Block chain cross-chain asset transfer method based on committee and block chain information terminal
A transfer method and committee technology, applied in the field of interoperability and inter-communication between blockchains, can solve problems such as difficulty in collaboration, information islands, and security problems, achieving a high degree of decentralization and reducing the difficulty of implementation , fast processing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
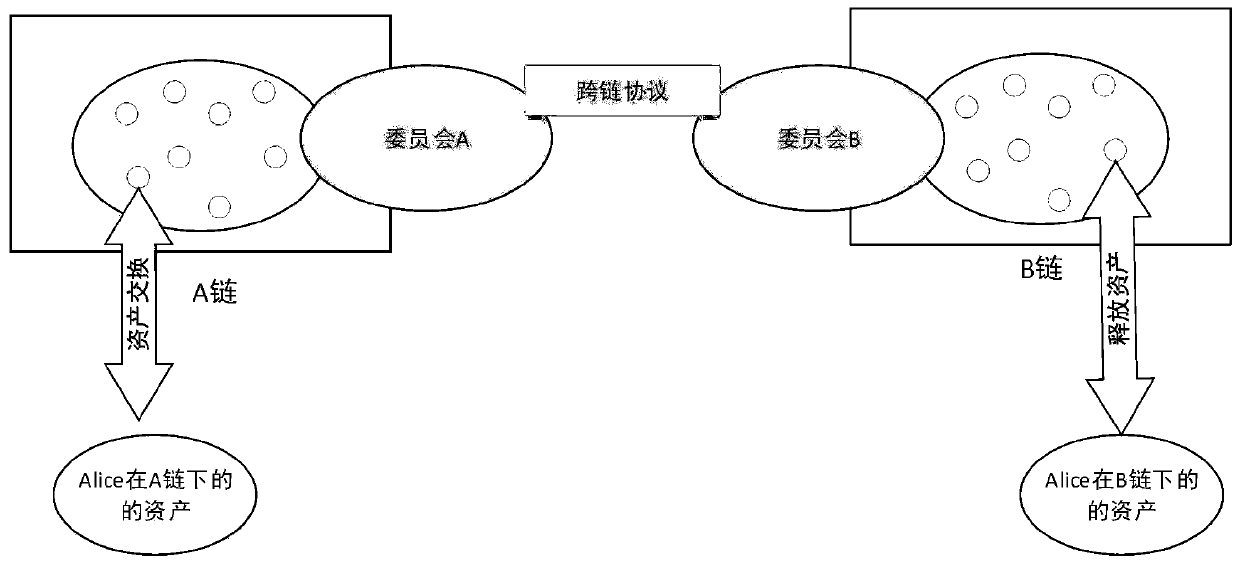
[0077] The embodiment of the present invention assumes that each user has an account on a different blockchain. That is, Alice has accounts on both Chain A and Chain B. What needs to be guaranteed is the atomicity of asset transactions and the relative total assets on the two chains remain unchanged.
[0078] Suppose there are two chains A and B, and their respective "confirmation committees" have been generated according to the committee extraction rules. Alice has a 1BTC asset on chain A, and wants to transfer this 1BTC asset to chain B and exchange it for 20ETH (A:B=1:20), such as figure 2 shown. The asset model is UTXO.
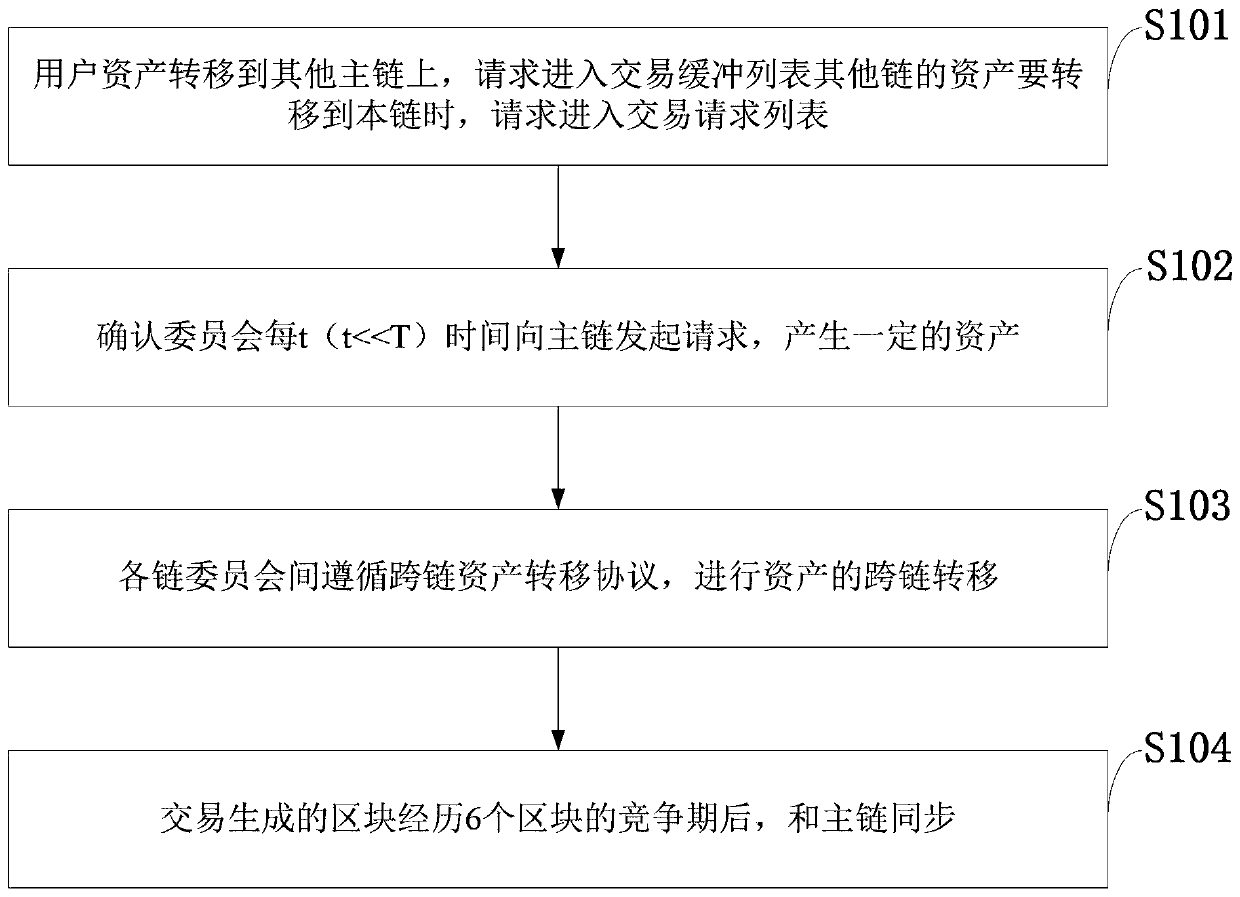
[0079] When the user Alice initiates a request under the A chain to transfer her assets to the B chain, he will go through the following steps (such as image 3 shown):
[0080] 1. Alice is under the A chain and "confirms the committee" C A To initiate an asset transfer request, the asset X a (1BTC) is transferred to the B chain, (the request sent i...
Embodiment 2
[0088] When multiple chains interact, the principle is the same as in Embodiment 1. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the existing four chains A, B, C, and D need to interact, A needs to cross-chain with B, C, and D, and B needs to cross-chain with D. Then the communication method is as follows:
[0089] Committee C A respectively with C B 、C C 、C D Correspondence, and have a corresponding "transaction buffer list C in the committee A →*" and "Trade Request List*→C A ". Similarly, Committee C B 、C C 、C D There is also a corresponding list. Committee C B with C D Correspondence, there is also a corresponding "transaction buffer list C in the committee B →C D ” and “Transaction Request List C D →C B ", correspondingly, C D There is also a corresponding list.
[0090] After that, every two committees communicate as described in Embodiment 1. In this way, the cross-chain asset exchange of the four chains is completed.
Embodiment 3
[0092] Cycle rotation and committee selection:
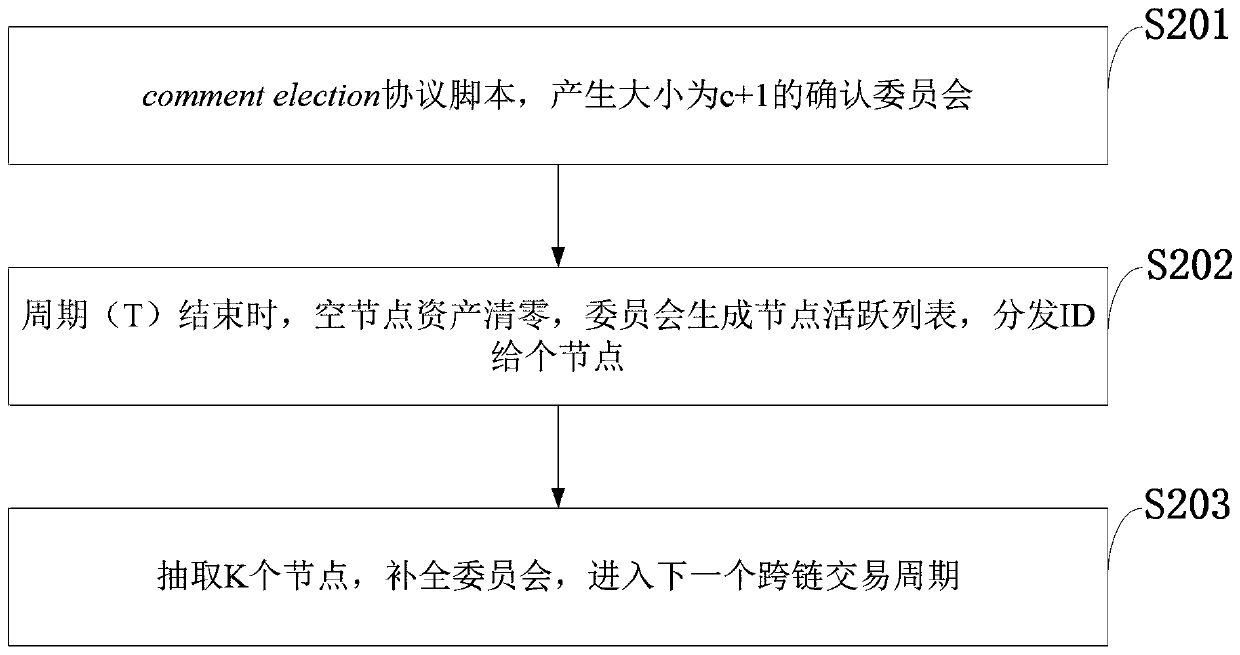
[0093] On each chain, use the reservoir algorithm to extract c nodes with equal probability, and form a "confirmation committee" of size c+1 with 1 empty node. Every T time, the "Confirmation Committee" draws again, which is called a drawing cycle. This is done to prevent malicious nodes from taking control of the "confirmation committee".
[0094] The specific rules are as follows: At the beginning, when the first committee is formed, the equal probability sampling algorithm of the reservoir is executed to extract c nodes, and empty nodes are added to form a "confirmation committee". This step is performed once, and then at the end of each cycle, the "confirmation committee" generates an active list of nodes in the current main chain, and then randomly removes nodes to make the current number of nodes c+1-k. Then use the same sampling algorithm to select k nodes on the main chain to form a new committee. These k nodes need t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com