Lidar three-dimensional mapping method based on semantic point cloud registration
A laser radar, point cloud registration technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of high complexity, high complexity, and deviation of point clouds, and achieve the effect of low registration complexity, improved accuracy, and improved reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
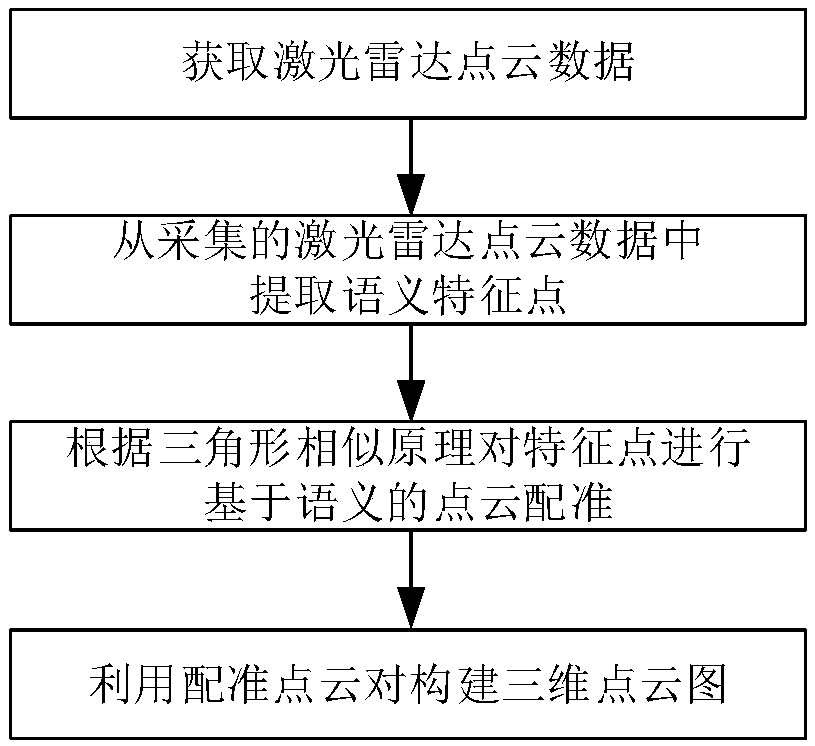
[0041] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0042] refer to figure 1 , to further describe the specific steps of the present invention.
[0043]Step 1. Obtain lidar point cloud data.
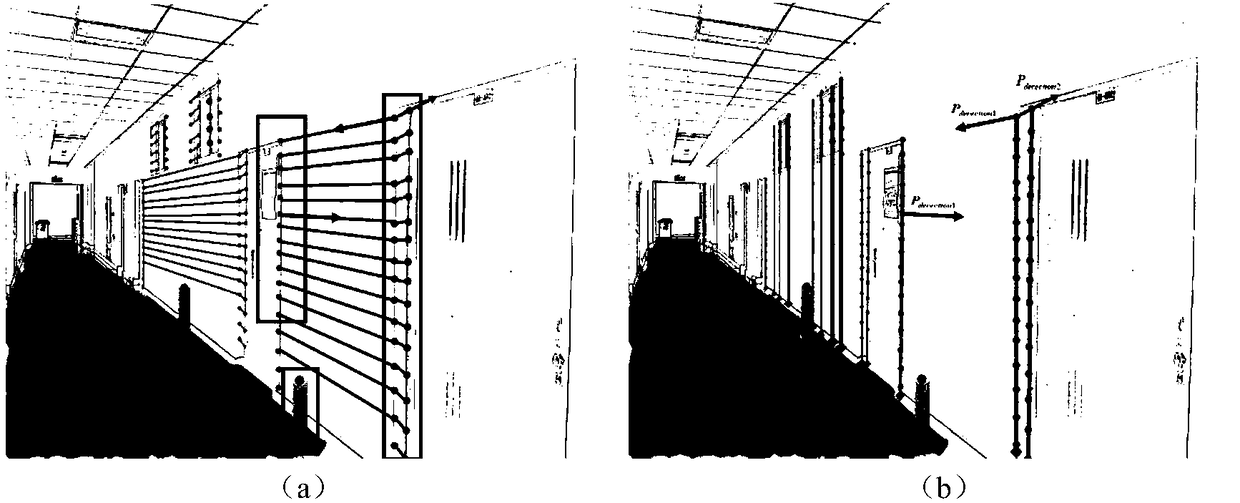
[0044] Fix the lidar to the rotating platform controlled by the motor, follow the right-hand rule, take the current position of the lidar as the origin of the radar coordinate system, and establish the radar coordinate system directly in front of the lidar as the z-axis.
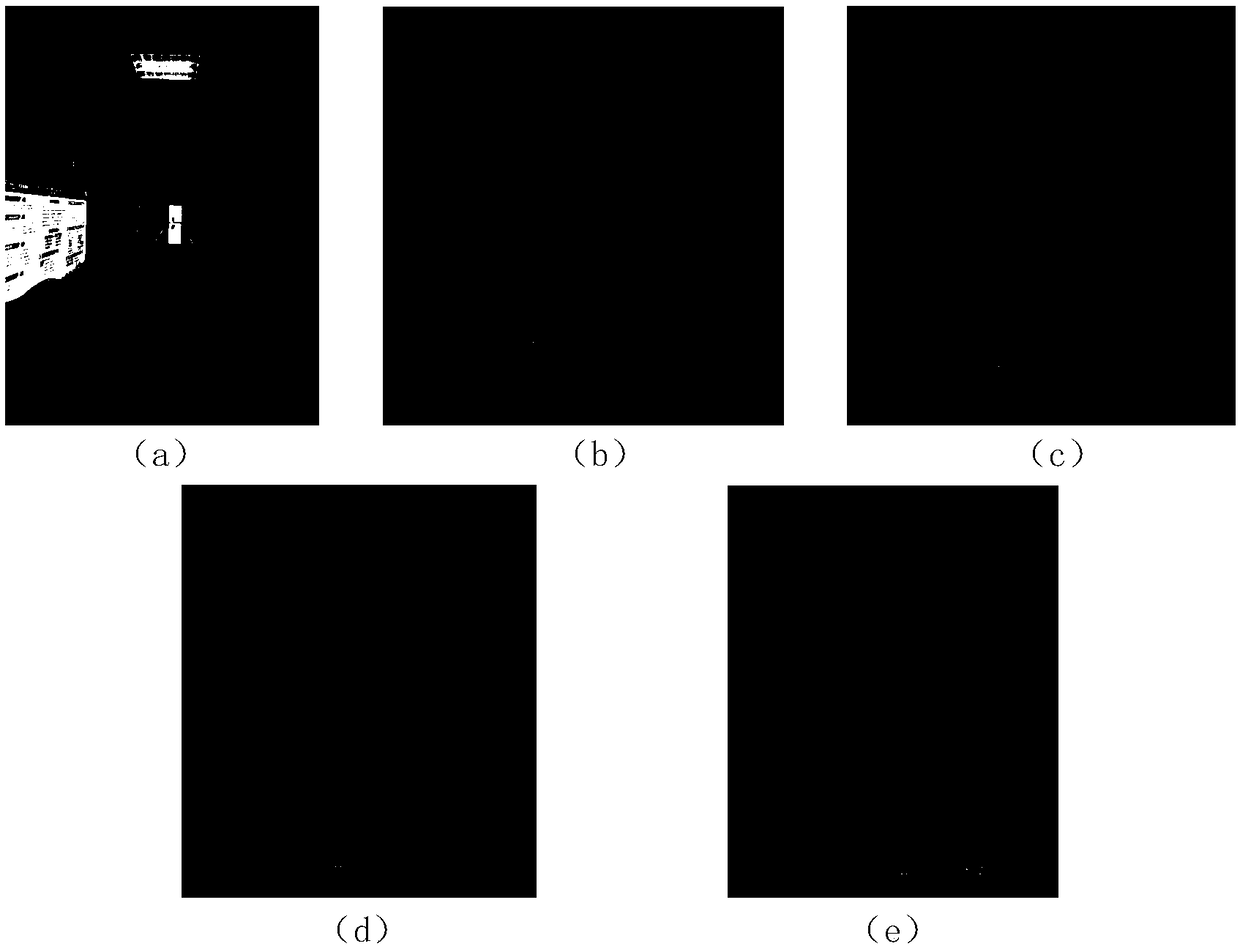
[0045] Use the cosine formula to calculate the coordinate value of each point scanned by the lidar on each axis in the radar coordinate system, and output a point cloud with coordinate information.
[0046] The described cosine formula is as follows:
[0047] a l =b l ×cosθ l
[0048] Among them, a l Indicates the coordinate value of the lth point in the point cloud corresponding to the axis of the three axes of the radar coordinate system, b l Represen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com