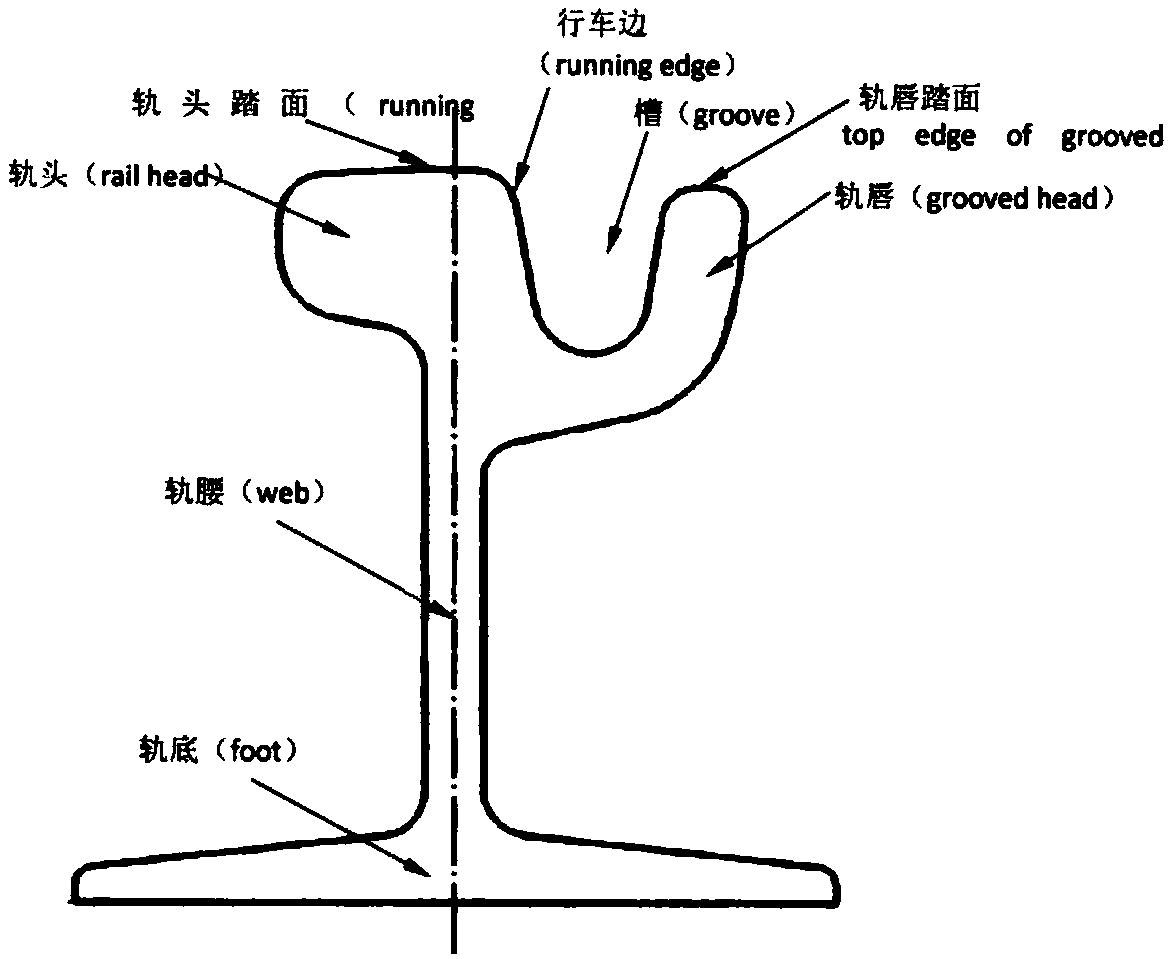
Post-welding thermal treatment method for channel type steel rail flash welding head
A technology of post-weld heat treatment and grooved rails, applied in heat treatment furnaces, heat treatment equipment, furnace types, etc., can solve the problems of low impact toughness and low hardness of rail head profile
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
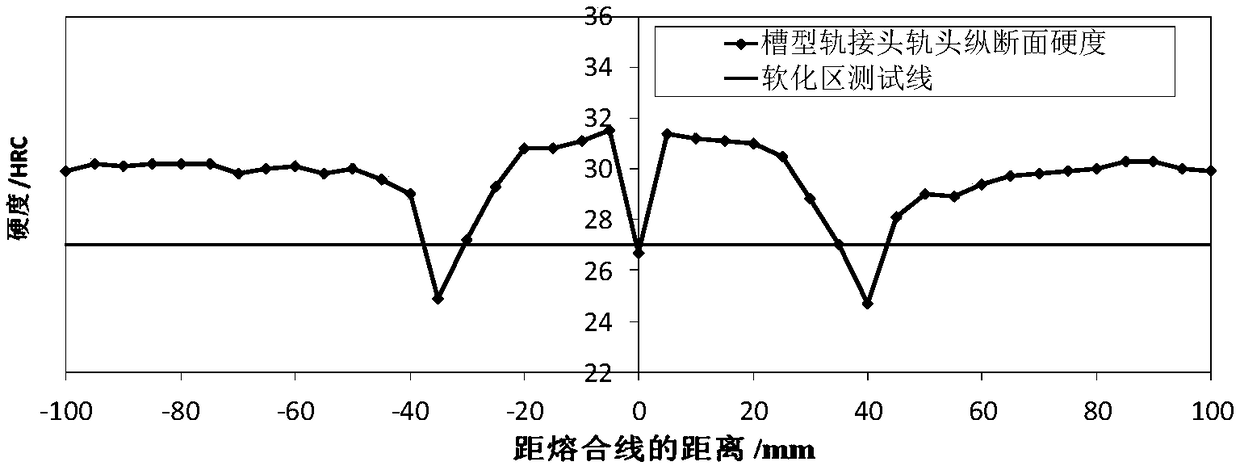
[0046] Air-cool the welded joints of channel rails obtained by flash welding at a temperature of 1400°C. When the joints are cooled from 1400°C to 150°C, use medium-frequency induction profiling electric heating coils to heat the entire section of the welded joints of channel rails. Stop heating when the rail head longitudinal section temperature of the rail reaches 900°C, then immediately spray the heated rail welded joint to 520°C, and finally air-cool the welded joint to room temperature (25°C), thereby obtaining the process of the present invention Channel rail welded joints with post-weld heat treatment. The longitudinal section hardness data at the position 5mm below the rail head tread of the welded joint is shown in Table 1, and the distribution of the longitudinal section hardness is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0047] Table 1
[0048]
[0049] From Table 1 and figure 1 It can be seen that when the post-weld heat treatment method provided by the present inventi...
Embodiment 2
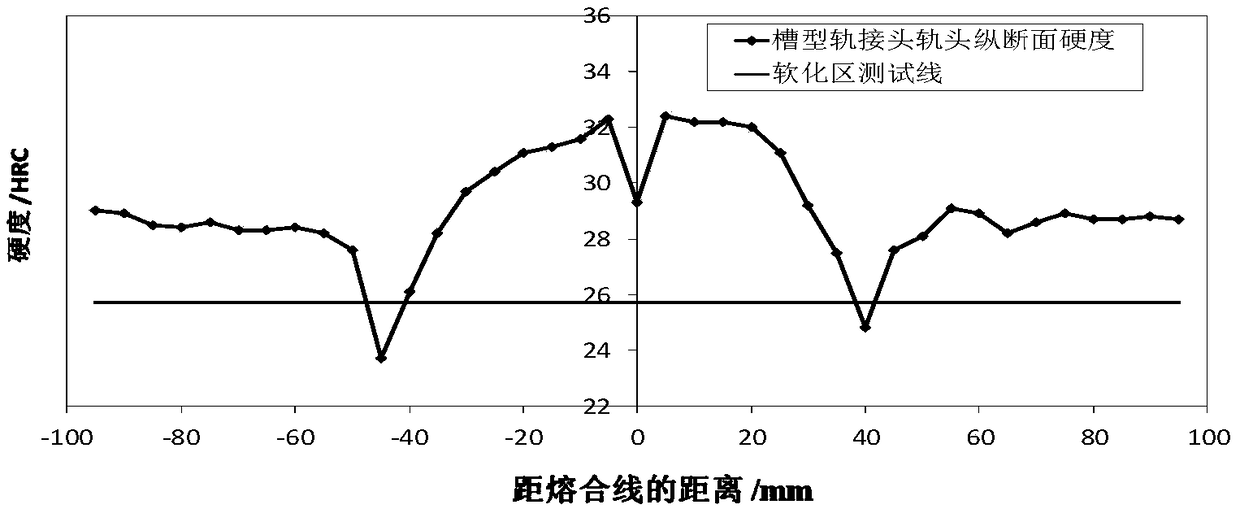
[0051] The trough-shaped rail welded joints obtained by flash welding at a temperature of 1300 °C were air-cooled. When the joints were cooled from 1300 °C to 50 °C, the medium-frequency induction profiling electric heating coil was used to heat the entire section of the rail welded joint area. Stop heating when the rail head longitudinal section temperature of the rail reaches 920°C, then immediately cool the obtained rail welded joint to 500°C, and finally air-cool the welded joint to room temperature (25°C), thereby obtaining the welded joint of the present invention Post-heat-treated channel rail welded joints. The longitudinal section hardness data at the position 5mm below the rail head tread of the welded joint is shown in Table 2, and the distribution of the longitudinal section hardness is as follows image 3 shown.
[0052] Table 2
[0053]
[0054] From Table 2 and figure 2 It can be seen that when the post-weld heat treatment method provided by the present i...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The trough rail welded joint obtained by flash welding at a temperature of 1400 °C was air-cooled. When the welded joint was cooled from 1400 °C to 40 °C, the entire section of the rail welded joint area was heated with an oxy-acetylene flame profiling heater. Stop heating when the rail head longitudinal section temperature of the rail reaches 900°C, then spray the welded joints of the rails to 430°C, and finally air-cool the welded joints to room temperature (25°C), thereby obtaining the post-weld heat treatment of the present invention Channel rail welded joints. The longitudinal section hardness data at the position 5mm below the rail head tread of the welded joint is shown in Table 3, and the distribution of the longitudinal section hardness is as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0057] table 3
[0058]
[0059] From Table 3 and image 3 It can be seen that when the post-weld heat treatment method provided by the present invention is used to treat the welded joints ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com