Omnidirectional WLAN antenna with common-mode current suppression
A common-mode current and antenna technology, applied in the field of antennas, can solve problems such as pattern distortion, achieve the effects of reducing out-of-roundness, reducing physical size, and suppressing common-mode current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
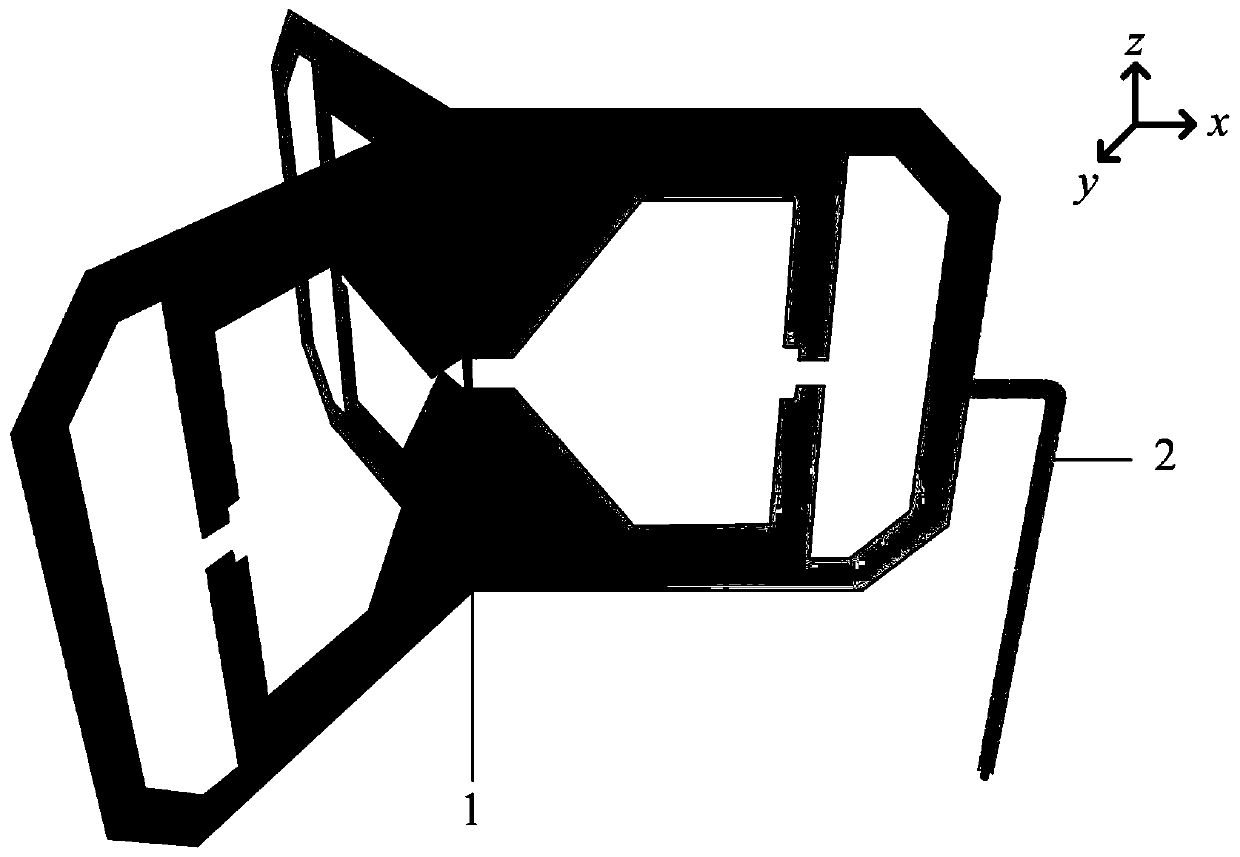
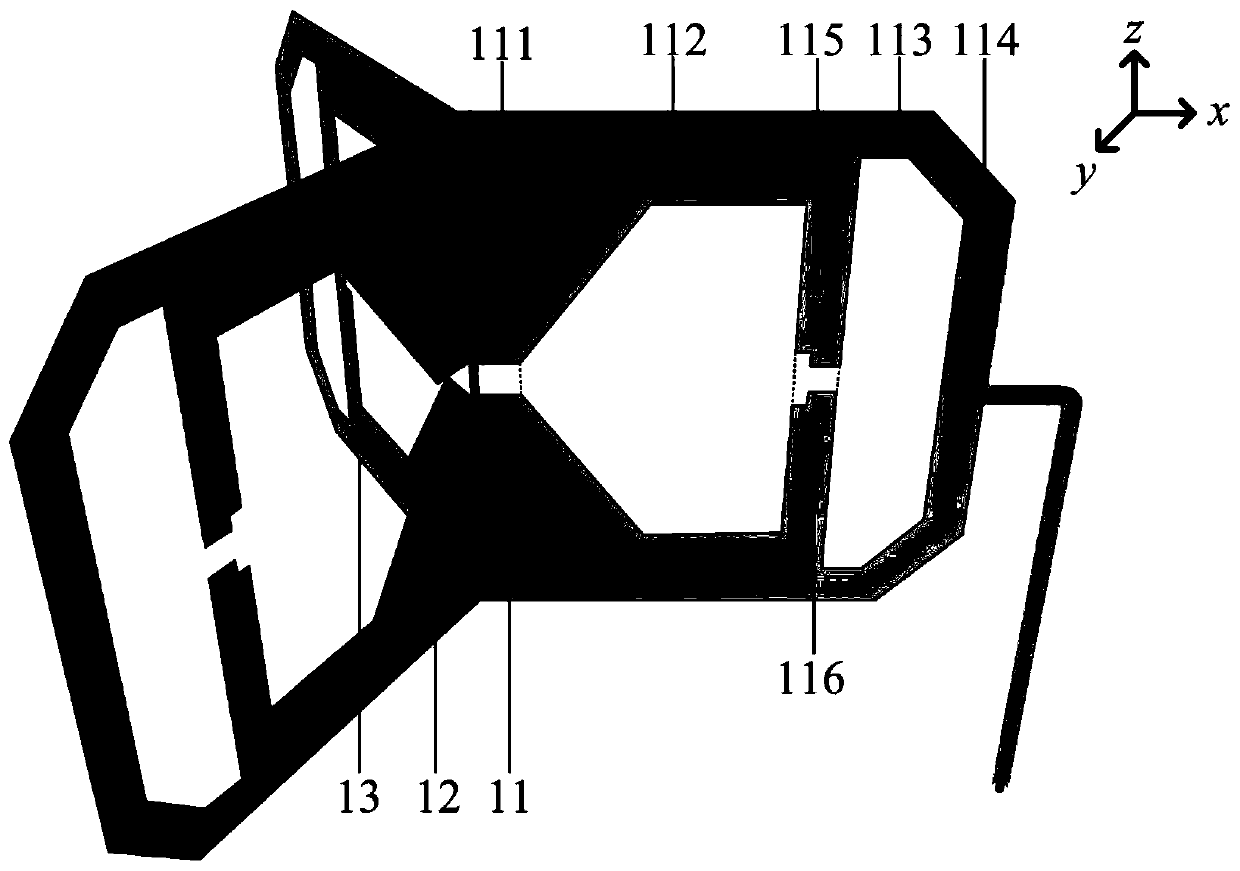
[0031] refer to figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3
[0032] An omnidirectional WLAN antenna based on common mode current suppression, comprising a radiation structure 1 and a coaxial line 2, the radiation structure 1 is composed of three first radiation units 11, second radiation units 12 and third radiation units of the same structure Each radiating unit is provided with three feeding ports 111 of the same structure, a first polygonal slot 112, a second polygonal slot 113 and two identical cut corners 114, and the feeding ports One side of 111 is connected to the axis of the Z axis;
[0033] Between the first polygonal groove 112 and the second polygonal groove 113, metal branches 115 are respectively provided, and the center positions of the metal branches 115 are respectively provided with notches 116, and are distributed symmetrically about the axis of the X axis; One end of the coaxial line 2 is introduced along one side of the feeding port 111 and distributed along th...
Embodiment 2
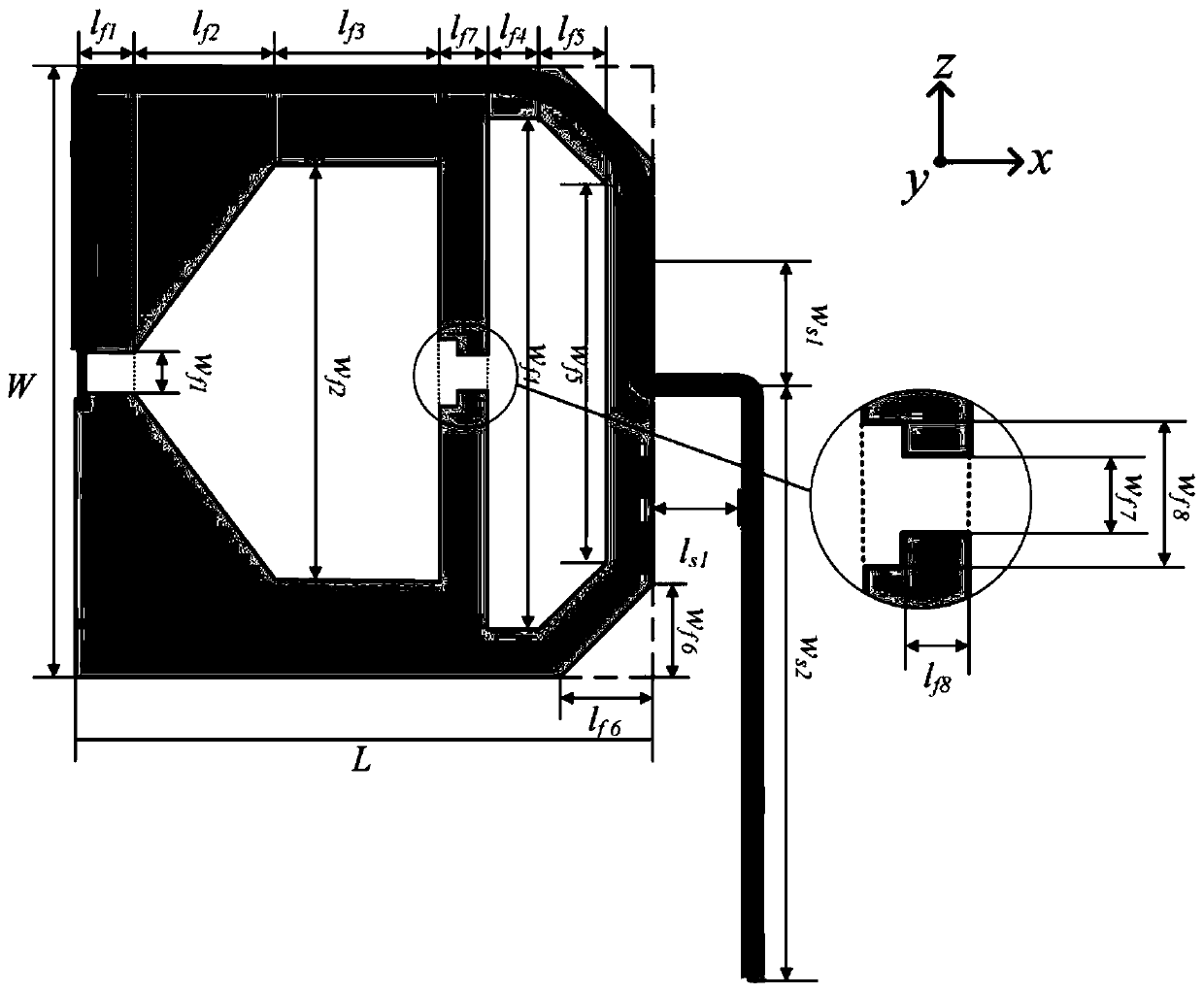
[0048] The width of the metal branch 115 is expressed as lf7, wherein the value range of lf7 is 1-5 mm. In the present invention, lf7=1mm.
[0049] The notch 116 is in a stepped shape, the first step width is expressed as wf7, and the length is expressed as lf8; the second step width is expressed as wf8, wherein the value range of wf7 is 0.5-4mm, and the value range of lf8 is 1- 4mm, the value range of wf8 is 1~5mm. In the present invention, wf7=0.5mm, wf8=1mm, and lf8=1mm.
[0050] The said coaxial line 2, the variation range of the position of the leading end and the XOY plane with respect to the Z axis is expressed as ws1, wherein the value range of ws1 is -10-10mm. In the present invention, ws1=-10mm.
[0051] The coaxial cable 2 is welded on the surface of the radiation unit 11 .
[0052] The two same cut corners 114 are located on the corresponding side of the feed port 111, and the lengths of the right-angle sides of the cut corners are expressed as lf6 and wf6, whe...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The width of the metal branch 115 is expressed as lf7, wherein the value range of lf7 is 1-5 mm. In the present invention, lf7=5mm.
[0058] The notch 116 is in a stepped shape, the first step width is expressed as wf7, and the length is expressed as lf8; the second step width is expressed as wf8, wherein the value range of wf7 is 0.5-4mm, and the value range of lf8 is 1- 4mm, the value range of wf8 is 1~5mm. In the present invention, wf7=4mm, wf8=5mm, and lf8=4mm.
[0059] The said coaxial line 2, the variation range of the position of the leading end and the XOY plane with respect to the Z axis is expressed as ws1, wherein the value range of ws1 is -10-10 mm. In the present invention, ws1=+10mm.
[0060] The coaxial cable 2 is welded on the surface of the radiation unit 11 .
[0061] The two same cut corners 114 are located on the corresponding side of the feed port 111, and the lengths of the right-angle sides of the cut corners are expressed as lf6 and wf6, wher...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com