A method for recycling mixed salt produced by waste acid treatment
A waste acid treatment and recycling technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, filtration treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor quality of solid salt products and high treatment costs, and achieve low energy consumption and treatment costs. Dealing with costs, avoiding impact effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
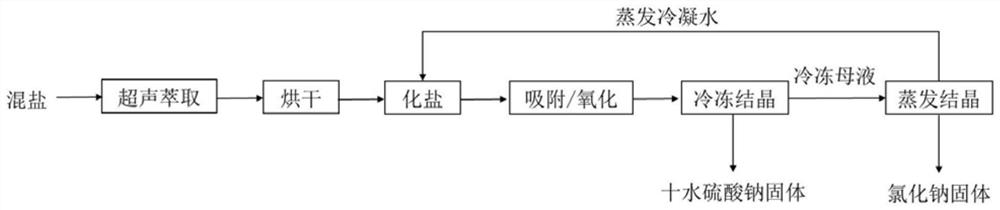
[0042] A chemical waste acid was neutralized to obtain 12,000 tons / year of solid mixed salt, of which sodium sulfate was about 32%, sodium chloride was about 55%, and the organic matter content was 1250mg / kg.
[0043] Select n-hexane as the extractant, mix it with mixed salt, ultrasonically extract the organic impurities in the mixed salt, and centrifuge after extraction to obtain solid salt residue and extract. During the extraction, the amount of n-hexane was 0.8mL / g, the ultrasonic power was 200w, and the single extraction time was 10min. After repeated extraction for 3 times, the content of organic matter in the salt residue was 680mg / kg.
[0044] Dry the solid salt residue obtained by solid-liquid separation after extraction at 70°C for 60 minutes to remove the residual extractant in the solid salt residue, and dissolve the dried solid salt residue in water to prepare a 310g / L salt solution. Add precipitant sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate and flocculant sodium polya...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The basic content of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that this embodiment selects dichloroethane as the extraction agent. Mix it with mixed salt, ultrasonically extract the organic impurities in the mixed salt, and centrifuge after extraction to obtain solid salt residue and extract. During the extraction, the amount of dichloroethane was 1.2mL / g, the ultrasonic power was 300w, and the extraction time was 30min. The content of organic matter in the salt residue after ultrasonic extraction was 565mg / kg.
[0050] Dry the solid salt residue obtained by solid-liquid separation after extraction at 90°C for 100 minutes to remove the residual extractant in the solid salt residue, and dissolve the dried solid salt residue in water to prepare a 280g / L salt solution , add precipitant sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate and flocculant sodium polyacrylate to remove calcium and magnesium ions, and filter to remove insoluble matter to obtain liquid A.
...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The basic content of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that this embodiment selects dichloroethane-acetone as the extractant. Mix it with mixed salt, ultrasonically extract the organic impurities in the mixed salt, and centrifuge after extraction to obtain solid salt residue and extract. During the extraction, the dosage of dichloroethane-acetone was 1.5mL / g, the ultrasonic power was 400w, and the single extraction time was 15min. After repeated extraction twice, the content of organic matter in the salt residue was 410mg / kg.
[0056] Dry the solid salt residue obtained by solid-liquid separation after extraction at 80°C for 120 minutes to remove the residual extractant in the solid salt residue, and dissolve the dried solid salt residue in water to prepare a 260g / L salt solution and put it into Add precipitant sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate and flocculant sodium polyacrylate to remove calcium and magnesium ions, and filter to remove ins...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com