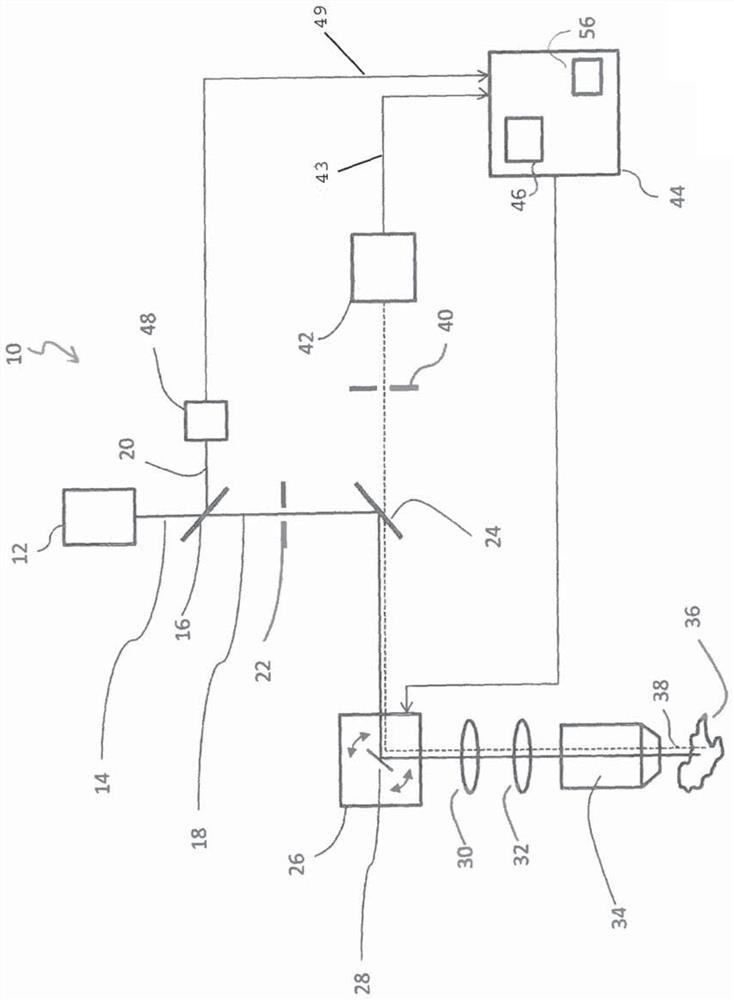
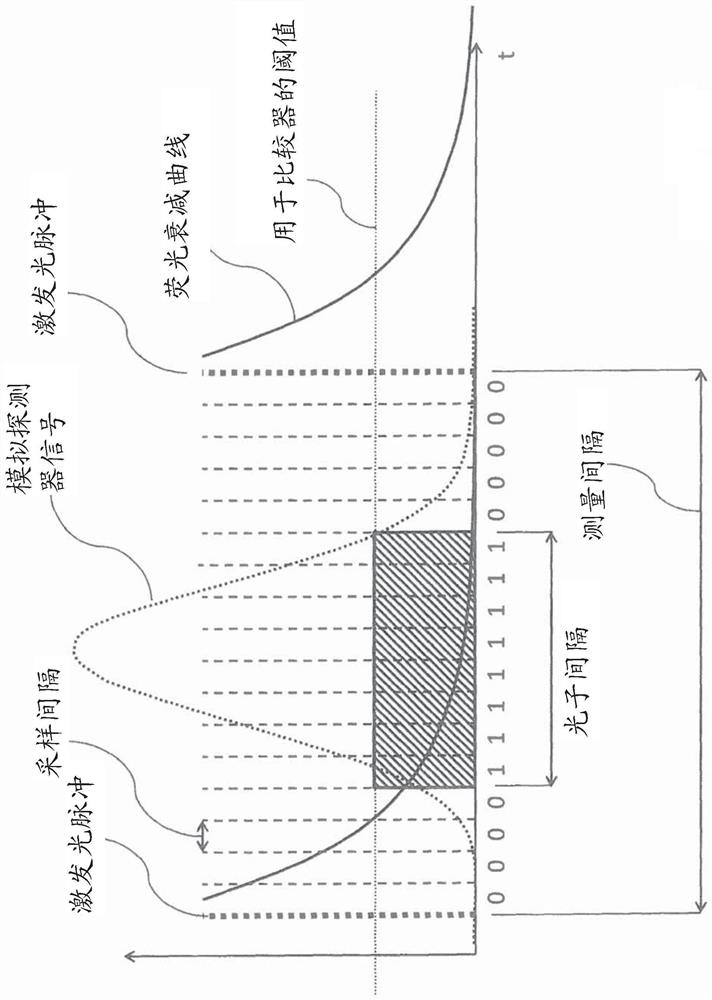
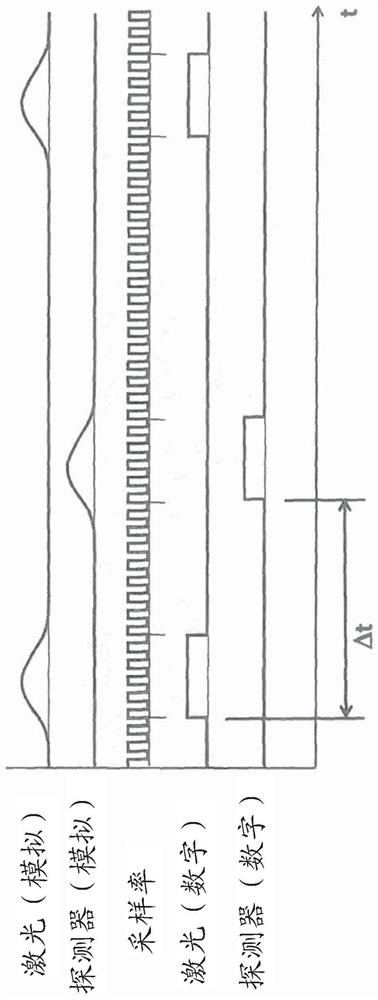
Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy method using time-correlated single-photon counting allowing higher light intensities
A single-photon counting, fluorescence lifetime technology, applied in the field of microscopy, can solve the problems of expensive implementation, time resolution and signal utilization limitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
t
E
It is the same for all interval segments A, B and C.
[0072] The segments shown by way of example in FIGS. 6 to 9 can also be combined with one another in a suitable manner. So, for example in Figure 8
Interval segments A to F, which adjoin each other without temporal overlap, may overlap each other in time, as is the case for the two
A and B as illustrated in interval subsections A and B.
In the following, with reference to FIGS. 10 to 13, it is explained how the set of fluorescence decay curves determined individually for each interval segment is
A total curve is synthesized which covers the entire measurement interval. Here, purely by way of example, there will be two spacer segments A and B
The segments serve as the basis for Figures 10 to 13, where interval segment A is equal to the measurement interval, while interval segment B gives the relative measurement
An interval in which the interval is shortened, and the start time of the interval is delayed re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com