A quantitative evaluation method for wellbore instability risk based on reliability theory
A technology for wellbore instability and quantitative evaluation, applied in earthwork drilling, data processing applications, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve problems such as narrow adaptability and wellbore instability, and achieve the effect of effective decision-making basis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
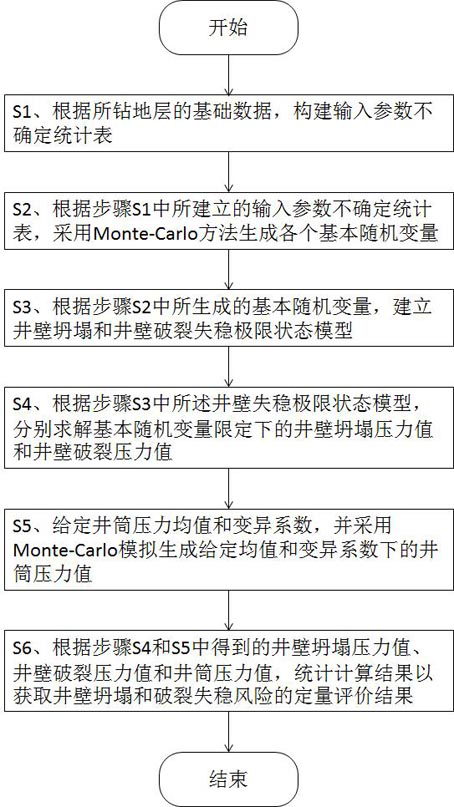
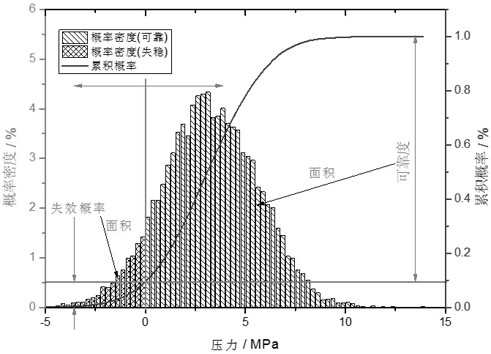
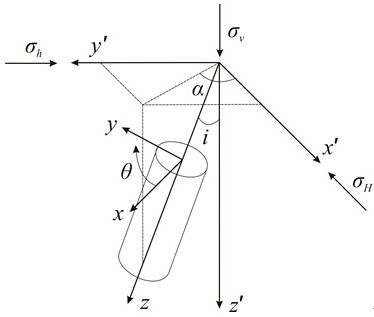
[0096] Taking Xujiahe Formation in Well CW-101X in an oilfield in the Sichuan Basin as an example, the burial depth of Xujiahe Formation is 2500-3500 m. Stress 52.10-69.52MPa, maximum horizontal in-situ stress 42.55-59.47MPa (N37.86°E), minimum horizontal in-situ stress 35.63-49.68MPa, pore pressure 26.95-33.24, rock cohesion 12.15-18.63MPa, rock internal friction angle 33.54- 36.67°, the tensile strength of the rock is 3.47-5.63MPa, the Poisson's ratio of the rock is 0.23-0.27, and the porosity is 0.05-0.16. After statistical analysis, a statistical table of uncertainty of input parameters is constructed. The input parameters include vertical stress, maximum level In-situ stress, minimum horizontal in-situ stress, porosity, Poisson's ratio, cohesion, internal friction angle, well inclination angle, well inclination azimuth, Biot coefficient, permeability coefficient and caving width parameters mean and variation coefficient statistics are shown in the following table:
[0097...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com