Geometric matching in visual navigation systems
A local and map technology, applied in the field of visual navigation system, can solve problems such as limited applicability and increased search space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
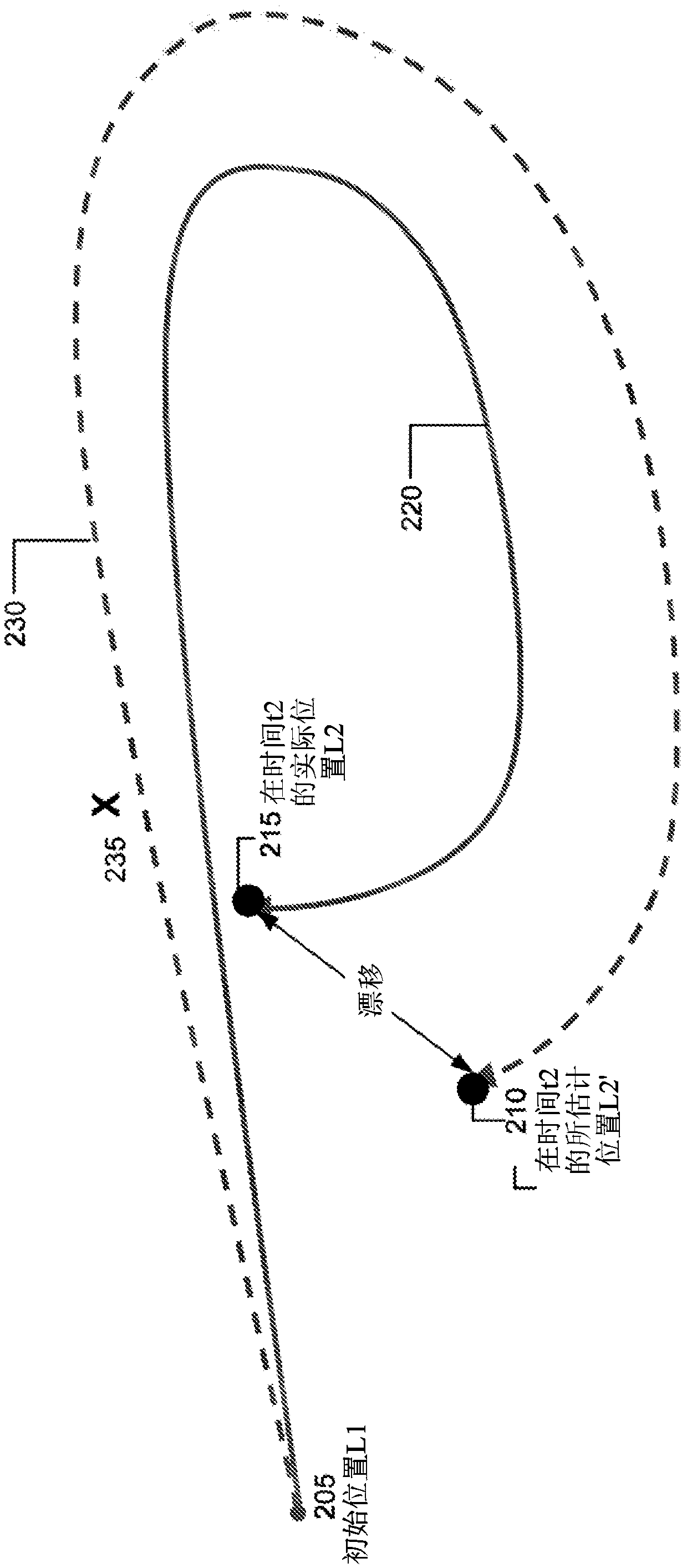
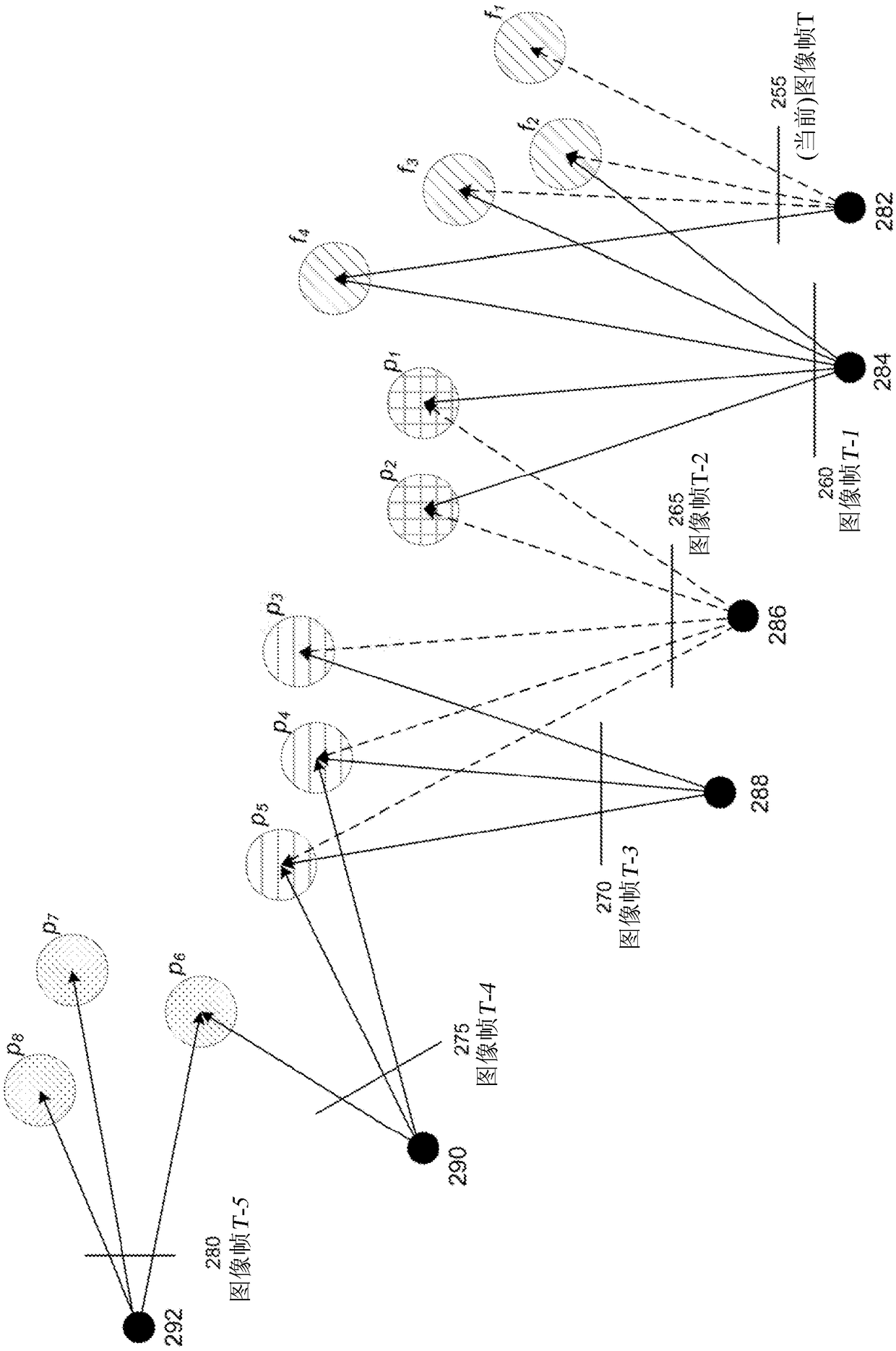
[0021] In mapping and / or navigation systems, the term "odometry" refers to the estimation of a change in position over time based on measurements from sensors. In VNS, several visual features can be tracked frame by frame, which can be used to determine accurate estimates of camera relative motion. However, VNS suffers from pose drift, which can accumulate and gradually increase from image frame to image frame unless corrected. Pose drift describes the error between the actual position of the mobile device and the position determined by the VNS of the mobile device. Pose drift, or drift, occurs due to residual errors in pose calculations for individual frames and accumulates frame-by-frame from such errors. One way to reduce or alleviate pose drift is "loop closure". In loop closure, the mobile device may determine whether, after some arbitrary length of time, a currently observed feature corresponds to some previously observed feature on its trajectory.
[0022] The disclo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com