Method for detecting additive and dominant genetic effects of DNA methylation sites on quantitative traits and application technology thereof
A technology of dominant inheritance and quantitative traits, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, chemical libraries, combinatorial chemistry, etc., to achieve important theoretical and technical effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The specific operation steps are as follows:
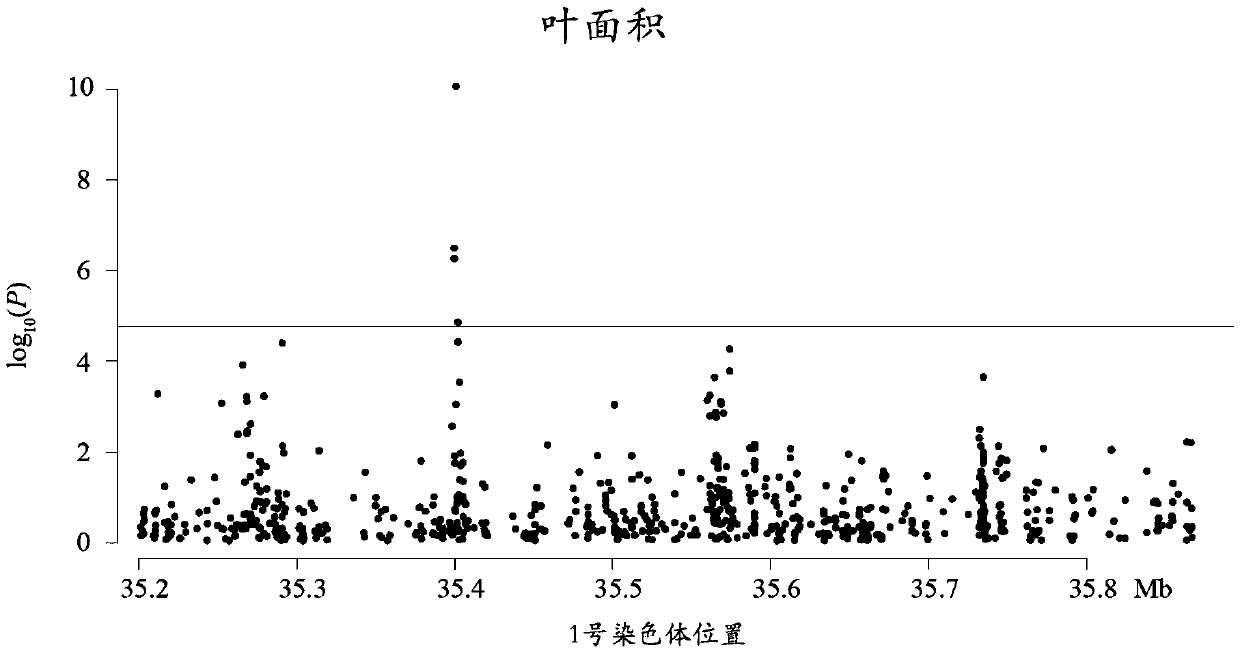
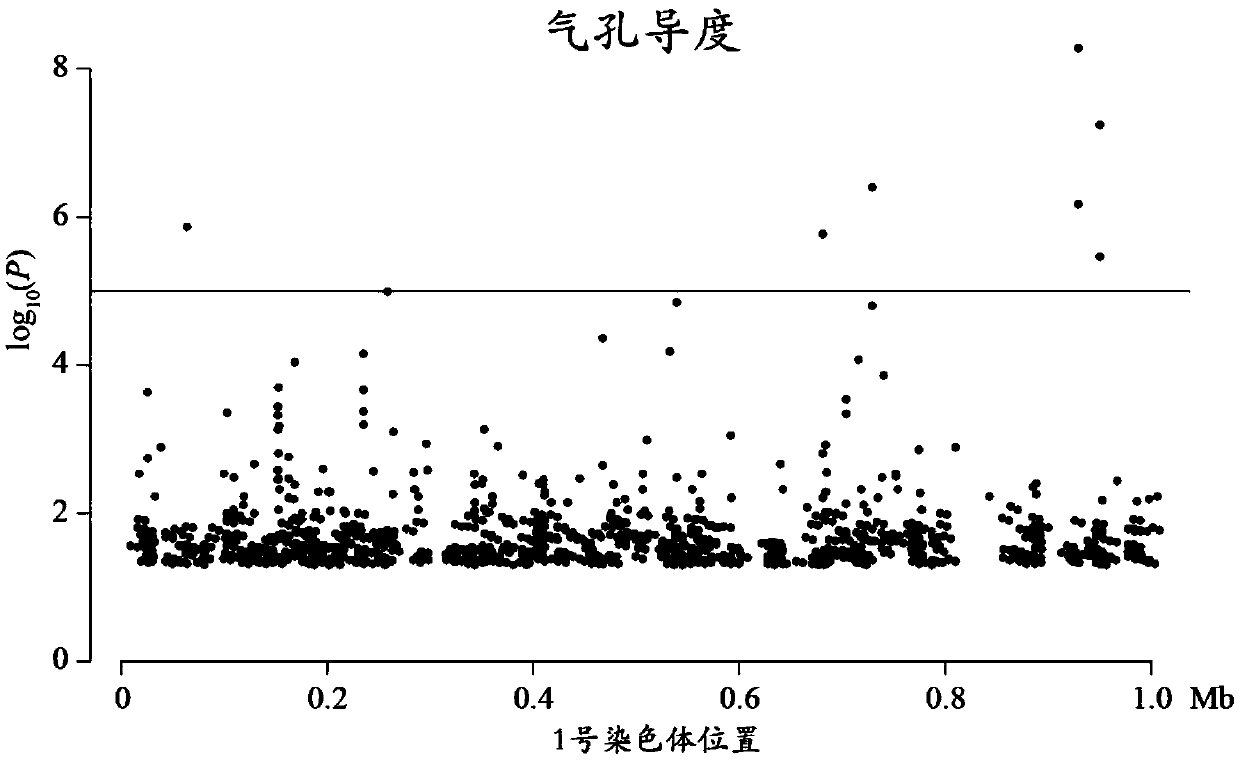
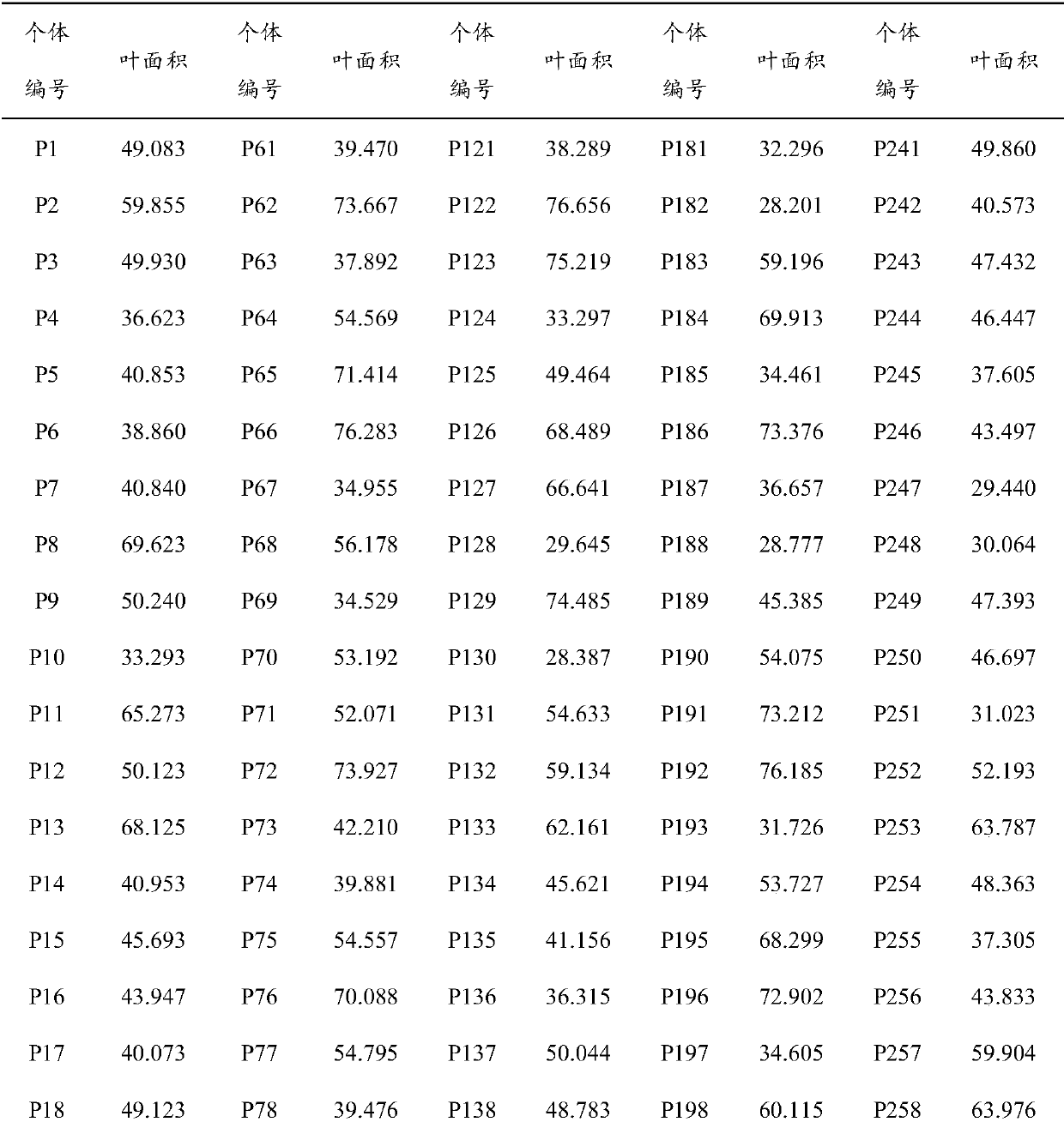
[0043] Step 1) Randomly select 300 individuals from the Populus tomentosa germplasm resource bank planted in Guan County, Shandong Province as an associated population, and collect their functional leaves (the 3rd to 5th mature leaves at the top of the branches) at 9:00 to 11:00 in the morning. ), in order to prevent changes in the DNA methylation status, immediately put them into a liquid nitrogen environment (-196°C) for storage after collection.
[0044] Step 2) Genomic DNA of leaf samples was extracted using DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen China, Shanghai, China).
[0045] After completing the above steps, the obtained genomic DNA can be further detected, specifically: 2.1, use agarose gel electrophoresis to determine the degree of degradation of the DNA sample and whether there is RNA contamination; 2.2, use RNsae-free water as a blank control, Use Nanodrop to detect the OD260 / OD280 ratio of each DNA sample to determine...
specific Embodiment approach
[0046] Then implement step 3) carry out bisulfite sequencing to the extracted genomic DNA, the method for the DNA library that builds bisulfite treatment according to genomic DNA has become conventional technical method, and the specific embodiment of the present invention is as follows:
[0047] Step 3.1, using Covaris S220 to randomly fragment the genomic DNA to 200-300bp;
[0048] Step 3.2: Carry out end repair and A-tailing on the fragmented DNA fragments, and connect sequencing adapters with all cytosines modified by methylation, the purpose of which is to provide primers required for the next sequencing-by-synthesis process. sequence information;
[0049] In step 3.3, the DNA fragment in step 3.2 is subjected to bisulfite treatment. After treatment, the unmethylated C becomes U (after PCR amplification becomes T), while the methylated C remains unchanged. Specifically, the EZ DNA MethylationGold Kit (Zymo Research, Murphy Ave. Irvine, CA, U.S.A.) can be used;
[0050] ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0065] Step 1) Randomly select 300 individuals from the Populus tomentosa germplasm resource bank planted in Guan County, Shandong Province as the sequencing population, and collect their functional leaves (the 3rd to 5th mature leaves at the top of the branches) at 9:00 to 11:00 in the morning ), in order to prevent changes in the DNA methylation status, immediately put them into a liquid nitrogen environment (-196°C) for storage after collection.
[0066] Step 2) Genomic DNA of leaf samples was extracted using DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen China, Shanghai, China).
[0067] After completing the above steps, the obtained genomic DNA can be further detected, specifically: 2.1, use agarose gel electrophoresis to determine the degree of degradation of the DNA sample and whether there is RNA contamination; 2.2, use RNsae-free water as a blank control, Use Nanodrop to detect the OD260 / OD280 ratio of each DNA sample to determine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com