Fourier transform and chaotic double-random phase encoding color image encryption method
A chaotic random phase and Fourier transform technology, applied in the fields of information security and optical information processing, can solve the problems of reducing the key space of the encryption system, inconvenient key management and transmission, unable to encrypt color images, etc. Transmission difficulty, resistance to cryptographic attacks, and the effect of increasing key space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
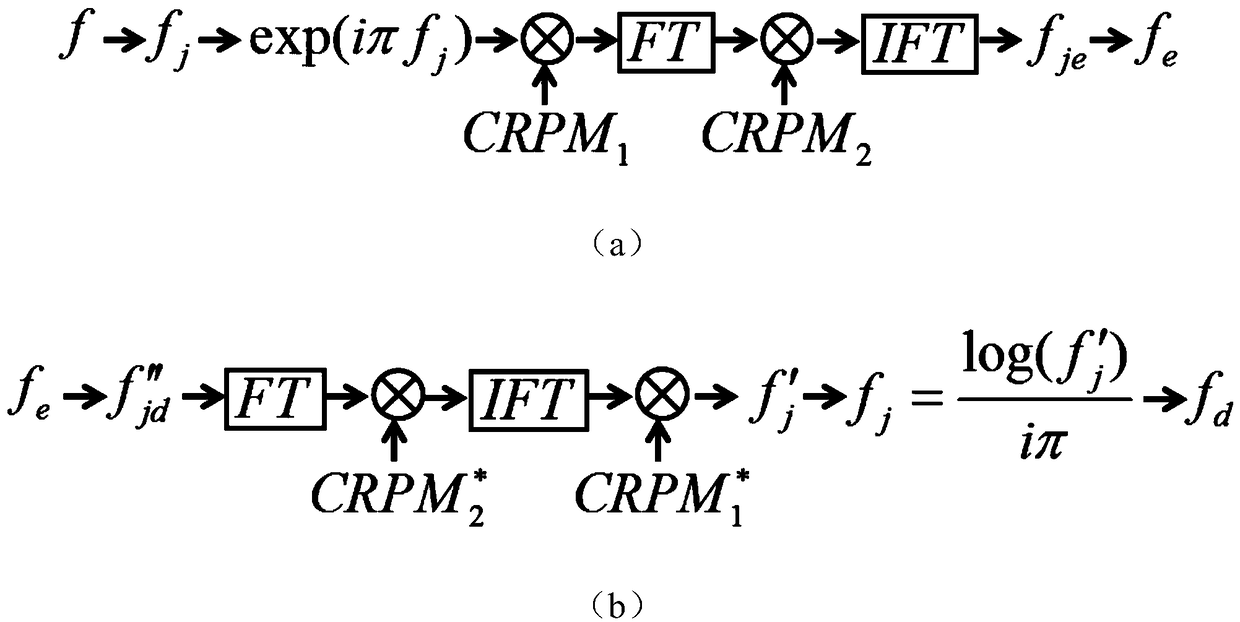
[0070] A phase-only color image encryption method based on Fourier transform and chaotic double-random phase encoding, the schematic diagram of its encryption and decryption principle is as follows figure 1 shown. The method consists of an encrypted part of the image and a decrypted part.
[0071] (1) The encrypted part of the image:
[0072] In the encryption process, the color image to be encrypted is firstly decomposed into three color channels of R, G, and B; then, these three color channels are respectively encoded into a pure phase form; next, the three color channels of a pure phase form are respectively It is modulated by the first chaotic random phase plate, and then Fourier transform is performed on the three modulated color channels; finally, the three color channels after Fourier transform are respectively modulated by the second chaotic random phase plate , and then inverse Fourier transform is performed on the modulated three color channels, and the three trans...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Combine below figure 1 The design principle introduces the scheme in embodiment 1 in detail, see the following description for details:
[0078] A phase-only color image encryption method based on Fourier transform and chaotic double-random phase encoding, the schematic diagram of its encryption and decryption principle is as follows figure 1 shown. The method consists of an encrypted part of the image and a decrypted part. The specific implementation manners of these two parts will be described in detail below.
[0079] (1) The encrypted part of the image:
[0080] 1) First decompose the color image f to be encrypted into three RGB color channels f R , f G and f B ; Then, encode the three color channels into a phase-only form f′ j :
[0081] f' j =exp(iπf j ) (1)
[0082] In the formula, j=R, G, B; i is the imaginary number unit; π is the circumference ratio.
[0083] 2) The three color channels in pure phase form are multiplied by the first chaotic random ...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Below in conjunction with specific accompanying drawing, the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
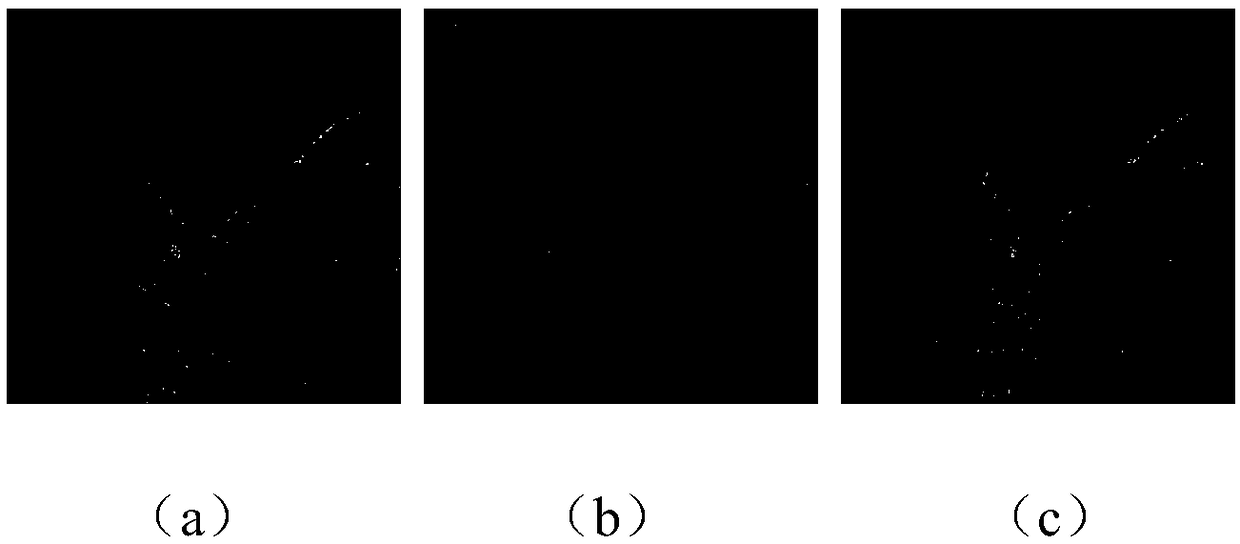
[0105] The image encryption method provided by the implementation of the present invention can convert a color image (such as figure 2 Shown in (a)) encrypted into a noise-like image (such as figure 2 (b) shown). Depend on figure 2 (b) It can be seen that the information of the original color image is hidden in the noise-like image, which shows that the encryption of the color image by this system is successful.
[0106] The image encryption method provided by the implementation of the present invention is used to restore the original color image from the encrypted image. When all keys are correct, the result obtained is as follows: figure 2 (c) shown. Depend on figure 2 (c) It can be seen that the original image can be fully restored when all keys are correct. In addition, when a certa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com