Qualitative and quantitative analysis method of indoor CO2 oil displacement rule
A quantitative analysis, CO2 technology, applied to the analysis of materials, measuring devices, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
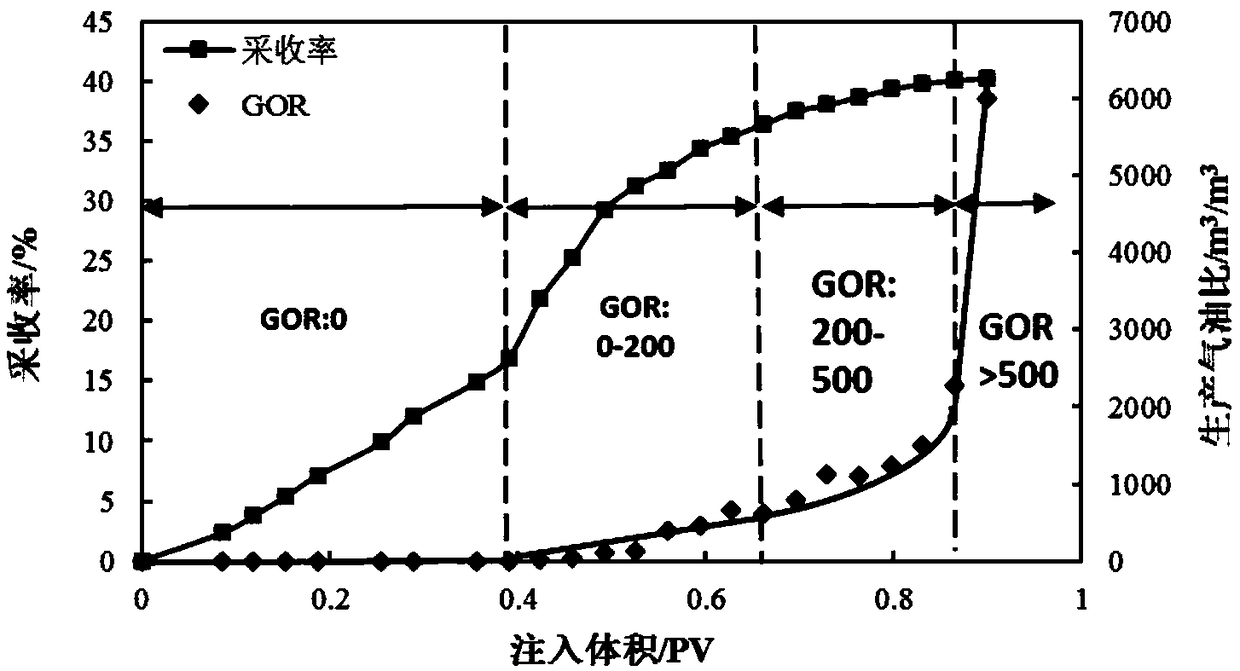
[0030] This embodiment provides a figure 1 Indoor CO as shown 2 The qualitative and quantitative analysis method of oil displacement law includes the following steps:
[0031] Step 1) select the core to dry, vacuumize, and then fill the pores of the core with formation water;
[0032] Step 2) Simulate live CO 2 The temperature and pressure of oil displacement, inject crude oil into the pore entrance of the core until all the pore exit of the core is crude oil. The experimental temperature range is 20°C-120°C and the pressure range is 2MPa-35MPa. By controlling the experimental temperature and pressure to achieve gaseous CO 2 immiscible displacement, supercritical CO 2 immiscible displacement, supercritical CO 2 Near miscible displacement and supercritical CO 2 Miscible displacement;
[0033] Step 3) Start injecting CO into the pore entrance of the core 2 , while recording CO 2 The injection rate, the oil production rate and the gas production rate at the core pore out...
Embodiment 2
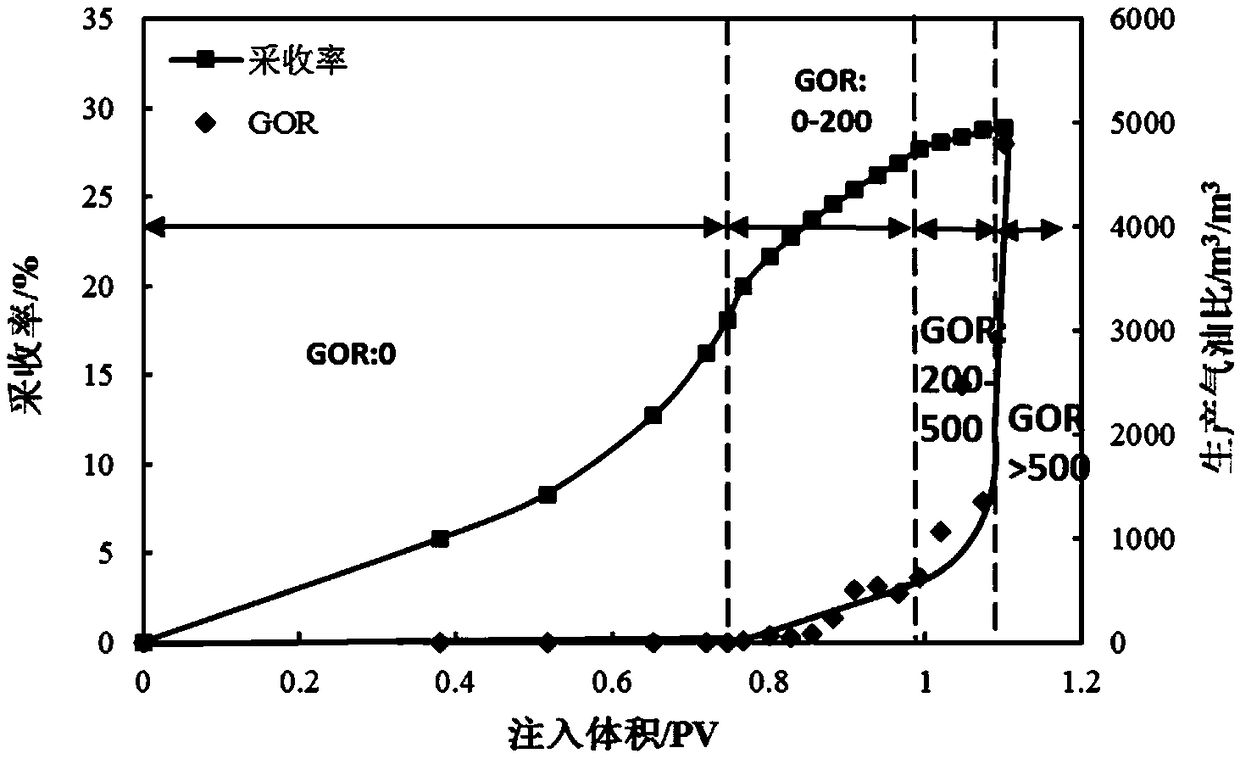
[0046] On the basis of Example 1, this example provides an indoor CO 2 Qualitative and quantitative analysis method of oil displacement law, select natural outcrop homogeneous core, conduct CO 2 Continuous gas flooding experimental research, set the back pressure to 5MPa, and analyze the change of gas-oil ratio in the process of displacement. Specific steps are as follows:
[0047] Step 1) selecting a natural outcrop homogeneous core to dry, vacuumize, and then fill the pores of the core with formation water;
[0048] The apparent volume of the core is calculated by its length, width and height. When calculating the pore volume of the core, first vacuumize the core, and then inject formation water into its inlet until the formation water comes out from the outlet of the core. The volume of the injected formation water is the volume of the core. pore volume;
[0049] Step 2) Control the experimental temperature to the reservoir temperature of 86.2°C, control the pressure at ...
Embodiment 3
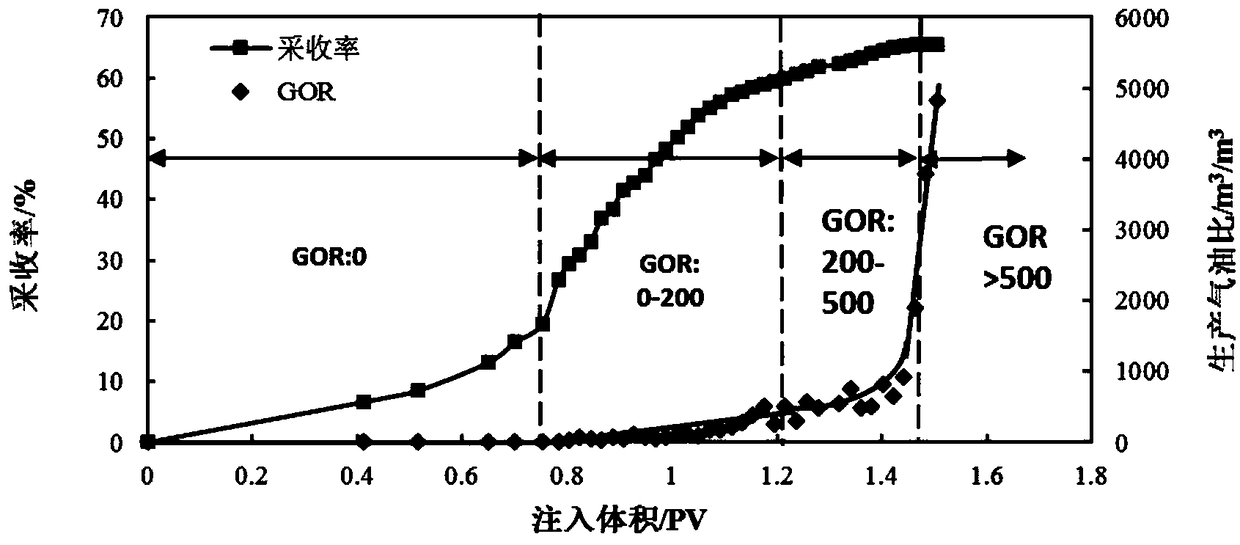
[0060] On the basis of Example 1, this example provides an indoor CO 2 Qualitative and quantitative analysis method of oil displacement law, select natural outcrop homogeneous core, conduct CO 2 Continuous gas flooding experimental research, set the back pressure to 15MPa, and analyze the change of gas-oil ratio in the process of displacement.
[0061] Step 1) selecting a natural outcrop homogeneous core to dry, vacuumize, and then fill the pores of the core with formation water;
[0062] The apparent volume of the core is calculated by its length, width and height. When calculating the pore volume of the core, first vacuumize the core, and then inject formation water into its inlet until the formation water comes out from the outlet of the core. The volume of the injected formation water is the volume of the core. pore volume;
[0063] Step 2) Control the experimental temperature to the reservoir temperature of 86.2°C, control the pressure at the outlet end of the rock core...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com