CEEMDAN algorithm-based power system low-frequency oscillation mode identification method
A low-frequency oscillation, power system technology, applied in the direction of reducing/preventing power oscillation, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve the problems of power supply equipment threats, cascading failures, power outages, etc., and achieve the effect of improving safe and stable operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] The present invention is a method for identifying low-frequency oscillation modes of power systems based on the CEEMDAN algorithm, such as Figure 9 as shown, Figure 9 It is a flow chart of the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0067] An application based on CEEMDAN and Hilbert-Huang transformation algorithm in power system oscillation mode identification, the calculation method includes the following steps:
[0068] 101 Use the data acquisition function of the wide-area measurement system to obtain the measured data of the power system, and use the Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN) algorithm to decompose each group of original low-frequency oscillation signals into The sum of several intrinsic mode functions (Intrinsic Mode function, IMF), each IMF component represents an oscillation mode;
[0069] 102 Preprocess each IMF component, and use the Teager energy operator to calculate the energy size and energ...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The scheme in embodiment 1 is further introduced below in conjunction with specific calculation formulas and examples, see the following description for details:
[0074] 201: Obtain the state measurement information of the power system from the wide area measurement system, and standardize the state measurement information;
[0075] Among them, standardization is a process of calculating the standard score, which is the process of dividing the difference between a number and the mean by the standard deviation. The standardized data is simple, easy to compare, and can fully show the relationship between the standard deviation of the data, and retain the original information of the data.
[0076] 202: The standardized generator rotor angle signal is used as the input signal to be identified, and the oscillation signal is decomposed by using the complete set of empirical mode decomposition of adaptive noise, so that each oscillation signal is decomposed into a signal that...
Embodiment 3
[0170] Below in conjunction with specific experimental data, the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
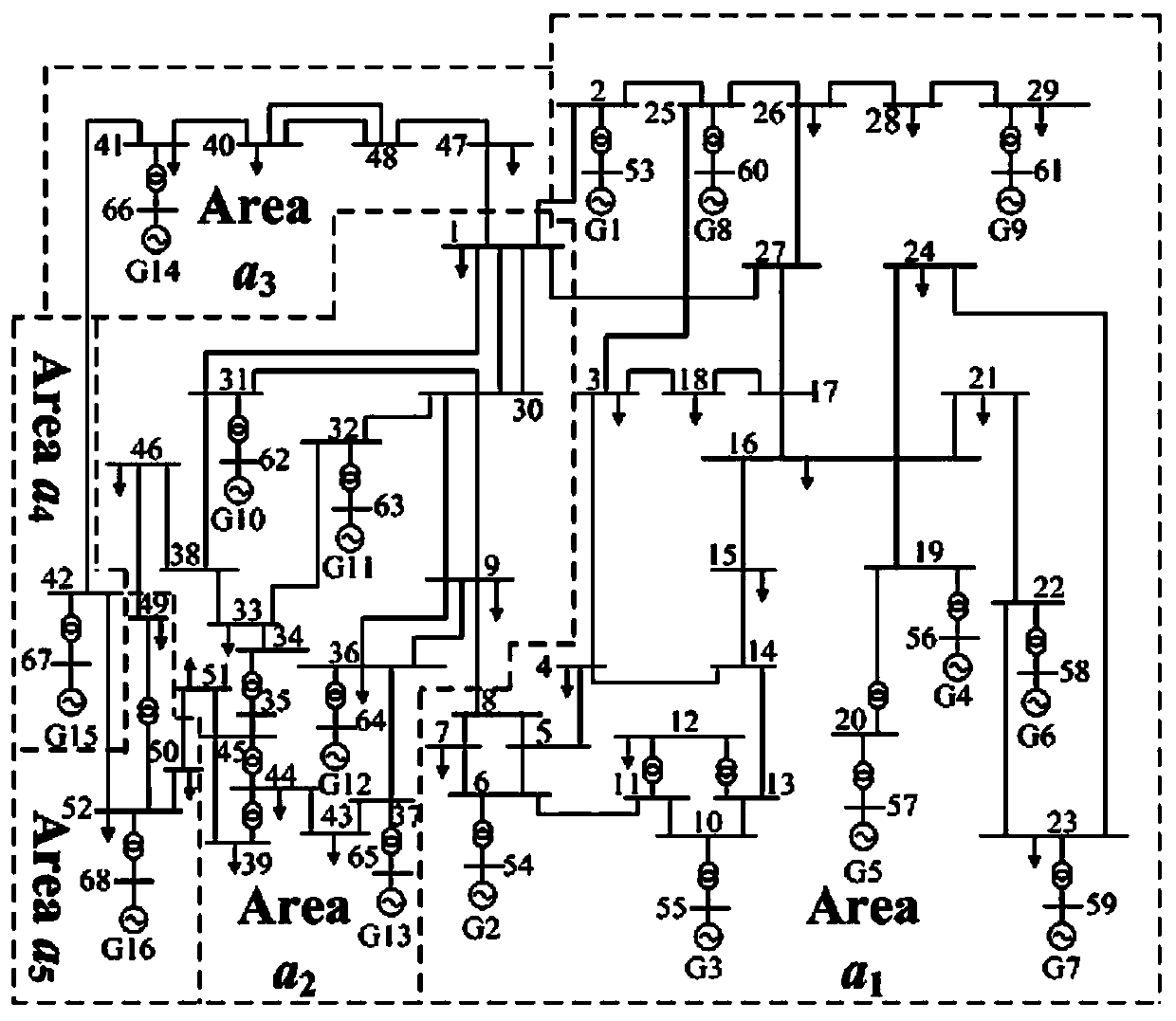
[0171] This example takes the 16-machine 68-node system as an example for simulation analysis. The 16-machine 68-node test system is as follows: figure 1 shown.
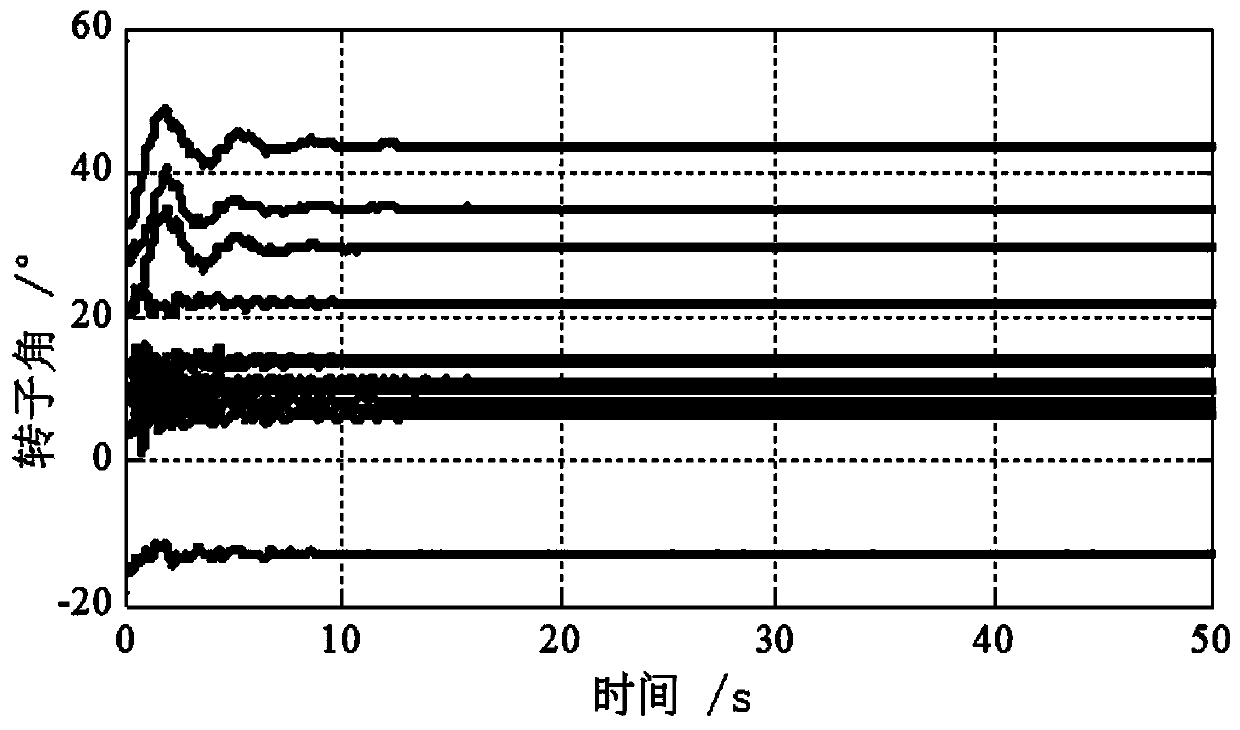
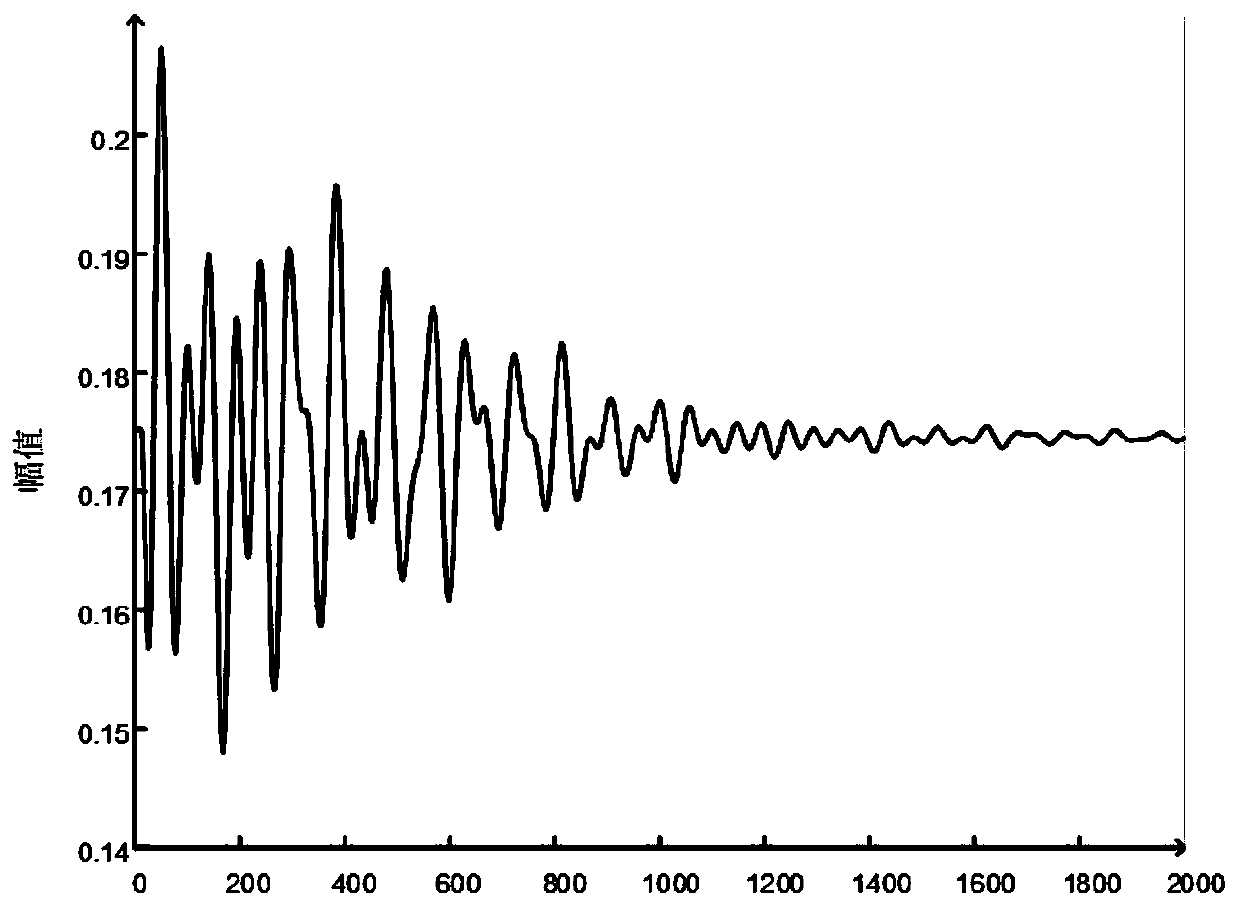
[0172] In the time-domain simulation process, a three-phase permanent short-circuit fault is set on the branch 46-49, and the fault occurs at 0.1s, the near-end fault is cut off at 0.2s, and the far-end fault is cut off at 0.22s. Unit 1 is selected as the reference unit, and the rotor angle signals of each generator set relative to G1 are used as input signals. The 16 generators generate a total of 15 sets of rotor angle signals, and the sampling frequency is 0.01s. After the power system is disturbed, the generator rotor angle swings curve like figure 2 As shown, the CEENDAN decomposition is performed on the rotor angle information of e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com