Device for generating acoustic fluid tweezers
A fluid and sound wave technology, applied in the field of microelectronic devices, can solve the problems of large eddy current size, low particle precision, and inability to meet the application requirements of similar optical tweezers operation, and achieve the effect of precise operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
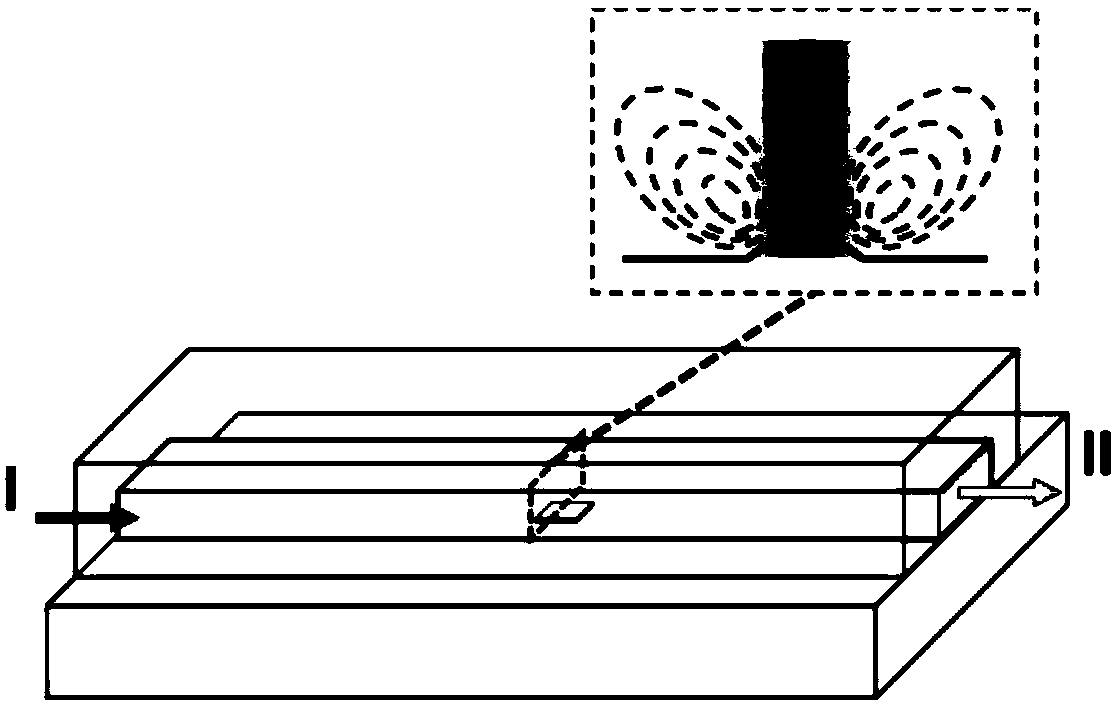
[0067] In the specific implementation process of this embodiment, the characteristic scale of the flow channel is mainly at the micron level, so the flow channel is also called a micro-channel. Microchannel is the basic unit of microfluidic system and the carrier of fluid operation. Such as figure 1 Shown is a three-dimensional schematic diagram of the device for producing acoustofluidic tweezers proposed by the present invention. Different fluid samples enter the microchannel from port I and flow out from port H. The fluid flows through the region where the bulk acoustic wave is generated (i.e. figure 1 above the boxed area shown in the microfluidic channel). figure 2 for figure 1 The center position of the bulk acoustic wave generation area in , along the cross-sectional schematic diagram perpendicular to the flow direction of the microfluid in the microchannel. Such as figure 2 As shown, the device for producing acoustic fluid tweezers includes:
[0068] The sub...
Embodiment 2
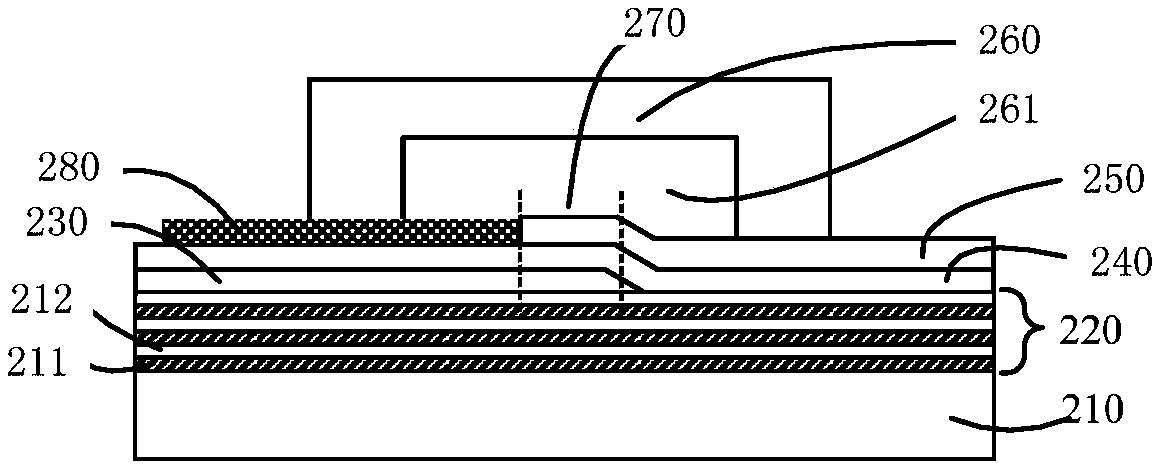
[0096] Such as image 3 As shown, the embodiment of the present application also provides a device for producing acoustic fluid tweezers, including:
[0097] Bulk acoustic wave generating components, including: a bottom electrode 330, a piezoelectric layer 340 and a top electrode 350;
[0098] Wherein, the bottom electrode 330 and the top electrode 350 are arranged on the lower and upper sides of the piezoelectric layer 340 respectively, and the bottom electrode 330 and the top electrode 350 have no overlap in the vertical direction; And a gap 370 of a specified size is formed between the portion where the piezoelectric layer 340 overlaps with the bottom electrode 330 and the top electrode 350 ;
[0099] An acoustic wave reflection part 320 arranged in contact with one side of the bulk acoustic wave generating component;
[0100] The overlapping area of the bottom electrode 330, the piezoelectric layer 340, the top electrode 350 and the acoustic wave reflection part 320 co...
Embodiment 3
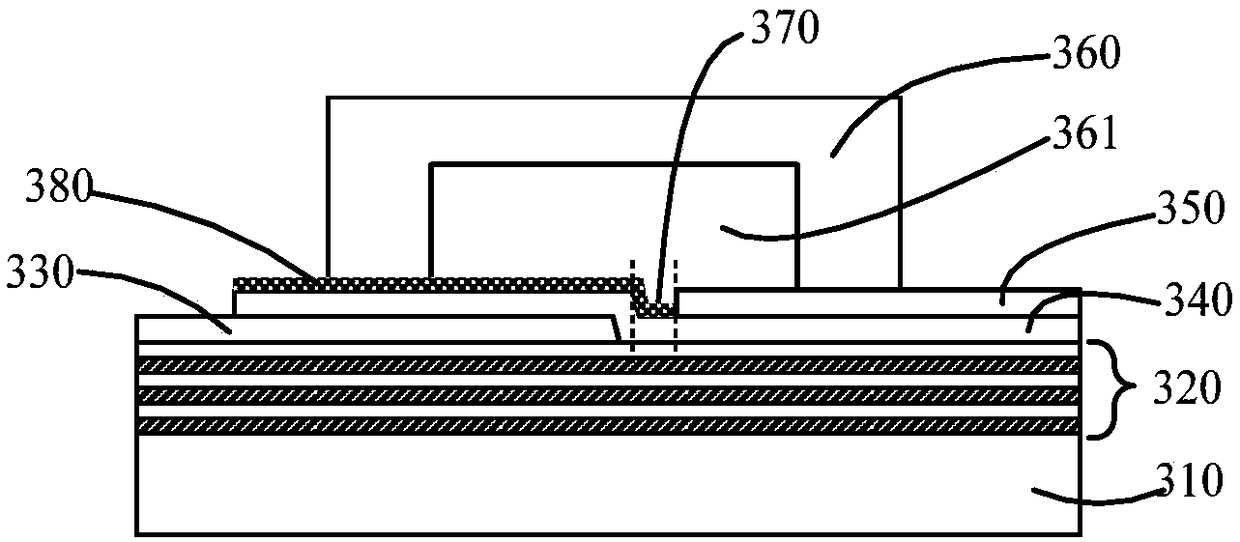
[0107] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the embodiment of the present application also provides a device for generating acoustofluidic tweezers. include:
[0108] Bulk acoustic wave generating components, including: a bottom electrode 440, a piezoelectric layer 430 and a top electrode 450;
[0109] Wherein, the bottom electrode 440 and the top electrode 450 are arranged on the upper side of the piezoelectric layer 430, and the bottom electrode 440 and the top electrode 450 are in the same horizontal layer; and the bottom electrode 440 and the A gap 470 is formed between the top electrodes 450;
[0110] An acoustic wave reflector 420 arranged in contact with one side of the bulk acoustic wave generating component;
[0111] The overlapping area of the bottom electrode 440, the piezoelectric layer 430, the top electrode 450 and the acoustic wave reflection part 420 constitutes a bulk acoustic wave generation area;
[0112] a backing layer 410 for supporting the bulk acoustic wav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com