Well wall instability risk quantitative evaluation method based on reliability theory
A technology of wellbore instability and quantitative evaluation, which is applied in earthwork drilling, wellbore/well components, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as narrow adaptability and wellbore instability, and achieve the effect of effective decision-making basis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
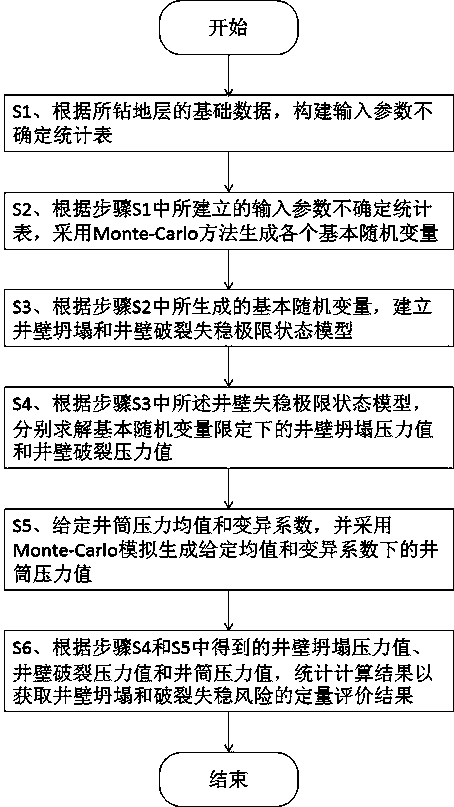
[0096] Taking the Xujiahe Formation strata in well CW-101X of an oilfield in the Sichuan Basin as an example, the Xujiahe Formation stratum is buried at a depth of 2500-3500 m. Stress 52.10-69.52MPa, maximum horizontal stress 42.55-59.47MPa (N37.86°E), minimum horizontal stress 35.63-49.68MPa, pore pressure 26.95-33.24, rock cohesion 12.15-18.63MPa, rock internal friction angle 33.54- 36.67°, the rock tensile strength is 3.47-5.63MPa, the rock Poisson's ratio is 0.23-0.27, and the porosity is 0.05-0.16. After statistical analysis, a statistical table of uncertain input parameters is constructed. The input parameters include vertical stress, maximum level In-situ stress, minimum horizontal in-situ stress, porosity, Poisson's ratio, cohesion, internal friction angle, well inclination angle, well inclination azimuth, Biot coefficient, permeability coefficient and caving width parameters are shown in the following table:
[0097] No.
Random Variables
average
s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com