Method and system for preventing repeated payment
A technology for repeated payments and transactions, applied in the blockchain field, can solve problems affecting the stability of the blockchain system, attacks, etc., and achieve the effects of avoiding the possibility of repeated payments, reducing burdens, and maintaining stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
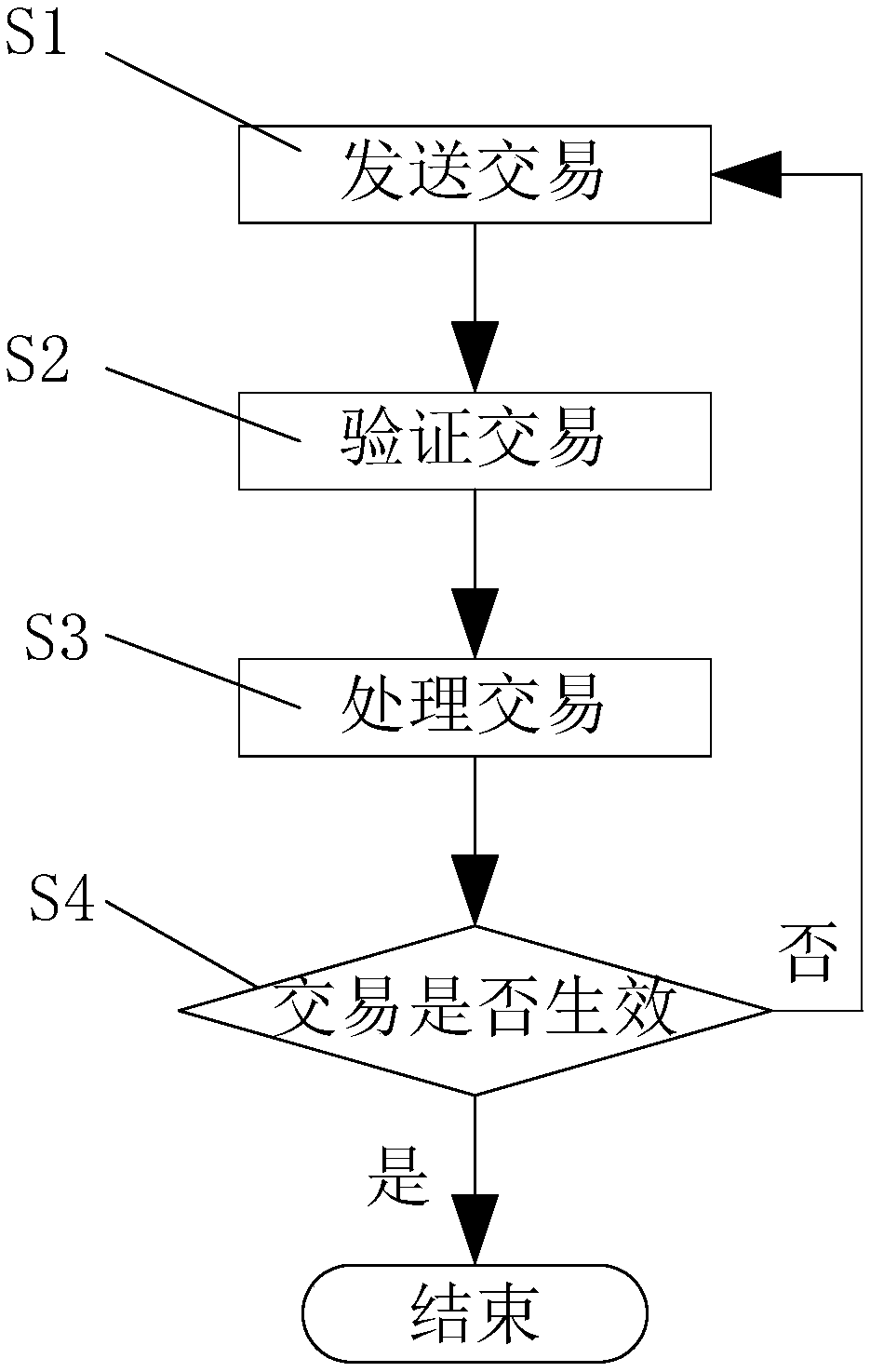
[0057] Such as figure 1 , 2 , 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, a method for preventing repeated payment, comprising the following steps:
[0058] S1. Send the transaction; the transaction with validity period is sent to any node of the blockchain network;
[0059] S2. Verify the transaction; whether the transaction is verified by the node is valid, if the verification is valid, the node will propagate the transaction to other nodes connected to the node, and at the same time, the transaction initiator will receive a return message indicating that the transaction is successful; if If the verification is invalid, the node will refuse to accept the transaction and at the same time return a message indicating that the transaction was rejected to the transaction initiator, and return to step S1;
[0060] S3. Processing transactions; successfully verified transactions are put into the pool of nodes, waiting to be processed into valid transactions or invalid transactions;
[0061] Considering that ...
Embodiment 2
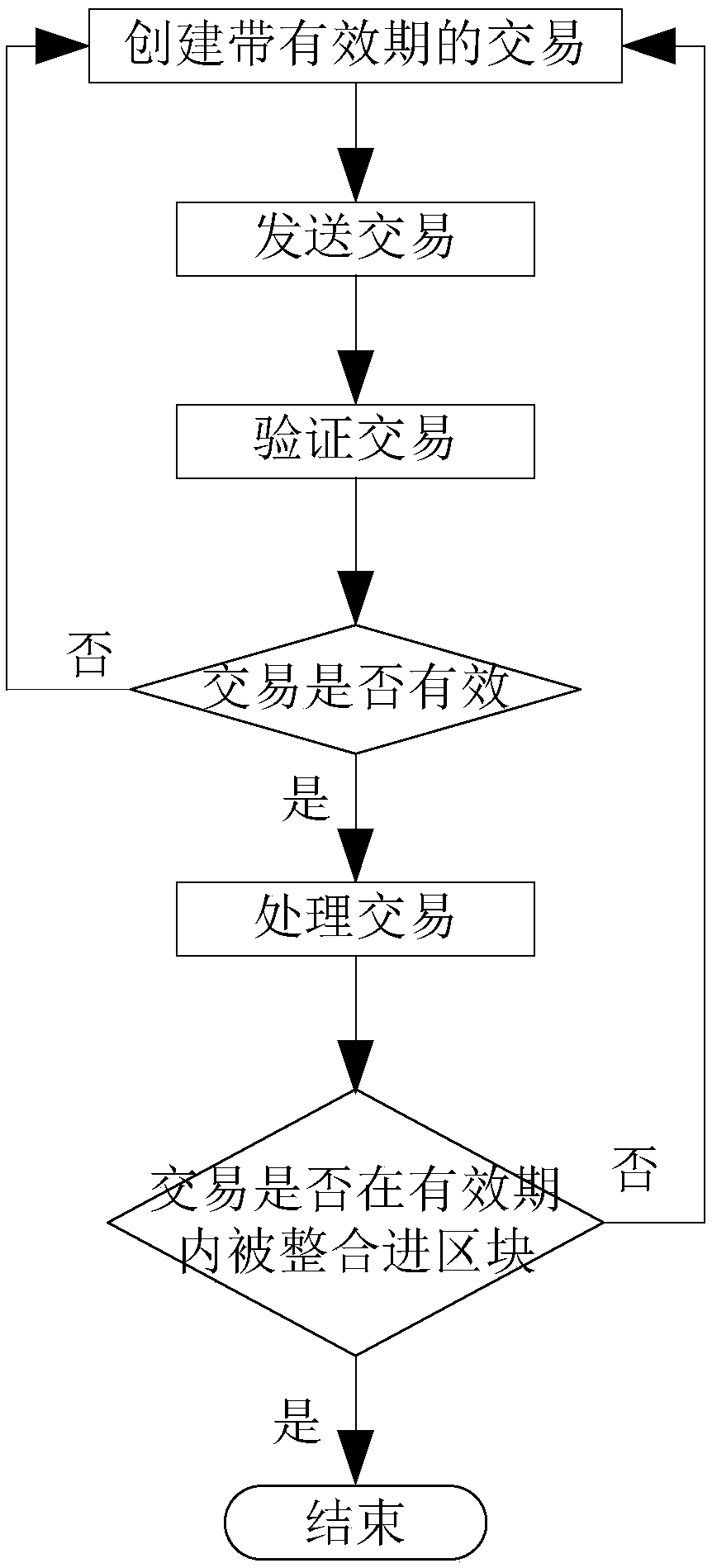
[0065] Such as figure 1 , 2 , 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7, a method for preventing repeated payment is further improved on the basis of embodiment 1, and the validity period is time, block number or block height; further , the processing method for the invalidation of the transaction in S3 is: after the validity period expires after the transaction is sent, delete the transaction from the pool of the node; preferably, the processing method for the transaction validation in S3 is: the transaction is integrated into the block within the validity period; The consensus mechanism adopted is workload proof mechanism, equity proof mechanism, share authorization proof mechanism or Poo1 verification pool.
[0066] Further, when the validity period is time T, the method for judging whether the transaction takes effect in S4 is:
[0067] Compare the cumulative time t and T after the transaction is sent, if t≤T, the transaction is integrated into the block, the transaction will take effect, and t...
Embodiment 3
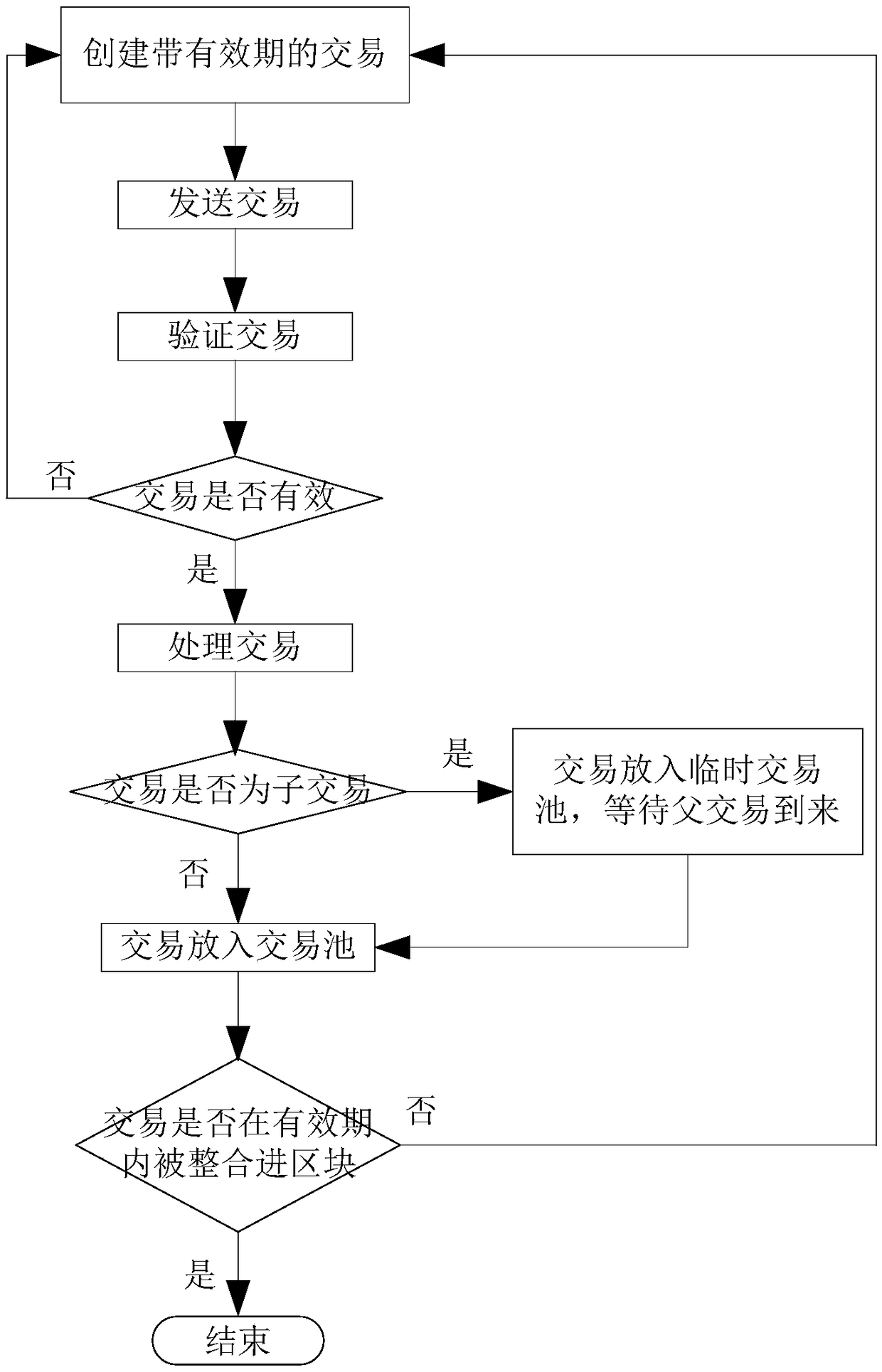
[0074] Such as figure 1 , 2 , 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7, a method for preventing double payment is further improved on the basis of embodiment 1 or 2. In S1, the transaction is assigned a validity period or a counter when it is constructed.
[0075] If the transaction is only assigned a validity period when it is constructed, and there is no counter, then the method for judging whether the transaction is resent is: if the validity period is the number of blocks, the transaction sender or the node of the transaction sender records the block when the transaction was last sent Block height. When the transaction needs to be resent, record the current block height. If the difference between the current block height and the block height when the transaction was sent last time is less than or equal to the number of blocks, it means that the transaction is still valid and still in the node If the difference between the height of the previous block and the height of the block at the time of s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com