Methods of increasing microbial diversity of a skin microbiota
A microbiota, diversity technology for the cosmetic and therapeutic treatment of mammalian skin that addresses imbalances, exacerbated skin microbiota imbalances, and reduced skin microbiota diversity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Microbiota analysis of the skin of subjects with atopic dermatitis
[0094] The microbial load associated with the microbiota of skin with atopic dermatitis is heavier than that of healthy skin. Use of zinc pyrithione in body washes reduces total bacterial levels.
[0095] Sequence analysis of microbiota samples from skin with atopic dermatitis to identify various genera present on the skin and measure relative abundance. In the first round of sequencing, read lengths of 150–800 bp were obtained using a closed OTU sorting method. Use the Mega-blast search engine to interrogate the GG-13-8-91 database. Using a closed OTU sorting method, the second round of sequencing yielded read lengths of 250-600 bp. Use the Bowtie2 search engine to interrogate the GG-13-8-91 database again. A third round of sequencing involved acquiring read lengths of 250-600 bp using a closed OTU sorting method. Use the Bowtie2 search engine to interrogate the GG-13-8-97 database. The result...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Atopic dermatitis skin microbiota compared to healthy skin microbiota
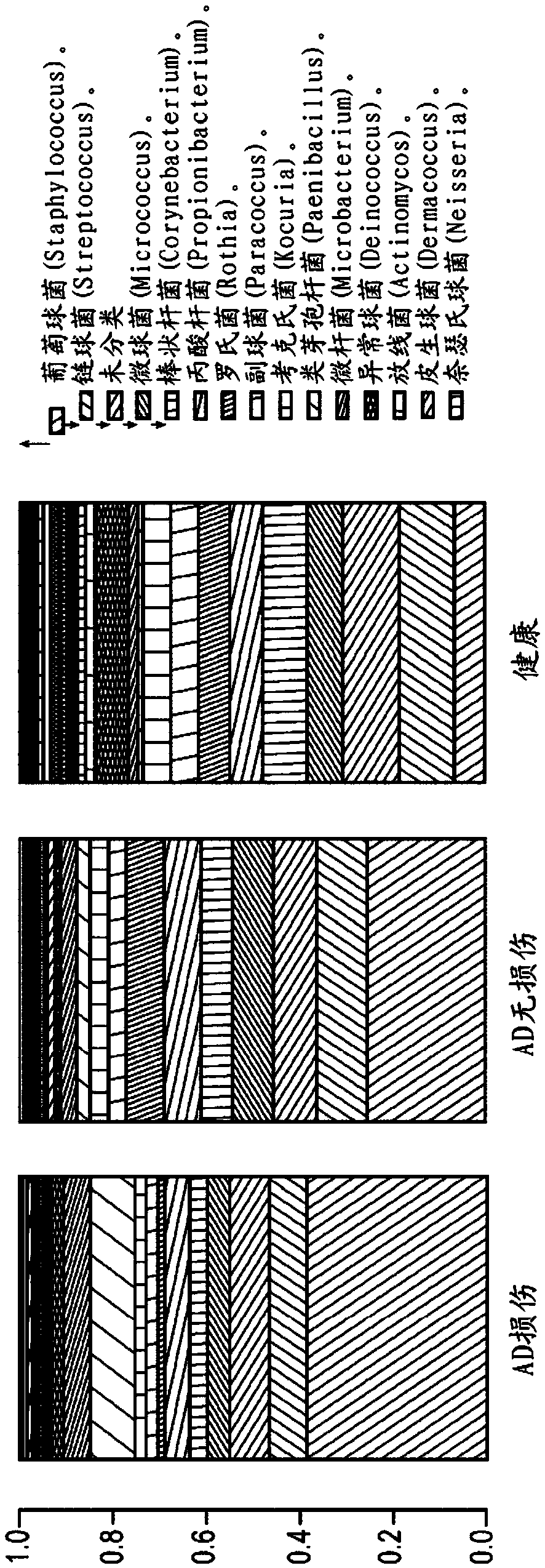
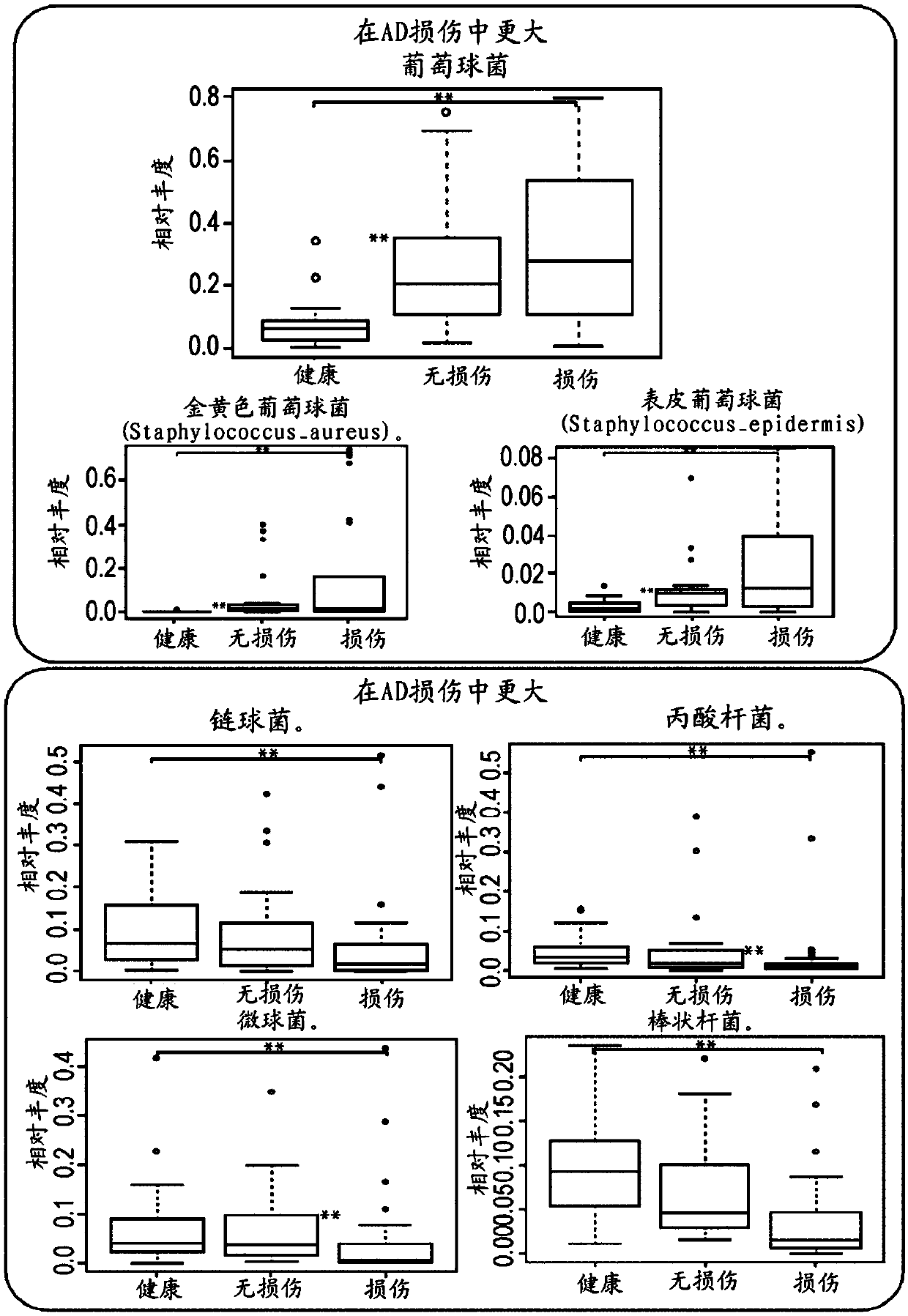
[0099] A detailed comparison of skin microbiota from healthy subjects with those with atopic dermatitis revealed several noteworthy features. Such as figure 2 showed that several Staphylococcal species were present in greater proportions in the skin microbiota of subjects with atopic dermatitis than in healthy subjects, and The difference was more pronounced when comparing subjects with atopic dermatitis with lesions to healthy subjects compared to subjects with atopic dermatitis without lesions and healthy subjects. S. aureus and S. epidermidis were each present in greater relative abundance in the atopic dermatitis skin microbiota than in the healthy skin microbiota, and the relative abundance of each of these staphylococcal species in The skin microbiota of subjects with atopic dermatitis and lesions was greater than that of subjects with atopic dermatitis but without lesions.
[0100] In c...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Bacterial diversity during the development of atopic dermatitis
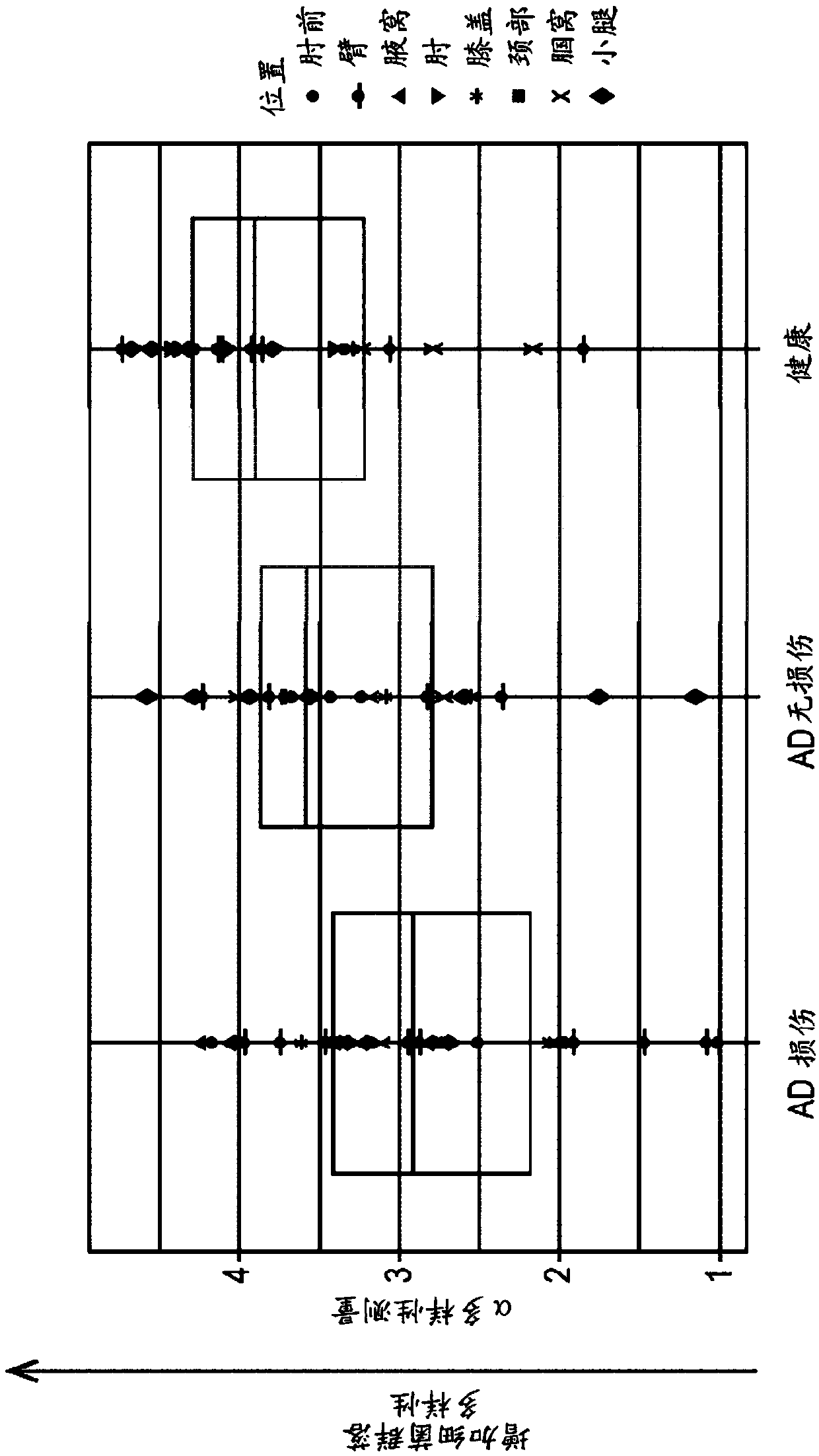
[0103] During the development of atopic dermatitis, healthy skin changes to exhibit the characteristic inflammatory indicators of atopic dermatitis, eventually leading to skin damage. Data were obtained from a sequential analysis (see Example 1) of skin microbiota samples collected from the following skin regions of subjects subjected to statistical analysis: antecubital, arm, armpit, elbow, knee, neck, Popliteal fossa and calves. Statistical analysis revealed alpha diversity values based on the Shannon Index. Such as image 3 As shown, the alpha diversity measure of the bacterial diversity of the atopic dermatitis skin microbiota showed that diversity was greatest in healthy skin, decreased in the uninjured atopic Lesioned atopic dermatitis subjects had the lowest diversity in their microbiota. It was also evident that the pattern of relative diversity remained constant across all skin sampling l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com