Method and system for positioning short-circuit fault of intelligent distribution network
A smart distribution network, short-circuit fault technology, applied in the fault location, information technology support system, fault detection according to conductor type, etc., can solve the problems of matrix method, such as weak fault tolerance, aggravated load impact, and small short-circuit current capacity, to achieve Both economical and reliable, reducing installation density and good reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
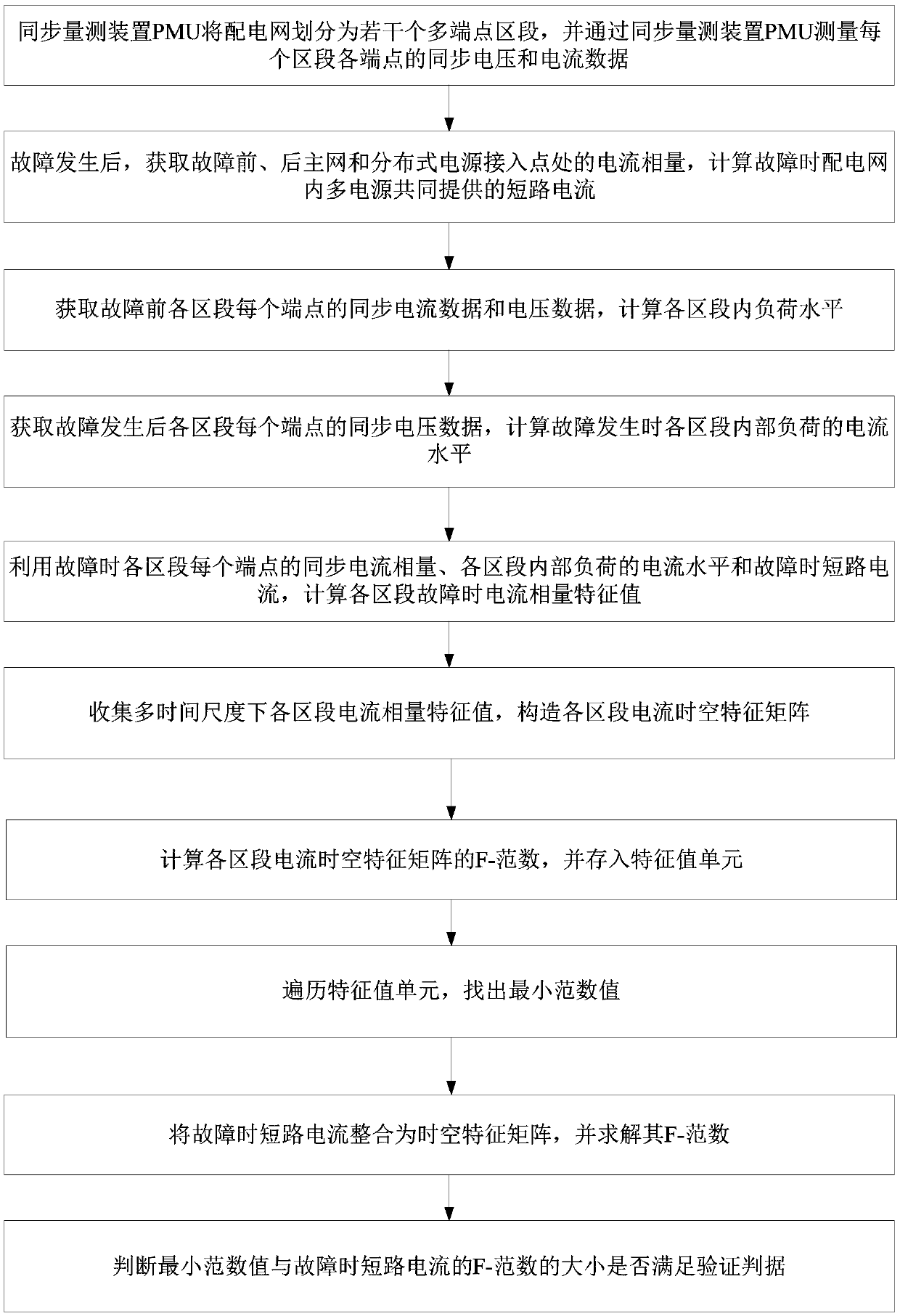
[0065] see figure 1 , an embodiment of the present disclosure provides a method for locating a short-circuit fault in a smart distribution network, the method comprising the following steps:
[0066] S101, the synchronous measurement device PMU divides the distribution network into several multi-terminal sections, and uses the synchronous measurement device PMU to measure the synchronous voltage and current data of each terminal of each section.
[0067] In this embodiment, assuming that the installation of the synchronous measurement device PMU in the distribution network meets the requirements of the global observability of the system, the synchronous measurement device PMU can divide the distribution network into multiple sections, and some sections contain loads or Passive branch lines.
[0068] S102. After a fault occurs, obtain the current phasors at the access points of the main network and distributed power sources before and after the fault, and calculate the short-c...
Embodiment 2
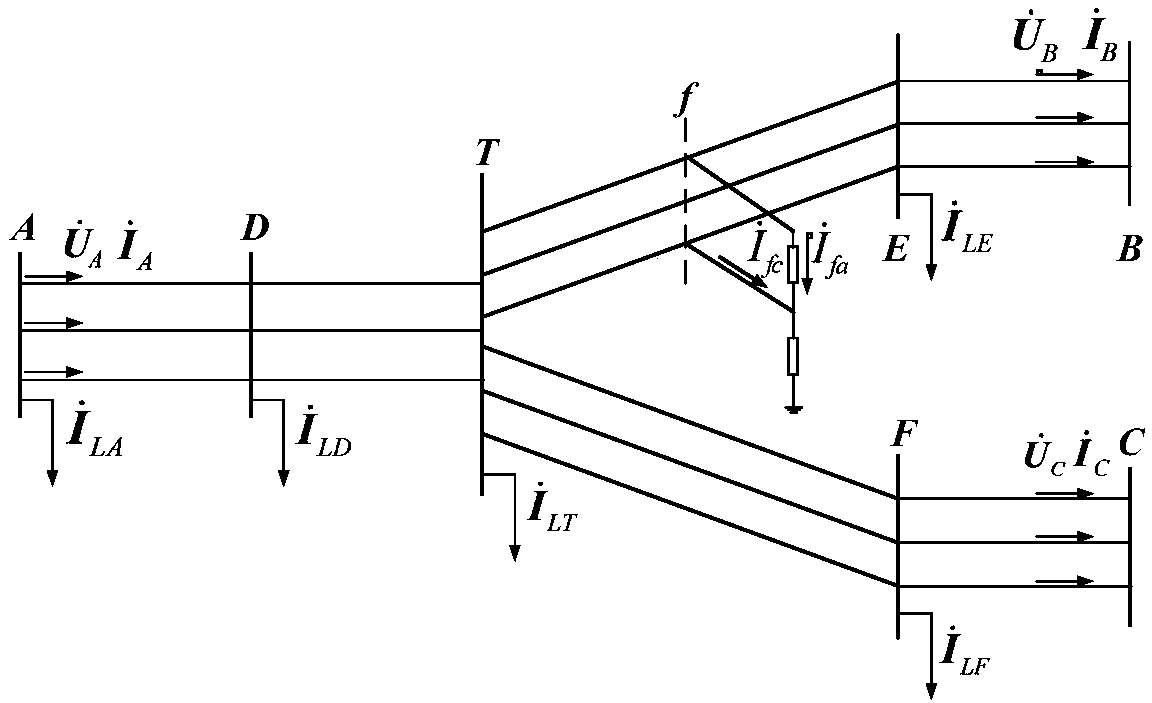
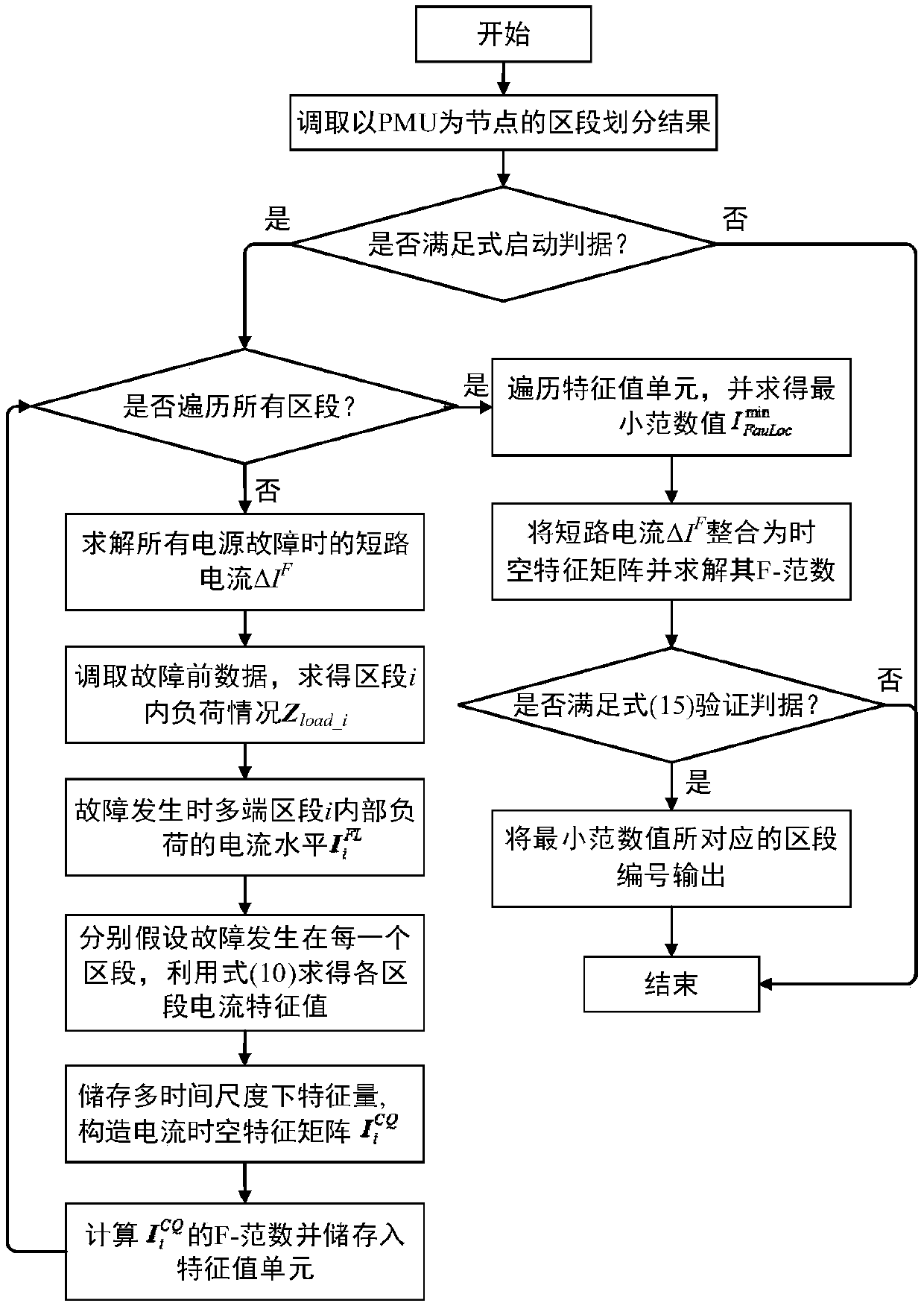
[0100] In order to make those skilled in the art understand the method of the present disclosure better, enumerate a more detailed embodiment below, see image 3 , an embodiment of the present disclosure provides a method for locating a short-circuit fault in a smart distribution network, the method comprising the following steps:
[0101] S201. The synchronous measurement device PMU divides the distribution network into m multi-terminal sections, and separately collects synchronous voltage and current data of each terminal of each section.
[0102] Specifically, in the step 201, it is assumed that the synchronous measurement device PMU divides the distribution network into m multi-terminal sections, wherein section i is an n-terminal section, and the synchronous voltage of a certain terminal j of section i and The current phasors are U ij and I ij ,in
[0103]
[0104]
[0105] In the formula, is the phase A voltage of terminal j in section i; is the phase B volt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com