Method for controlling the features of textile finished product with microscopic structure
A technology of microstructure and finished products, applied in the field of fabrics, can solve the problems of characteristic deviation, intelligentization, inability to be popularized and applied in wool spinning enterprises, and inability to meet industrial upgrading.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
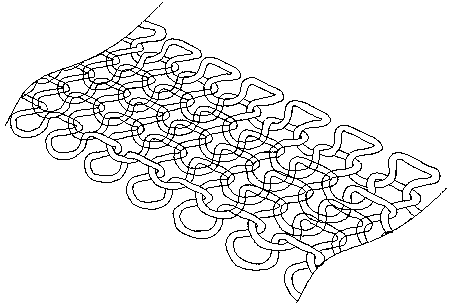
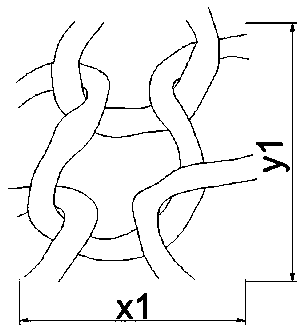
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is the internal microstructure of an Ω-shaped fabric knitted by warp and weft knitting. figure 2 where is the Ω-type warp and weft knitted fabric unit, the parameter x1 represents the length of the smallest unit interval of the fabric, the parameter y1 represents the width of the smallest unit interval of the fabric, and the parameter h1 represents the height of the fabric unit interval. Such as image 3 , 4 As shown, the microstructure parameter y1 of the Ω-type fabric represents the length of the Ω-type unit of the fabric, the parameter x1 represents the width of the Ω-type unit of the fabric, the parameter h1 represents the height of the fabric unit, and the parameter d1 represents the yarn cross-sectional diameter of the fabric unit.
[0040]Description of the shape of the yarn space curve within the unit when designing and evaluating. The shape of the yarn space curve in the unit is obtained by fitting the 3-dimensional curve of th...
Embodiment 2
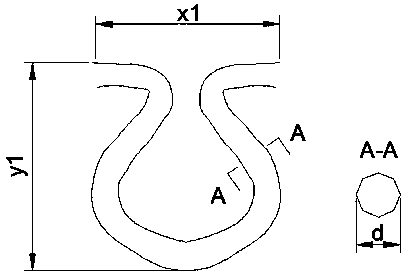
[0047] Image 6 The internal microstructure of the "well" shaped fabric interwoven with warp and weft yarns. Such as Figure 7 As shown, the "well"-shaped fabric unit parameter x2 represents the length of the smallest fabric unit interval, the parameter y2 represents the width of the fabric smallest unit interval, and the parameter h2 represents the height of the fabric unit interval. Such as Figure 8 As shown, the microstructure parameter x2 of the "well"-shaped fabric represents the width of the "well"-shaped unit of the fabric, the parameter h2 represents the height of the fabric unit, and the parameter d2 represents the yarn cross-sectional diameter of the fabric unit.
[0048] Description of the shape of the yarn space curve within the unit when designing and evaluating. The shape of the yarn space curve in the unit is obtained by fitting the 3-dimensional curve of the spline space of the fabric unit yarn. Establish a method of simulating the spline curve of the fabr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com