Image compression method based on direction lifting wavelet and improved SPIHT under IoT (Internet of Things)
A technology for image compression and the Internet of Things, applied in image communication, digital video signal modification, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low coding efficiency and inability to retain image details, achieve good coding performance, improve subjective quality, and low complexity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0054] Specific implementation mode one: the specific process of the image compression method based on direction-lifting wavelet and improved SPIHT under the Internet of Things in this embodiment is as follows:
[0055] Step 1, performing image block segmentation on the remote sensing image to obtain segmented image blocks;
[0056] Step 2, calculating the best prediction direction for the segmented image blocks respectively, to obtain the best prediction direction of the segmented image blocks;
[0057] Step 3. By calculating weighted directional interpolation filter coefficients, weighted directional interpolation is performed on the fractional sample values needed in the direction boosting process to obtain interpolated image blocks;
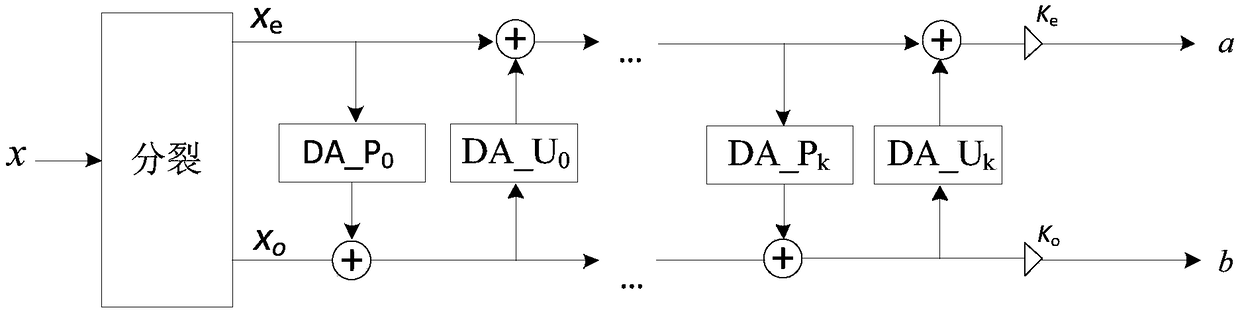
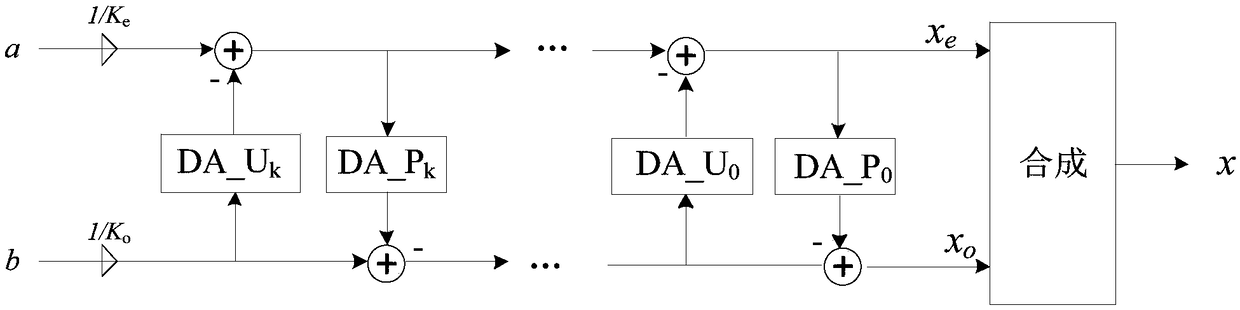
[0058] Step 4, using the best prediction direction obtained in step 2, respectively carry out wavelet transformation based on direction lifting to the interpolated image block, and obtain each transformed image block, that is, each transfor...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0061]Specific embodiment 2: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, the remote sensing image is segmented into image blocks to obtain the segmented image blocks; the specific process is:
[0062] In order to make the lifting direction consistent with the local texture direction of the image, image segmentation is performed first. In [19], a quadtree-based rate-distortion optimization segmentation method is adopted. However, the efficiency of this segmentation method is closely related to the image content. For some image types, such as remote sensing images, which usually reflect complex landforms, the detailed information is usually rich, and there are few large flat areas. At this time, it is difficult for the adaptive segmentation method to show its advantages. The reason is that for images with complex content, the result of using the adaptive segmentation method is very likely that almost all blocks are the smallest blocks...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0091] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in the step two, the best prediction direction is calculated respectively for the divided image block, and the best prediction direction of the divided image block is obtained; the specific process for:
[0092] For wavelet transform based on direction lifting, the prediction error and high frequency subband are closely related. The larger the prediction error, the more information in the high-frequency subbands, and the lower the coding performance. For an image block, its optimal prediction direction should be the direction that can minimize the residual information of the high-frequency sub-band.
[0093] The process of calculating the best prediction direction of an image block is as follows: Figure 4 as shown,
[0094] Suppose the reference direction set is θ ref , the reference direction set θ refContains 15 reference directions, which are recorded as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com