Methods for assessing risk using total and specific cell-free DNA
A cell-free, specific technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve limited and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
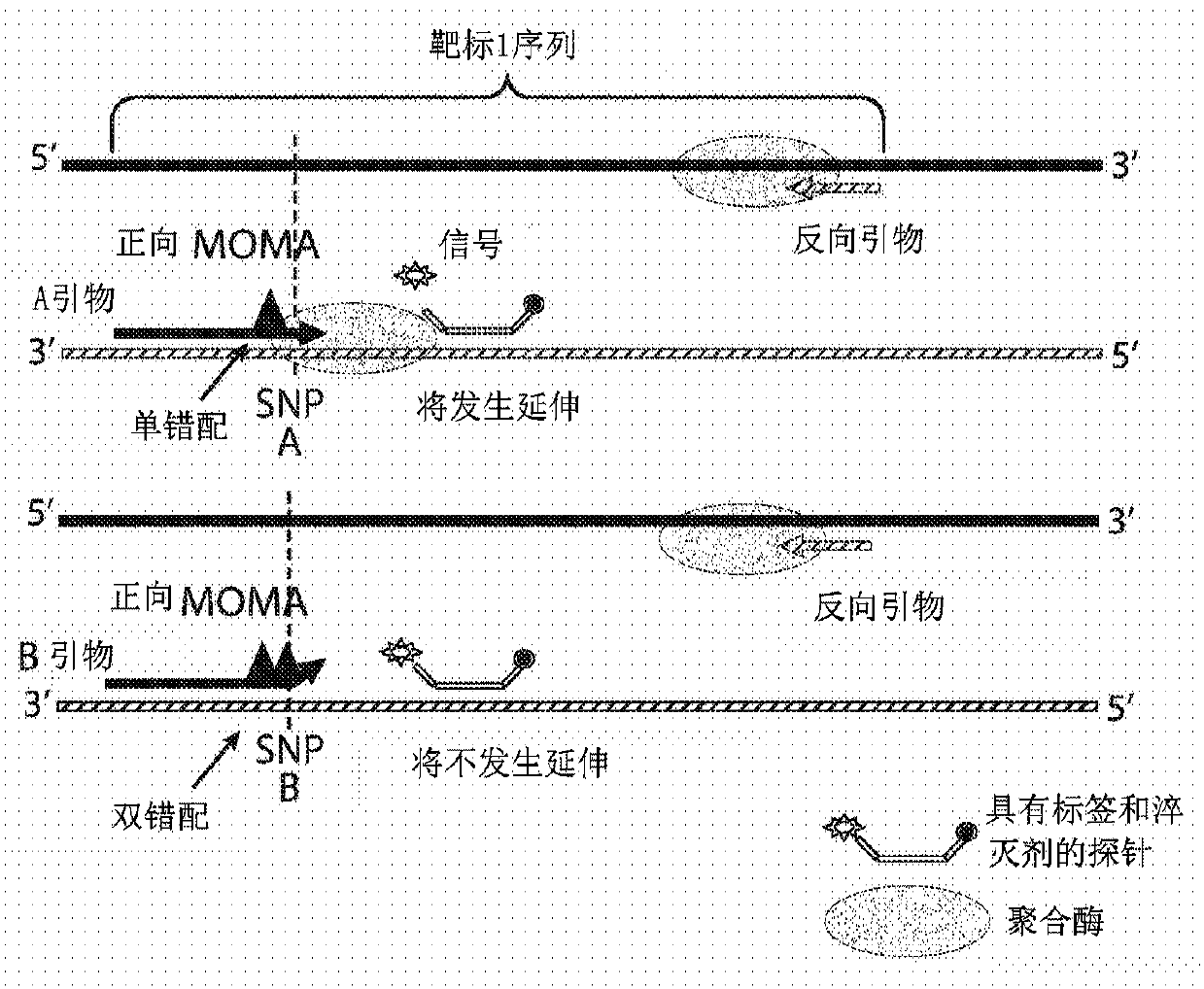
[0126] Example 1 - Mismatch Amplification Assay (MOMA)
[0127] SNV target selection
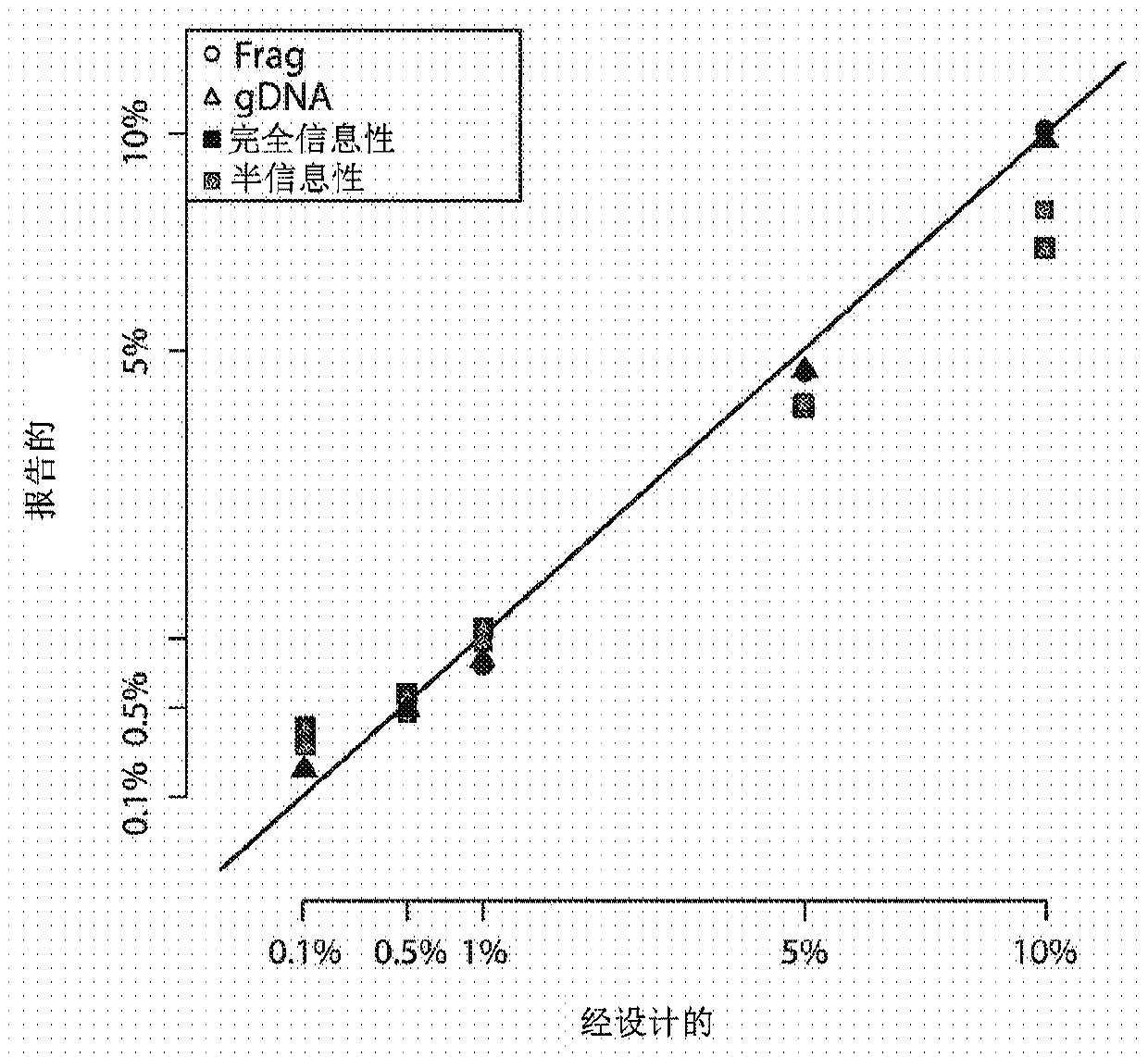
[0128] As presently described, identification of targets for multiplexing according to the present disclosure may comprise one or more of the following steps. First, highly heterozygous SNPs can be screened on several ethnic control populations (Hardy-Weinberg p > 0.25), excluding known regions of difficulty. Difficult regions include syndromic regions that may be abnormal in patients and regions of low complexity, including centromeres and telomeres of chromosomes. Target fragments of the desired length can then be designed in silico. Specifically, two 20 to 26 bp primers spanning a 70 bp window for each SNP can be designed. All candidate primers can then be queried to GCRh37 using BLAST. Those primers found to be sufficiently specific can be retained and monitored for off-target hits, especially at the 3' end of the fragment. Off-target candidate hits can be analyzed for generation of...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Example 3 - Determination of total cell-free DNA
[0147] In some embodiments, total cell-free DNA (cf-DNA) is determined. Three to ten milliliters (ml) of anticoagulated blood were collected in 10 ml cell-free DNA blood collection tube (BCT) tubes (Streck, Omaha, NE). Plasma was separated from whole blood by centrifugation and stored at -80°C until DNA extraction. ReliaPrep available TM HT Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit, Custom (Promega, Madison, WI) was used for cf-DNA extraction.
[0148] Total cf-DNA content from plasma was assessed in triplicate by quantitative real-time PCR as previously described (Hidestrand et al., Influence of temperature during transportation on cell-free DNA analysis. Fetal Diagn Ther 31, 122-128 (2012)). PCR analysis was performed on an Applied Biosystems QuantStudio7 Flex Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA).
Embodiment 4
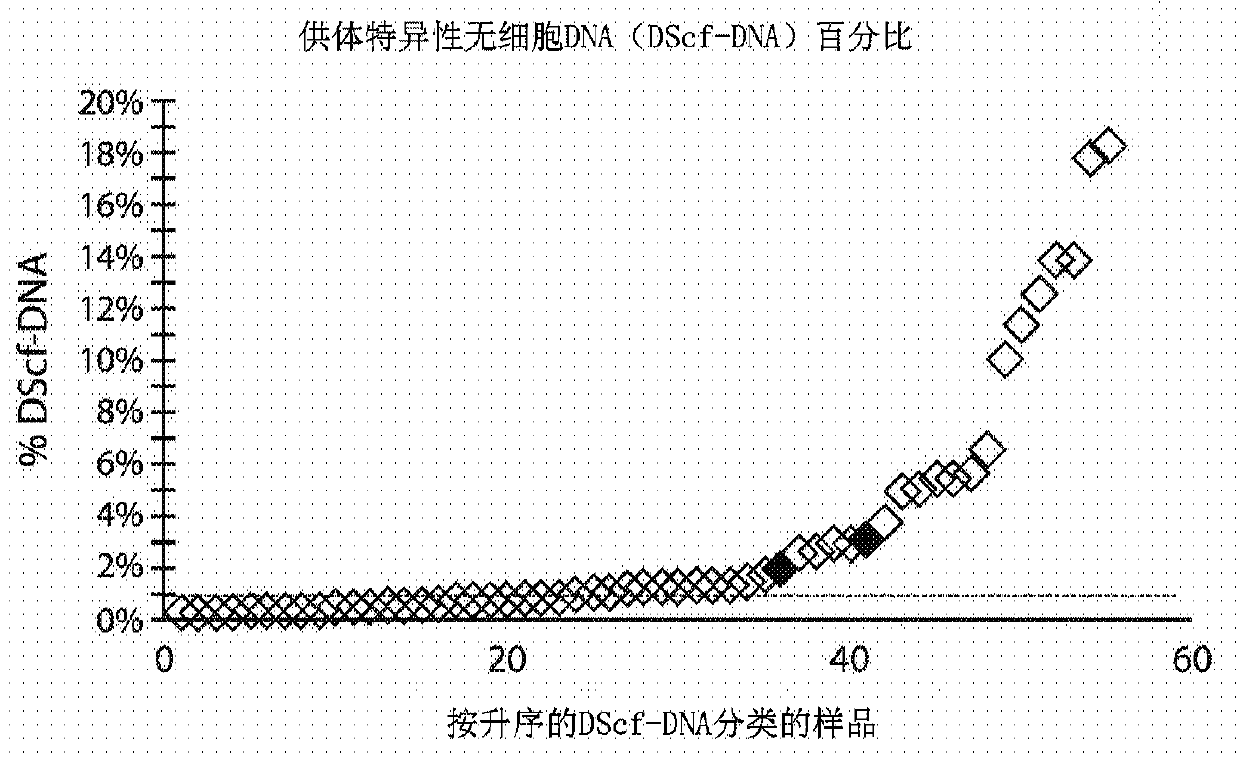
[0149] Example 4 - Risk assessment using total cell-free DNA and specific cell-free DNA
[0150] Such as Figure 7 As shown, values for total cell-free nucleic acid (eg, DNA) and values for specific cell-free nucleic acid (eg, DNA) can be displayed together at multiple time points in the report.
[0151] Figure 9 Another example of a report showing two types of data is shown. Data from 68 patients were analyzed. As expected, when both total cell-free DNA and specific cell-free DNA values were considered high, it indicated that rejection was likely to occur and drive an inflammatory process (upper right quadrant) or poor outcome or prognosis, such as death. When total cell-free DNA is considered high but specific cell-free DNA is not high, infection rather than rejection is likely to occur in the subject (upper left quadrant). However, when total cell-free DNA is considered low while specific cell-free DNA is considered high, it is likely that the subject is in the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com