Energy-efficient routing algorithm based on genetic algorithm
A genetic algorithm and algorithm technology, applied in the field of high-energy-efficiency routing algorithms, to achieve the effect of extending the life cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
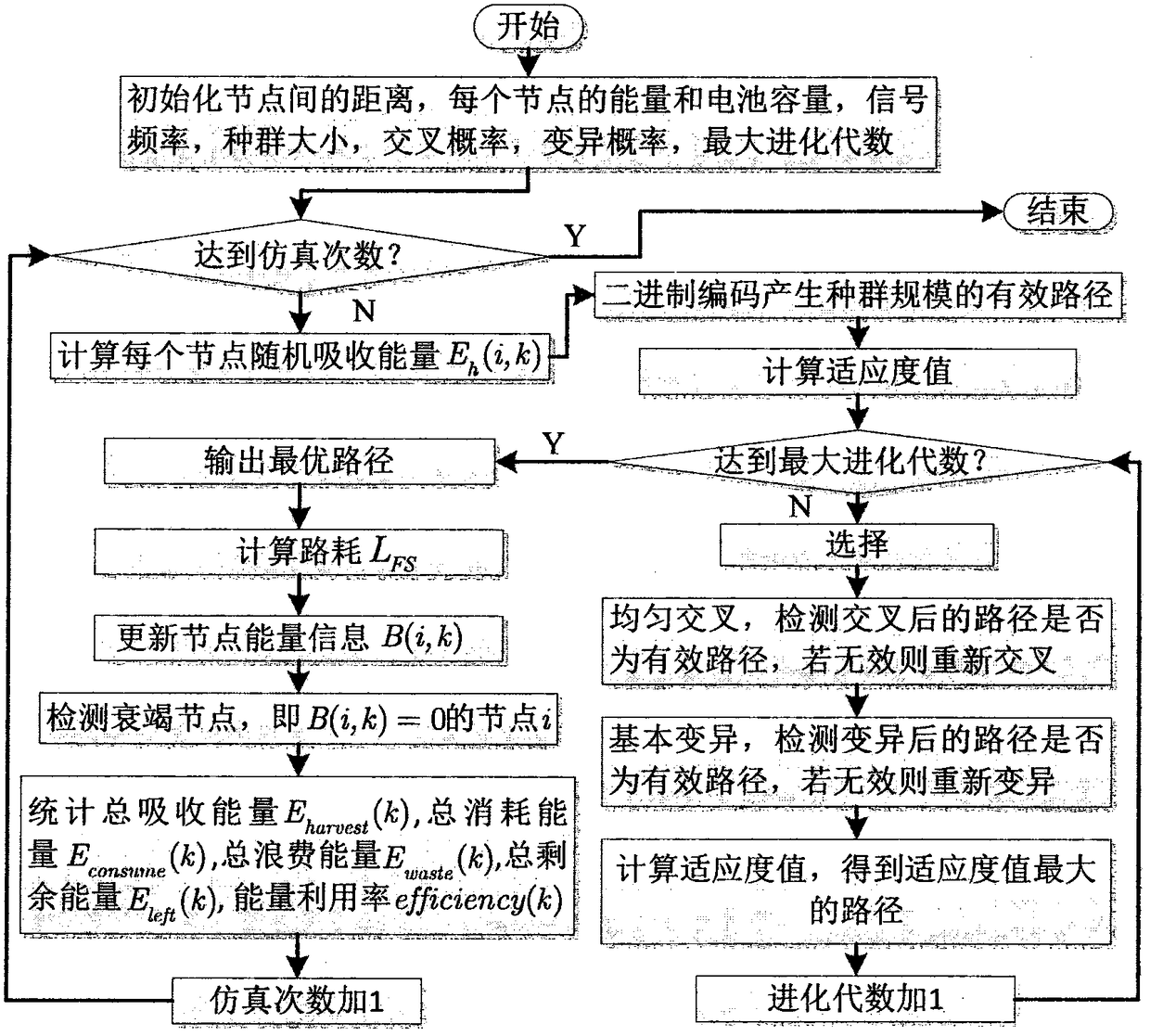
[0026] Road loss model: For an ideal omnidirectional antenna, the free space loss is: where L FS is the path loss (in dB), P t is the signal power of the transmitting antenna, P r is the signal power of the receiving antenna, f is the frequency of the radio wave (in MHz), d is the distance between the transmitting and receiving antennas (in km), and c is the speed of light (3*10 8 m / s).
[0027] On the basis of formula (1), the energy balance item is added to obtain the cost function shown in formula (2): where C(i, k) represents the cost function of node i at time k, L FS is the path loss, ζ and α are two constants, B(i, k) represents the remaining energy of node i at time k, B max (i) represents the battery capacity of node i, E h (i, k) is the absorbed energy of node i at time k. It can be seen that formula (2) increases on the basis of formula (1) The purpose of this energy balance item is to take into account the real-time remaining energy and absorbed energy o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com