LDPC decoding method based on variable node dynamic block update for MLC type NAND-Flash
A technology of LDPC codes and variable nodes, applied in the field of LDPC code decoding, can solve problems such as difficult to meet NAND-Flash error correction performance requirements, and achieve the effects of improving decoding performance, suppressing negative effects, and improving utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
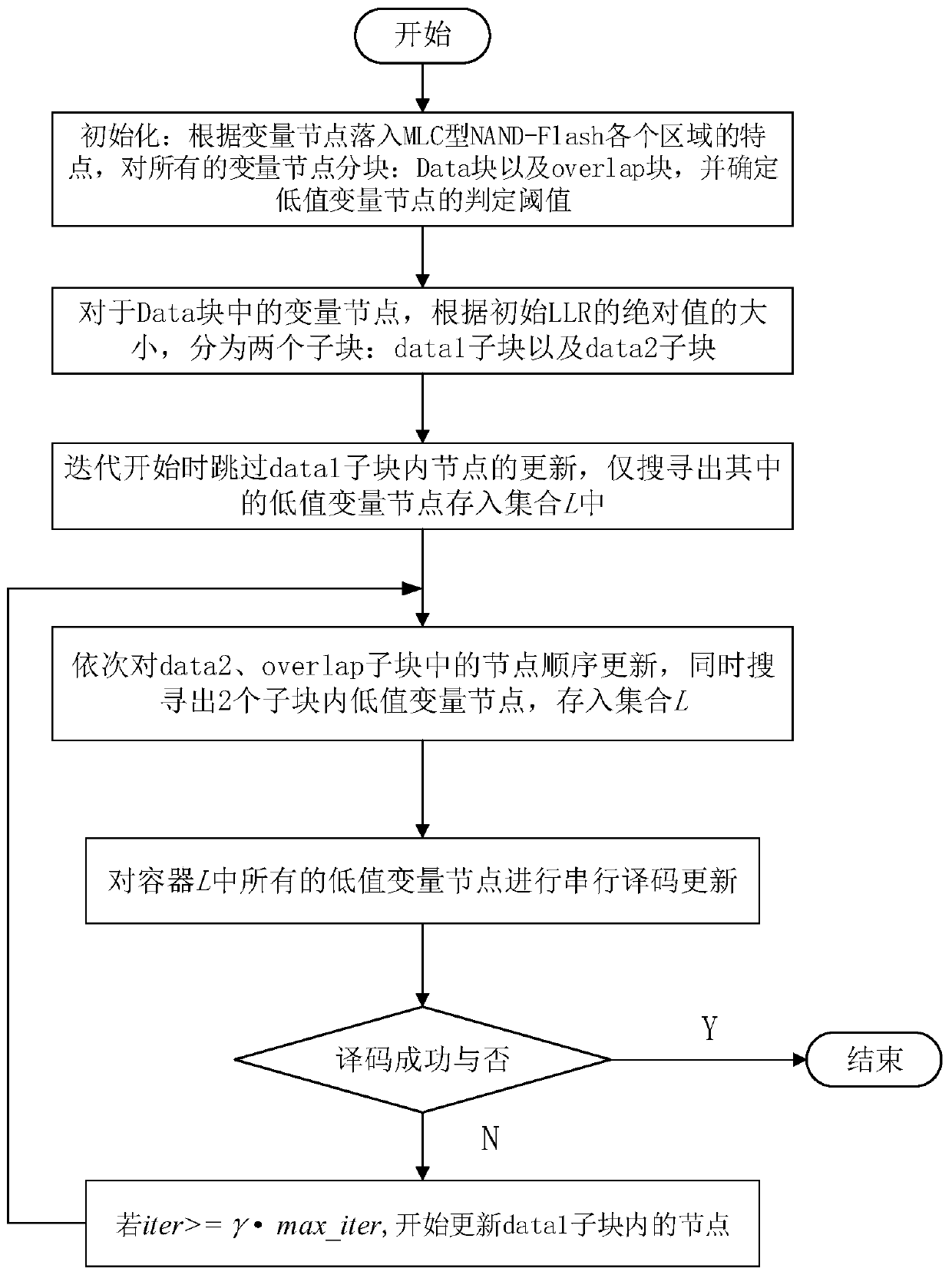
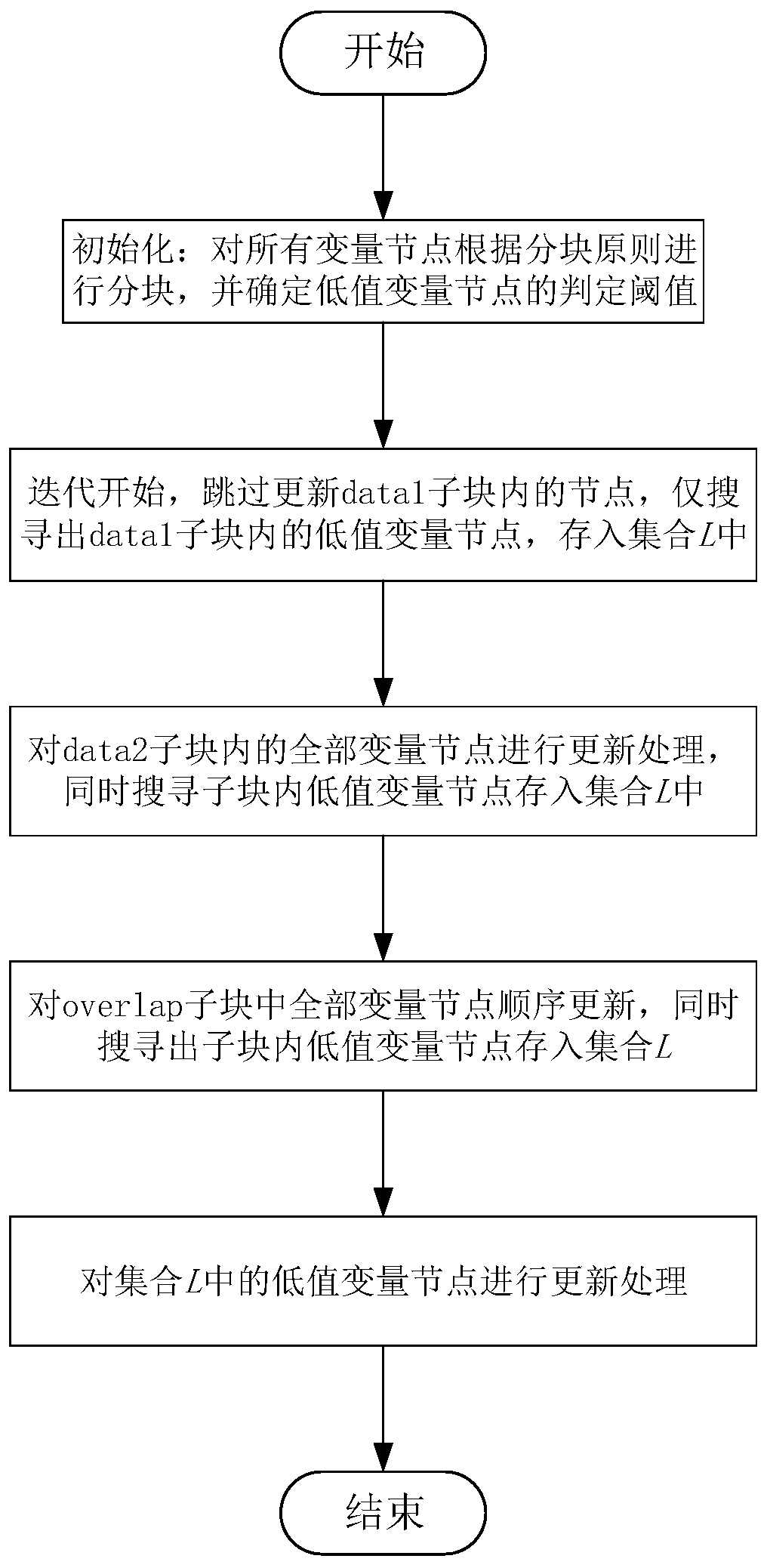
[0065] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, this embodiment provides an LDPC code decoding method based on variable node dynamic block for MLC type NAND-Flash, including the following steps:
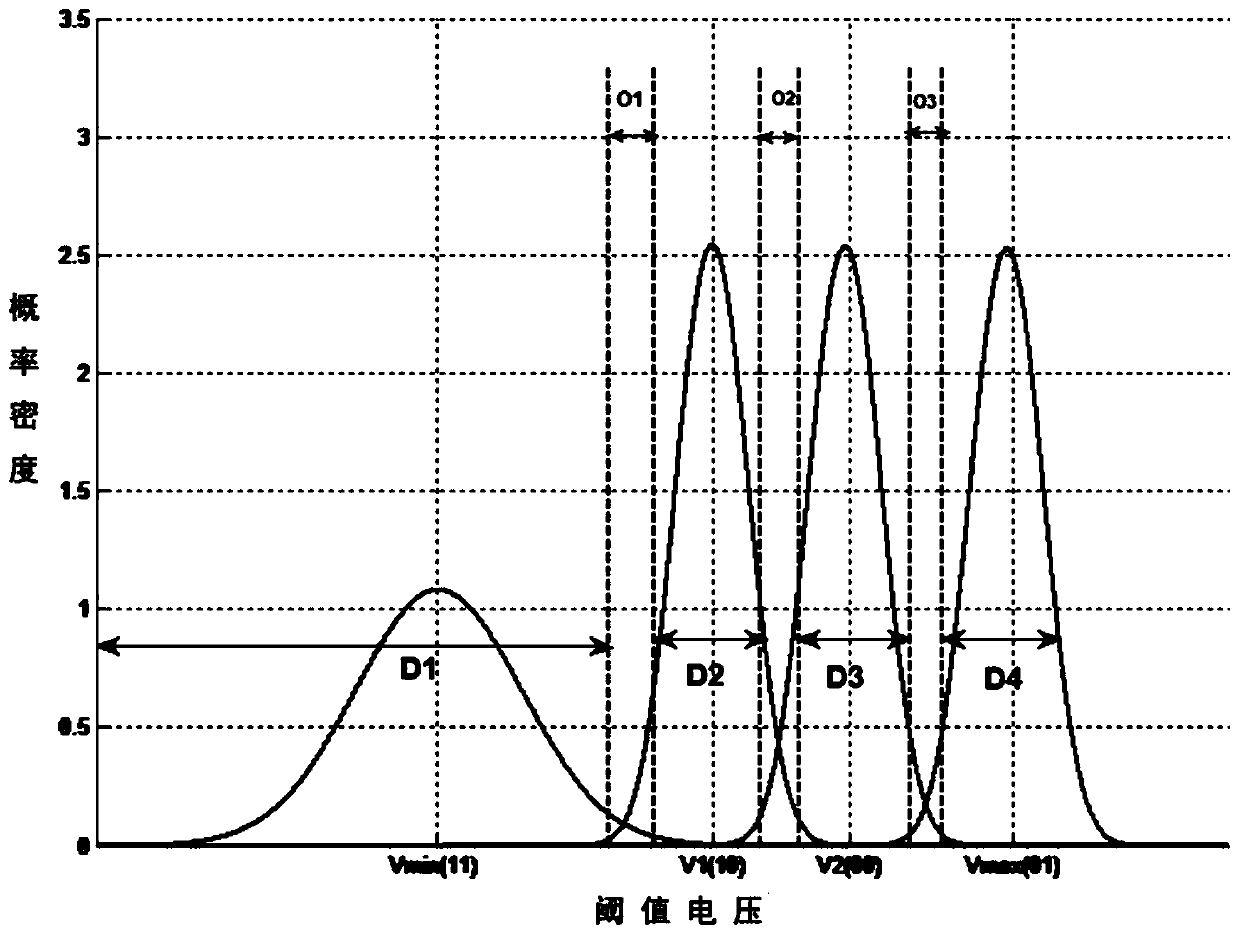
[0066] S1. In the NAND-Flash storage channel, all variable nodes are divided into blocks according to the probability that the voltage of the variable node falls into each area: the variable nodes in the non-overlapping area are divided into Data blocks, and the variable nodes in the overlapping area are divided into Divided into overlapping sub-blocks;
[0067] S2. Continue subdividing each sub-block into a plurality of sub-blocks according to the absolute value of the variable node initial LLR value in each sub-block: continue subdividing the Data block into a data1 sub-block and a data2 sub-block;
[0068] S3. Skip the data1 sub-block, update the variable nodes in the data2 sub-block and the overlap sub-block in sequence, and search out the data1 sub-block, data2 sub-block, and ov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com