Endoscopic demucosation auxiliary cannula
A technique of dissection and cannula, which is applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems that the direction and strength of pulling the mucosa cannot be adjusted in real time, the use part is limited, and the production cost is high, so as to achieve the effects of improved vision, safe operation and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
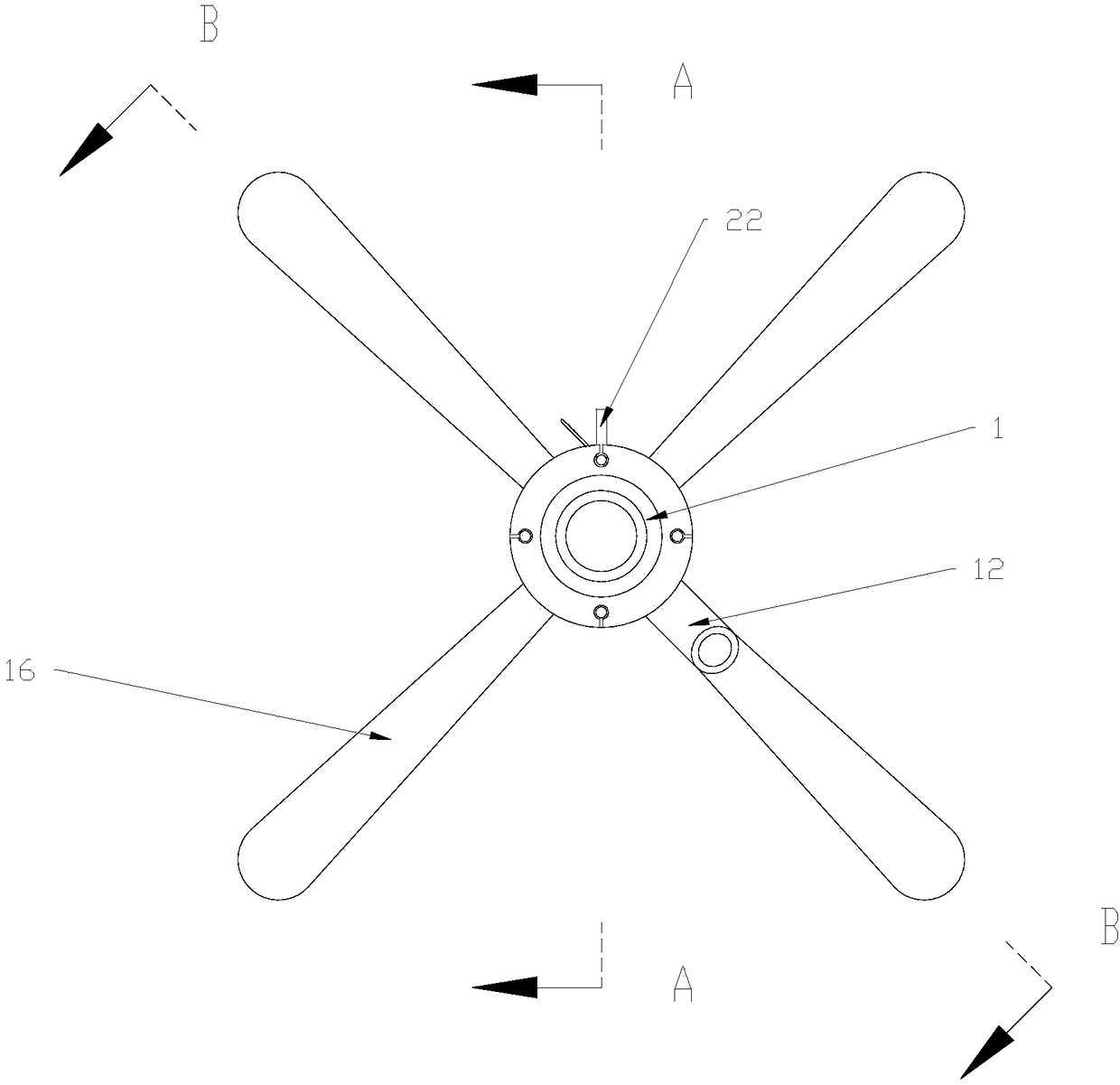
[0027] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown in . The auxiliary sleeve 1 has a concentric tubular structure, that is, the axis of the auxiliary sleeve 1 and the axis of the lumen inside the auxiliary sleeve 1 are on the same line. The total length of the auxiliary sleeve 1 is 5-20cm, and the length of the auxiliary sleeve 1 entering the human body is 2-7cm. On the outer periphery, the auxiliary sleeve 1 can rotate axially. Four through-hole pipes 10 are arranged on the pipe wall of the auxiliary sleeve 1 along the axial direction of the auxiliary sleeve 1 , and the difference between two adjacent through-hole pipes 10 is 90°. Of course, the number of through-hole pipes 10 is not limited to four, and can be increased or decreased according to the size of the anus of different patients. The control rod 2 is installed in the through-hole pipe 10 , and the inner diameter of the through-hole pipe 10 is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the control rod 2 to ensure that the cont...
Embodiment 2
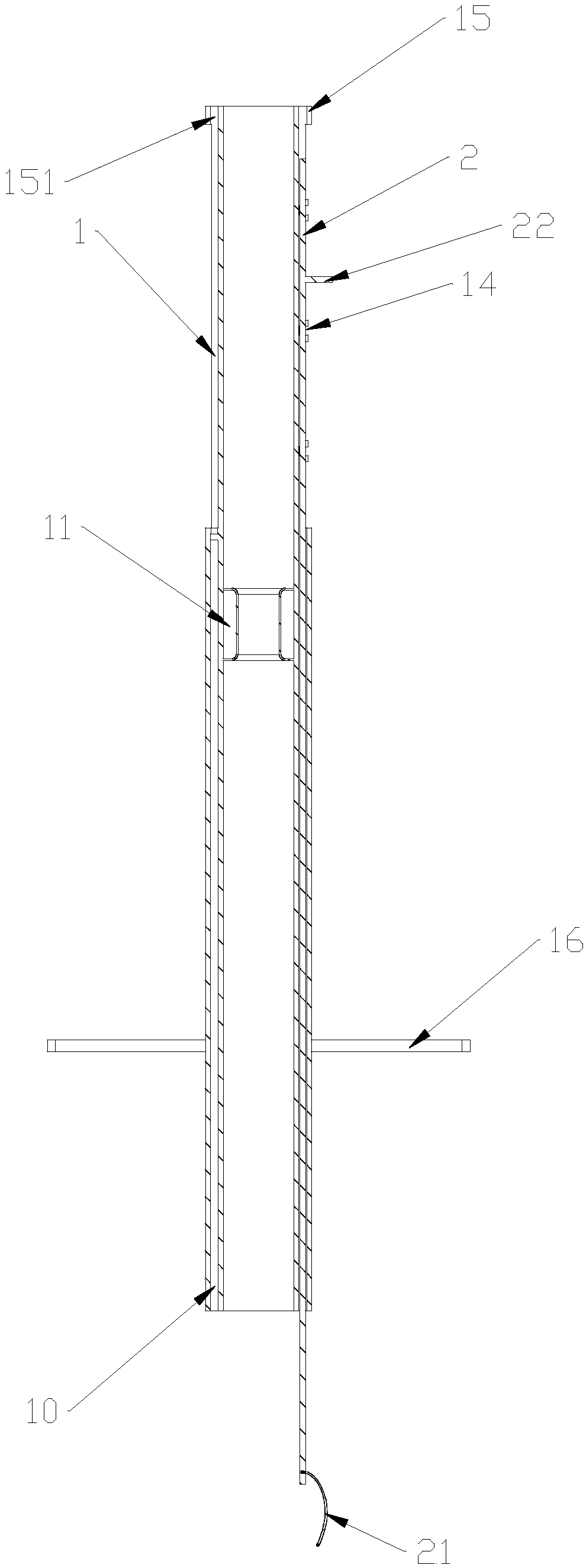
[0036] Such as Figure 4 , 5 , 6, and 7, the present embodiment provides an auxiliary sleeve for endoscopic mucosal dissection, which is mainly used for ESD or EMR surgery for lesions under a colonoscope. The auxiliary sleeve for endoscopic mucosal dissection includes an auxiliary sleeve 1 and joystick 2. The auxiliary sheath 1 in this embodiment has an eccentric tubular structure, that is, the axis of the auxiliary sheath 1 and the axis of the lumen inside the auxiliary sheath 1 are not on the same straight line. The length of the auxiliary sleeve 1 in this embodiment is longer than that of the auxiliary sleeve 1 in Embodiment 1. The wall of the auxiliary sleeve 1 in this embodiment is provided with two through-hole pipes 10 along the axial direction of the auxiliary sleeve 1, and the two through-hole pipes 10 are located at the thicker pipe wall of the auxiliary sleeve 1, and the two The difference between the two through-hole pipes 10 is 90°, but it is not limited to thi...
Embodiment 3
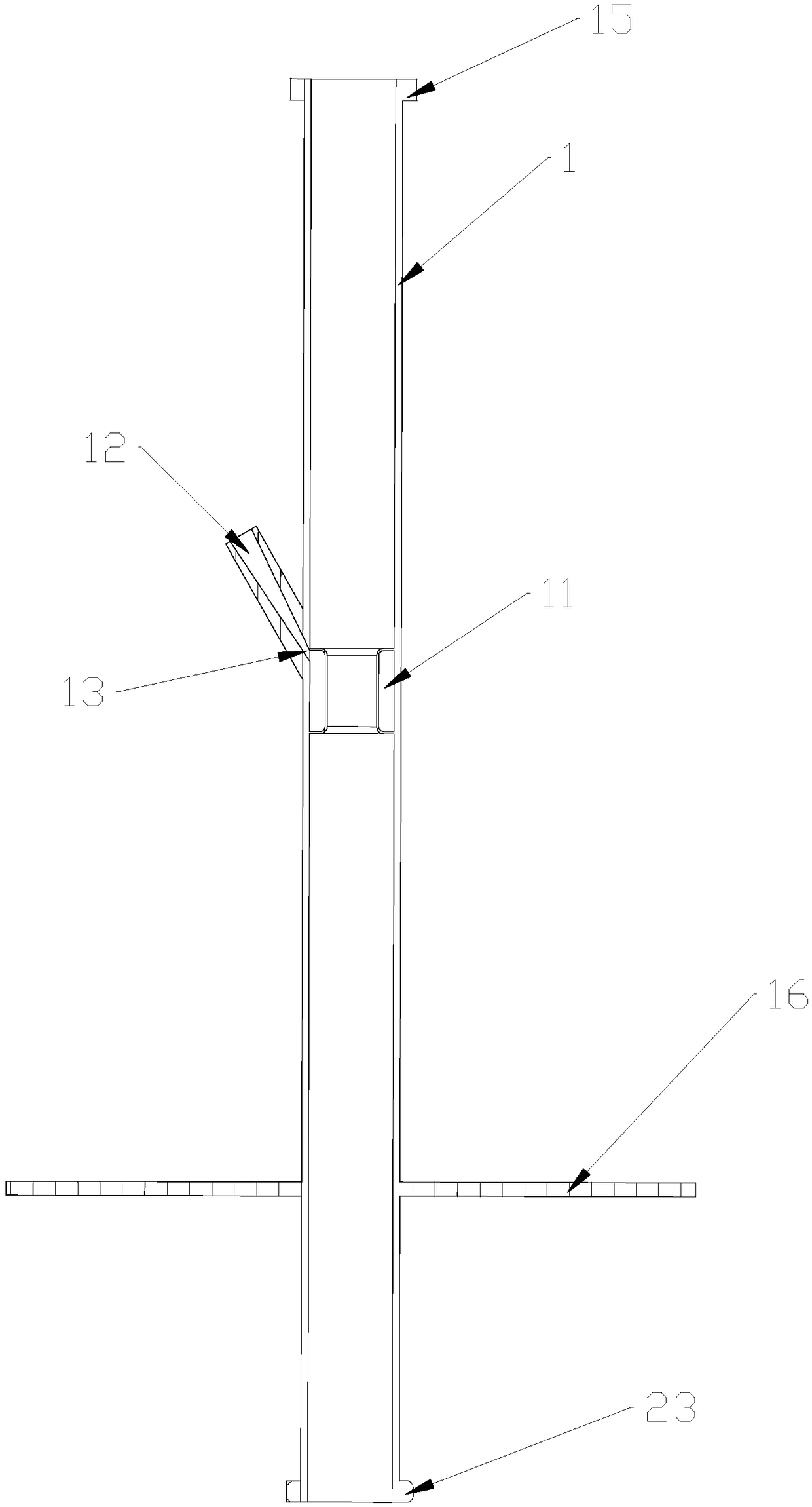
[0044] Such as Figure 8 , 9 As shown in 10 and 10, the auxiliary sleeve for endoscopic mucosal dissection in this embodiment is mainly used in ESD or EMR for upper gastrointestinal lesions. This embodiment is based on Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that the auxiliary sleeve 1 in this embodiment has a concentric tubular structure, and the wall of the auxiliary sleeve 1 is provided with four channels. For the hole pipes 10, the difference between two adjacent through hole pipes 10 is 90°. Compared with the auxiliary sleeve 1 in embodiment 2, the auxiliary sleeve 1 in this embodiment only needs to rotate a small angle to make the control rod 2 reach the ideal operating position, which is more convenient to operate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com