An odometer motion estimation method based on binocular vision
A technology of motion estimation and binocular vision, applied in computing, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of low robot pose accuracy, achieve the goal of improving pose accuracy, reducing calculation cost, and ensuring accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0033] Specific implementation mode one: the specific process of a binocular vision-based odometer motion estimation method in this implementation mode is as follows:
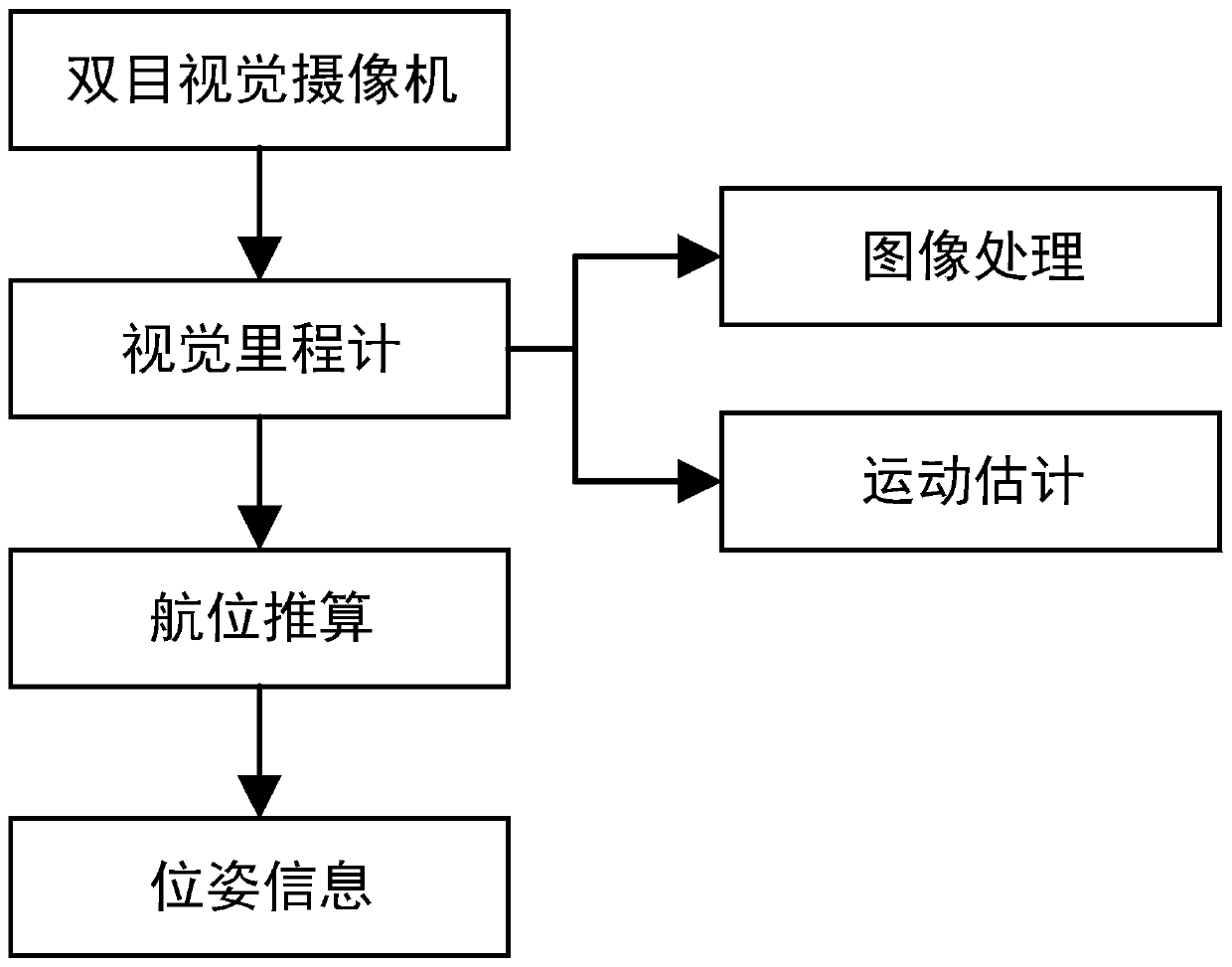
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the specific content of the present invention is to rely on the binocular vision camera as the sensor, obtain the three-dimensional information of the scene feature points by processing the obtained image sequence, and then obtain the relative motion relationship of the mobile robot through the method of motion estimation, and then calculate the real-time position Posture information, the specific implementation process is as follows:
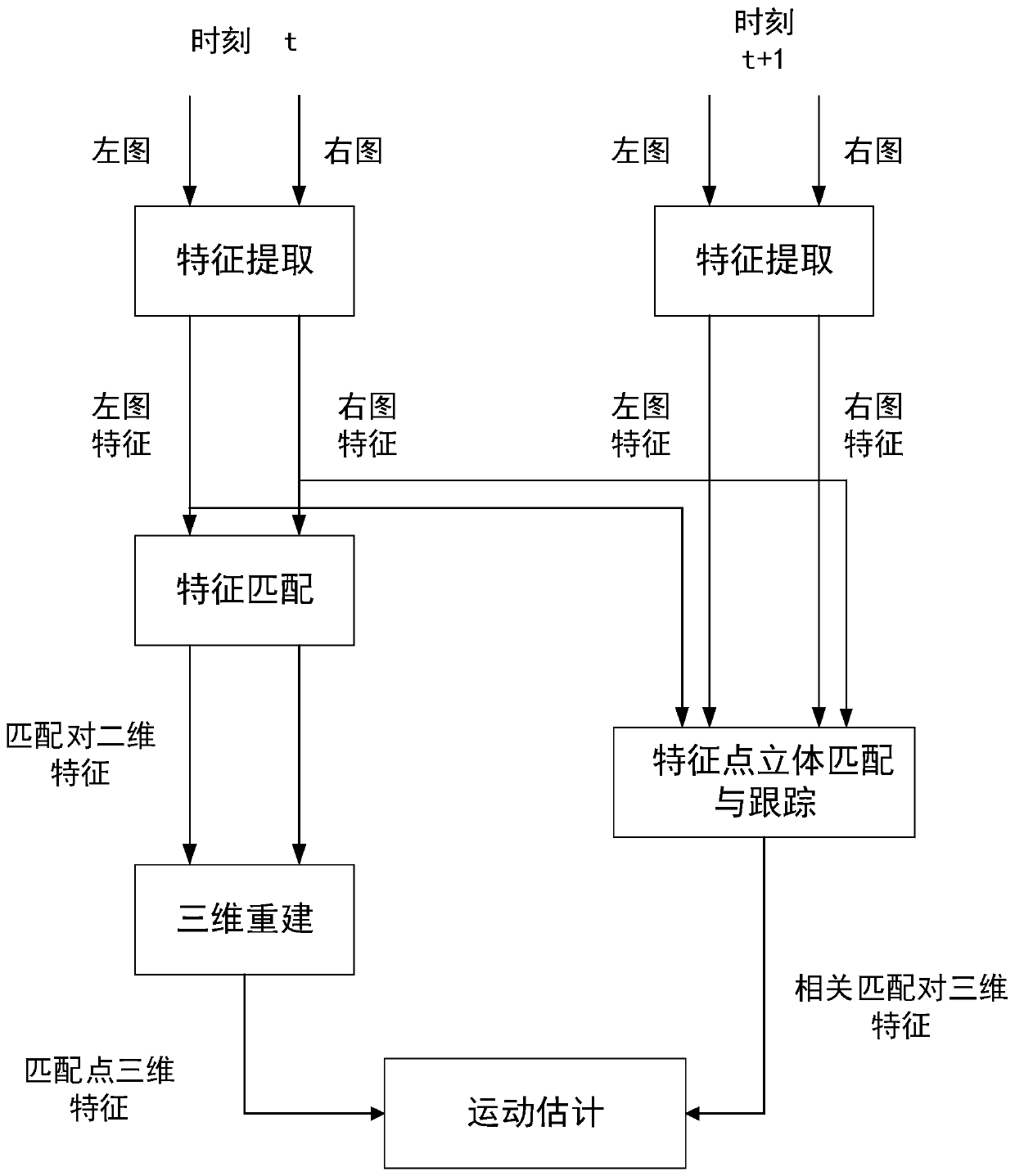
[0035] Step 1, such as figure 2 As shown, the binocular camera captures images of the current scene at the position of time t and the position of time t+1 respectively, and obtains the left image and right image collected by the binocular camera of the current scene at time t, and the binocular image at time t+1. The left image and right imag...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the method of Harris corner detection is adopted in the step 3 to extract the feature points of the image after the step 2 preprocessing, and the specific process is:
[0049] The Harris corner detection method is used to extract feature points from the left and right images preprocessed in step 2 respectively.
[0050] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
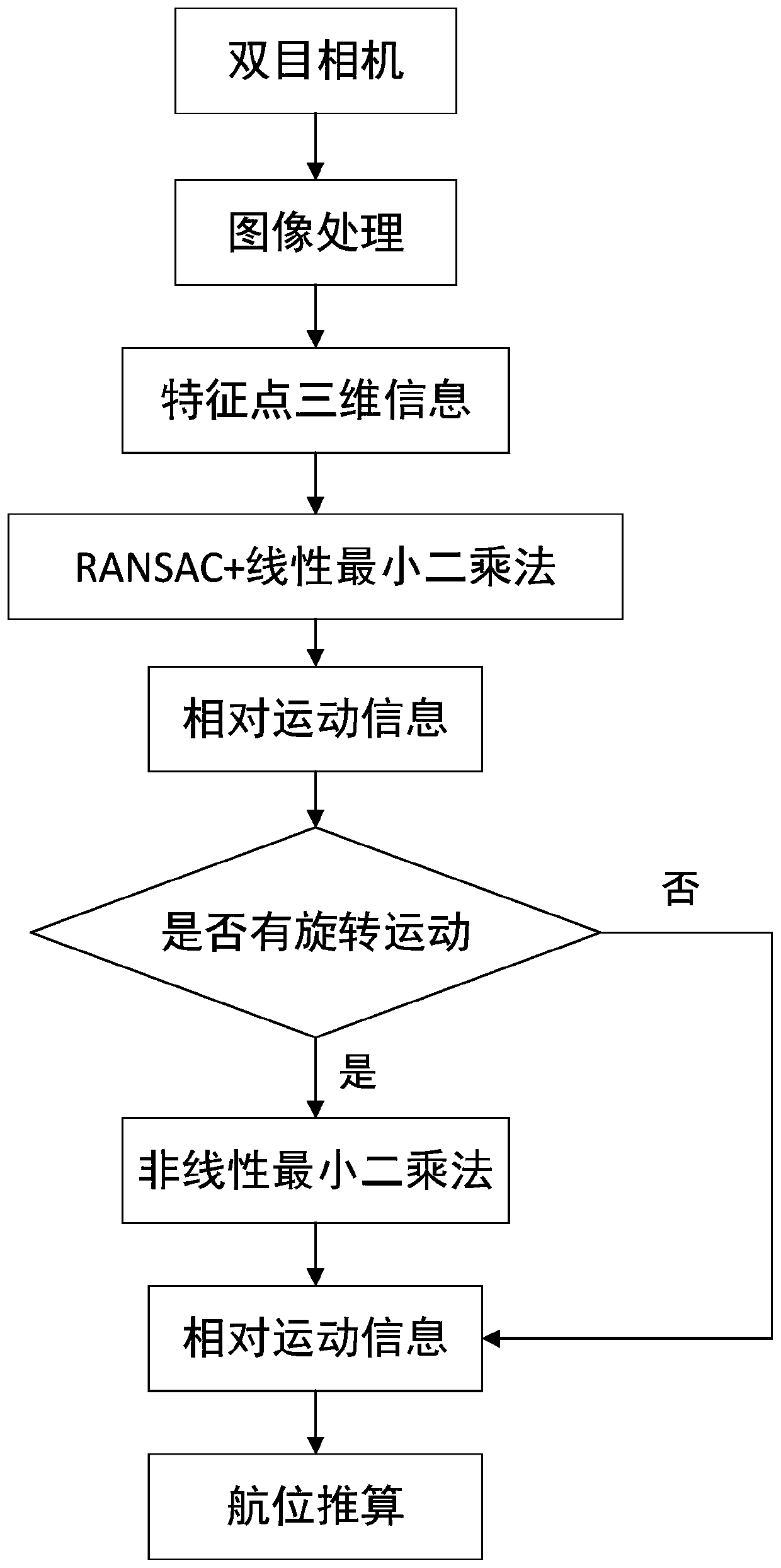
[0051] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in Step 7, the three-dimensional information of the feature points obtained in Step 6 is used for motion estimation according to the motion estimation method; the specific process is:
[0052] Step 7-1. Use the improved RANSAC combined with the linear least squares method to process the three-dimensional information of the feature points obtained in step 6, and the motion parameters obtained are the final rotation matrix R end and translation matrix T end ;
[0053] Step 7-2. According to the final rotation matrix R end and translation matrix T end Obtain the relative rotation angle, and determine whether the relative rotation angle is greater than 3°;
[0054] Step 7-3. If the relative rotation angle is greater than 3°, use the linear least squares method to obtain the final rotation matrix R end and translation matrix T end Perform optimization, and the optimized result is used as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com