Flying capacitor charging method and device
A technology for charging flying capacitors and capacitors, which is applied in the field of charging methods and devices for flying capacitors, can solve the problems of poor applicability and high circuit cost, and achieve the effects of strong applicability and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0102] for Figure 6 The multi-level topology circuit shown can charge the flying capacitors (ie Ca and Cb) in the following manner.
[0103] Generally, the operation of the power electronic power circuit needs to be controlled by the controller, and the method for precharging the flying capacitor provided by the embodiment of the present application can also be regarded as being controlled and executed by the controller independent of the multilevel topology circuit. The power supply that powers the controller can be referred to as an auxiliary power supply. Generally, the auxiliary power supply can adopt a switching power supply circuit with a high voltage input and a low voltage output such as 12V or 24V.
[0104] S1: After the auxiliary source is turned on, control and close the switching devices T1b and T4b in each topology. Connect the output capacitor Cout in parallel with the flying capacitor Cb.
[0105] S2: Use a DC power supply (such as a flyback power supply), c...
example 2
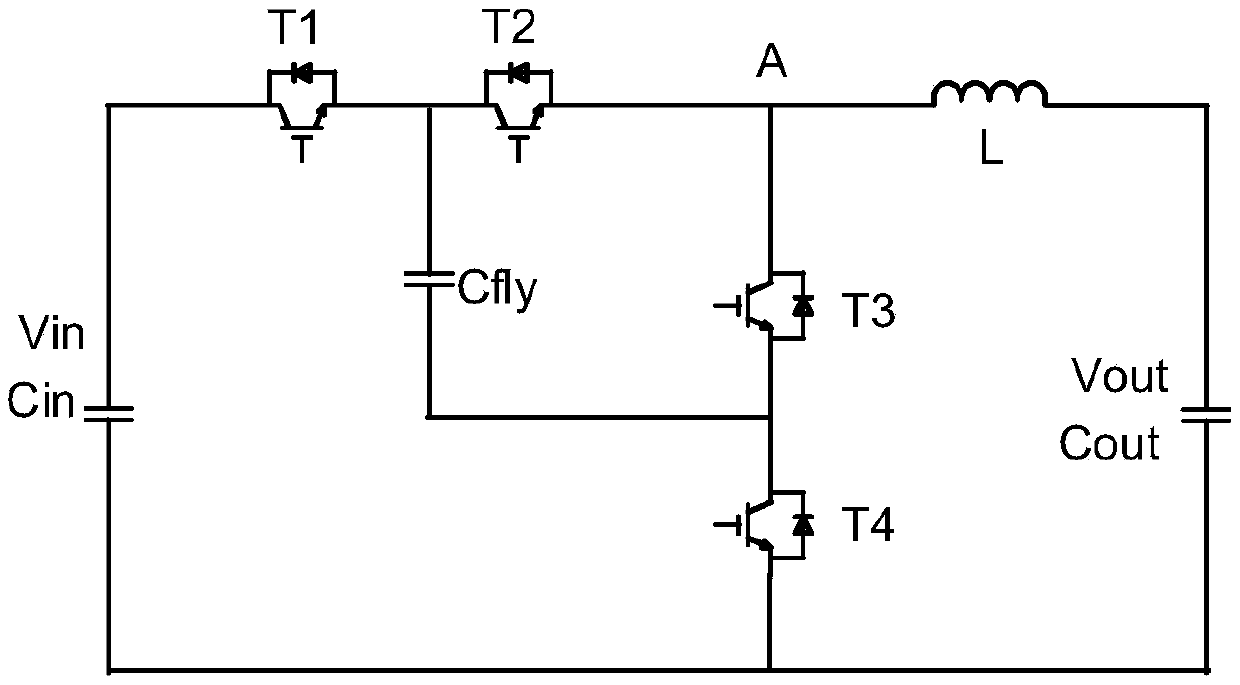
[0113] for Figure 4 The multi-level topology circuit shown can charge the flying capacitor (ie Cfly) in the following manner.
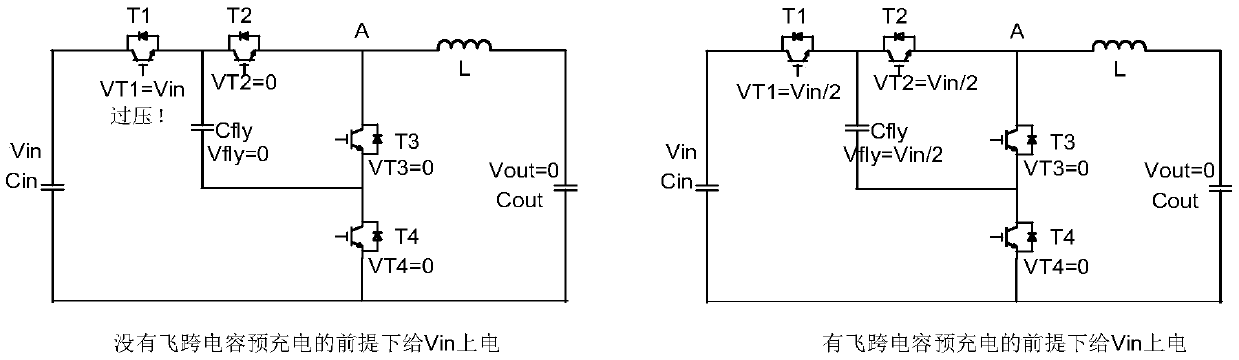
[0114] S1: After the auxiliary source is turned on, it controls the switching devices T1 and T4 in the closed topology circuit. Connect the input capacitor Cin in parallel with the flying capacitor Cfly.
[0115] S2: Use a DC power supply (such as a flyback power supply), connect the output of the power supply to both ends of the input capacitor Cin, and charge the input capacitor Cin and the flying capacitor Cfly connected in parallel. The charging target value is the flying capacitor Cfly The voltage during normal operation, that is, half of the DC source1 voltage.
[0116] S3: When the flying capacitor Cfly reaches the target value, disconnect T1 and T4, and disconnect the flying capacitor Cfly from the input capacitor Cin.
[0117] S4: continue to charge the input capacitor Cin, the target value is the voltage of DC source1.
[0118] S5: Afte...
example 3
[0123] for Figure 4 The multi-level topology circuit shown can charge the flying capacitor (ie Cfly) in the following manner.
[0124] S1: After the auxiliary source is turned on, it controls the switching devices T1 and T4 in the closed topology. Connect the input capacitor Cin in parallel with the flying capacitor Cfly.
[0125] S2: Use a DC power supply (such as a flyback power supply), connect the output of the power supply to both ends of the output capacitor Cout, and charge the three capacitors (ie Cin, Cfly, and Cout) connected in parallel. The target value of the charge is fly The voltage when the transcapacitor works normally, that is, half of the DC source1 voltage.
[0126] S3: When the flying capacitor Cfly reaches the target value, disconnect T1 and T4.
[0127] S4: continue to charge the output capacitor Cout and the input capacitor Cin, and the target value is the DC source1 voltage.
[0128] S5: After reaching the target value, stop charging, the voltage ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com