Signal synchronization method of satellite-borne GNSS receiver based on orbital dynamics assistance
A signal synchronization and receiver technology, applied in the field of satellite autonomous navigation, can solve problems such as unsuccessful GNSS signal synchronization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
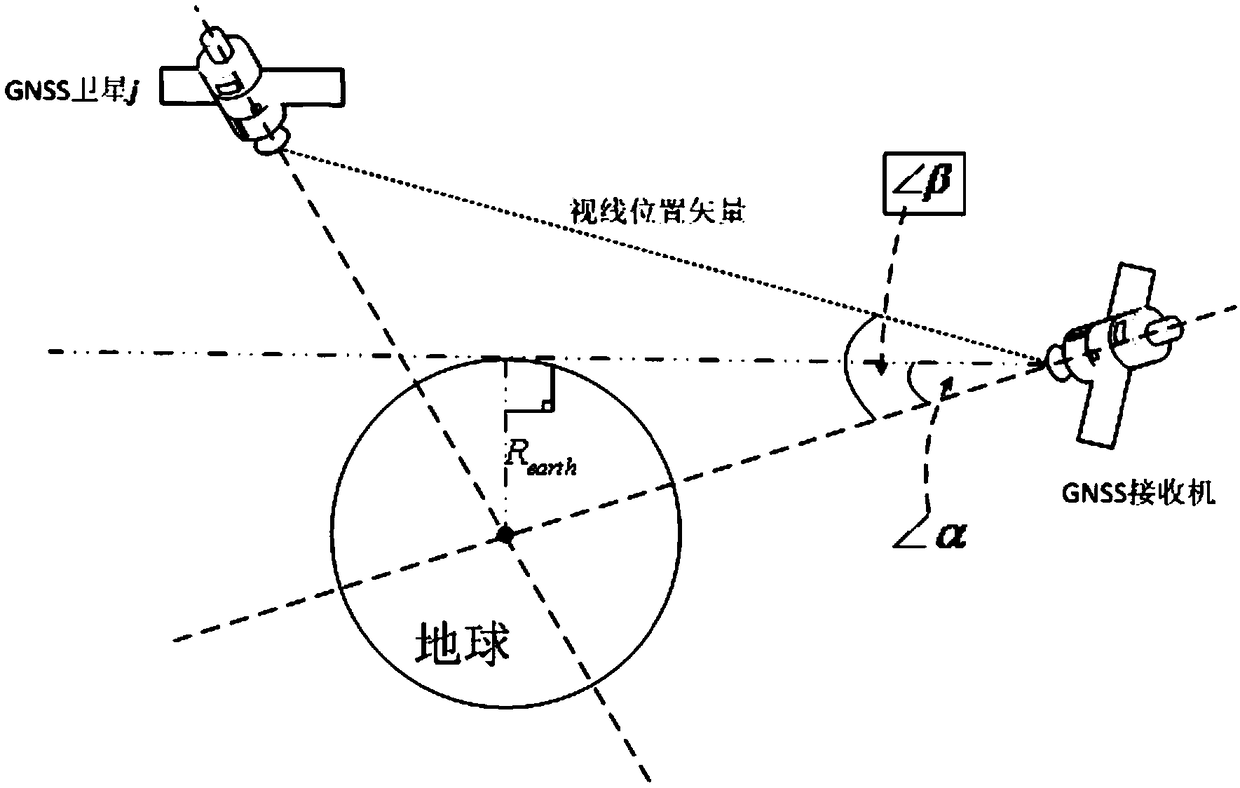
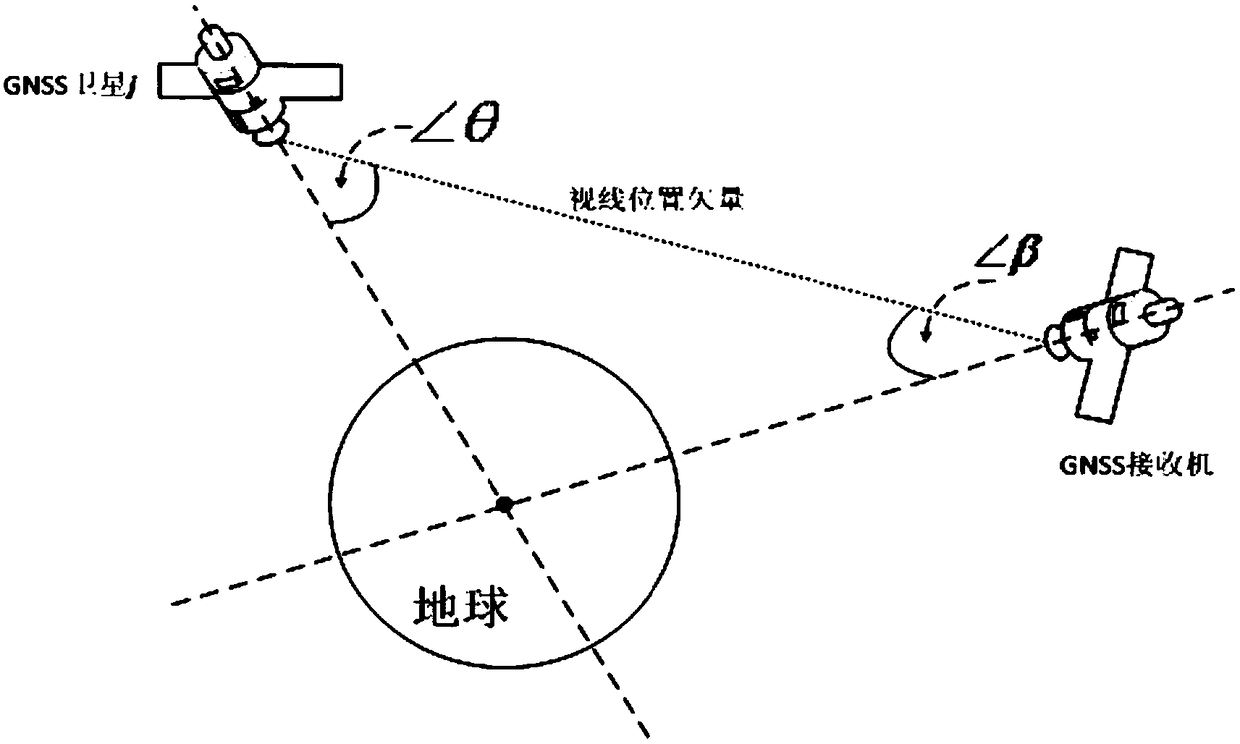
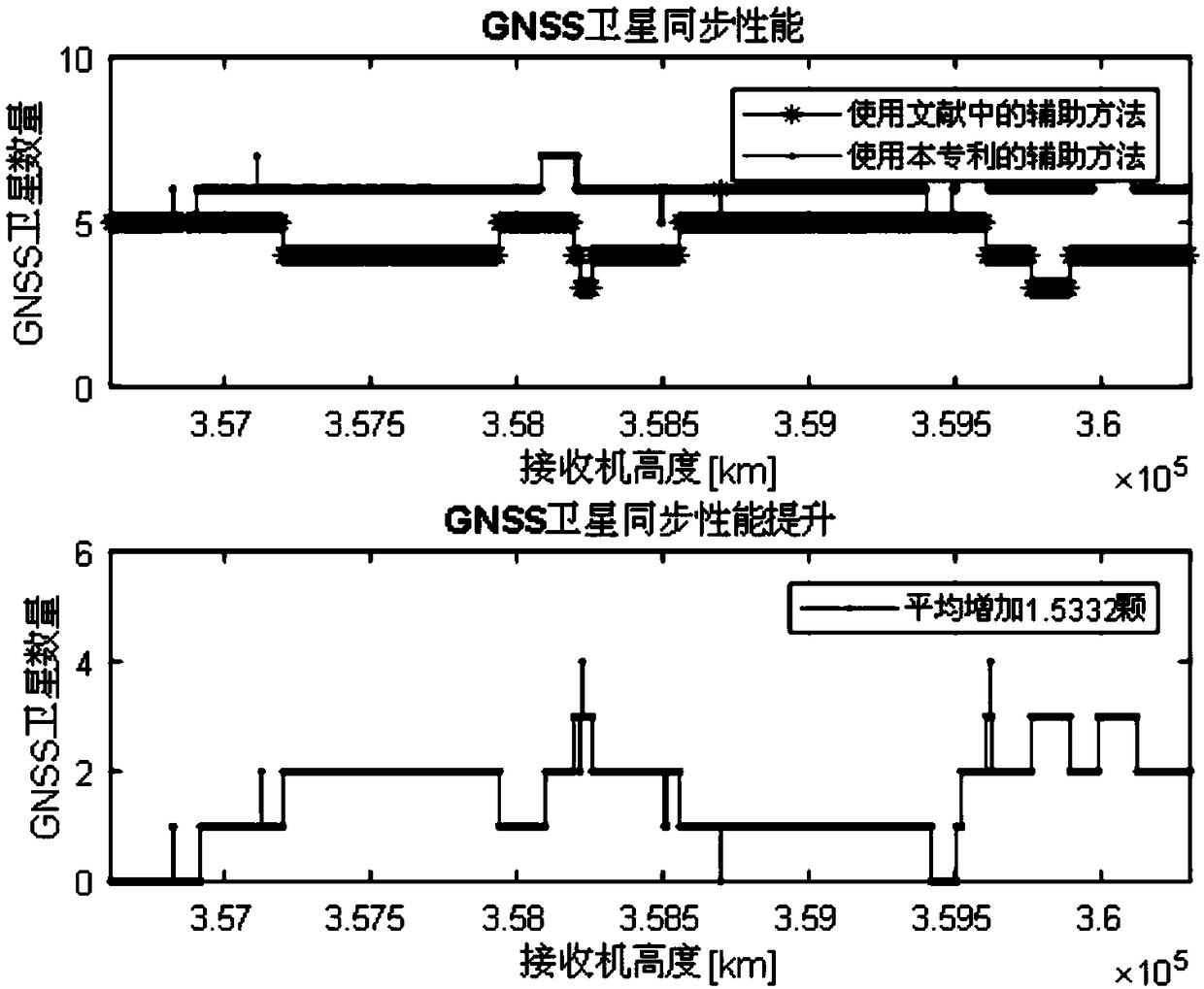
[0072] The satellite-borne GNSS receiver signal synchronization method based on orbital dynamics assistance proposed by the present invention can carry out signal synchronization real-time assistance to the satellite-borne GNSS receiver, and the specific content of assistance includes:
[0073] 1. Satellite search assistance. Use the auxiliary GNSS visible star list information to set the search range, eliminate invisible satellites, and reduce the time spent on capturing invisible satellites; use the auxiliary receiving power to set the priority of the satellites to be searched, and give priority to satellites with stronger power. Enable the receiver to quickly capture high-quality signals and enhance GNSS availability;
[0074] 2. Signal capture assistance. Use the auxiliary Doppler and delay information to set the Doppler and code phase two-dimensional search range of the received signal to reduce the search area; use the auxiliary received power information to set the pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com