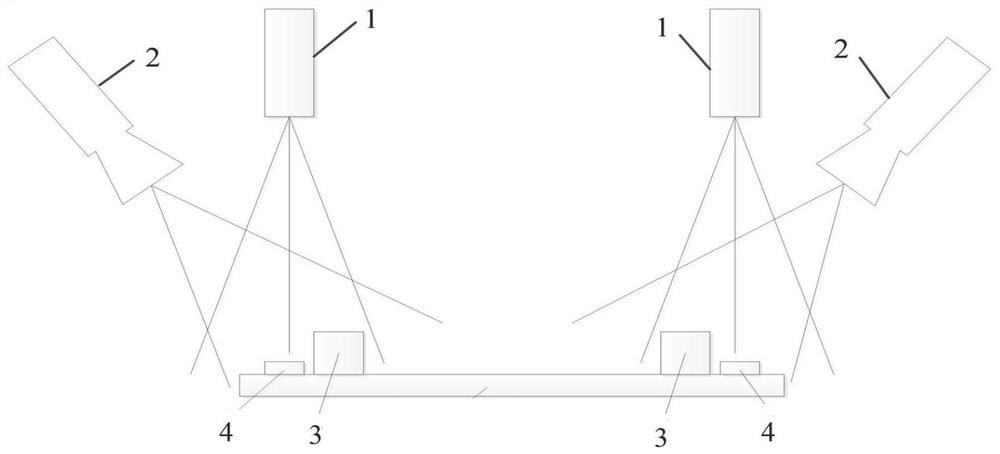
[0056] use figure 2 The shown line structured light scanning 3D imaging system acquires 3D shape data of rail fasteners. like figure 2 As shown, the line-structured light scanning 3D imaging system includes a line-structured light projector 1 and an area array camera 2, the positions and angles of the line-structured light projector 1 and the area array camera 2 remain fixed, and the line-structured light projector 1 generates a line structure The light sheet light is projected onto the fastener 4 perpendicular to the rail 3, forming a section profile on the surface of the fastener 4, and the section profile is photographed by the area array camera 2, and the distance between the light sheet light plane and the area array camera 2 is The geometric position relationship can calculate the coordinates of th...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The difference from Example 1 is that in step 4, the following method is used to calculate the nut height value:
[0074] Step b-4-1: Set the threshold T 1 , perform threshold segmentation on the pixels in the nut ROI to obtain the region R;
[0075]
[0076] Among them, f(x, y) represents the pixel gray value at (x, y) in the nut ROI, and the threshold T 1 =v max -a, where v max Indicates the maximum pixel gray value in the nut ROI, a=5;
[0077] Step b-4-2: Calculate the circumcircle radius r4 of the area R, when r4>r2+e1, calculate the average or median value of the pixels in the area R, as the nut height h c , otherwise go to step 4-3, e1=5.
[0078] Step b-4-3: Carry out circular fitting to the region R, take the center of the circle as the center, set a concentric ring C with radii r5 and r6, r5=r2+e2, r6=r3-e3, Take the average or median value of the pixels in the area of the ring C as the nut height h c ;
[0079] Among them, e2=5, e3=5; r2 is the r...
Embodiment 3
[0081] The difference from Example 2 is that in step b-4-2, when r4>r2+e1, take the non-zero pixel value with the most occurrences in the region R as the nut height h c .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com