A real-time fully distributed method for multi-robot system formation
A multi-robot and robot technology, applied in the direction of control/regulation systems, instruments, motor vehicles, etc., can solve the problems of lack of universality, inability to obtain robot status and information, maintain formation, etc., and achieve a universal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Combined with the symbol content defined in Table 1, the present invention is specifically implemented: a method of real-time fully distributed multi-robot system formation, at least a multi-robot, multi-robot, as follows:
[0067] Step 1) Then perform the next step, otherwise jump out of this algorithm;
[0068] Step 2) Get STOP_P i , And position i [N], and initialize
[0069] Step 3) Robot I judges in the current time K 0 Can I detect static or dynamic obstacles, if there is, add a static obstacle relative position coordinate to Adding a dynamic obstacle relative position coordinate
[0070] Step 4) Robot I broadcast your obstacle collection For other robots to the same group;
[0071] Step 5) Execute the next step, otherwise jump to step 8;
[0072] Step 6) Robot 1 Receive the relative coordinates of virtual obstacles sent by robot J Add Until And M 1 = M 1 +1;
[0073] Step 7) If M 1 = N-1, then And execute the next step, otherwise go to step 6;
[0074]...
Embodiment 2
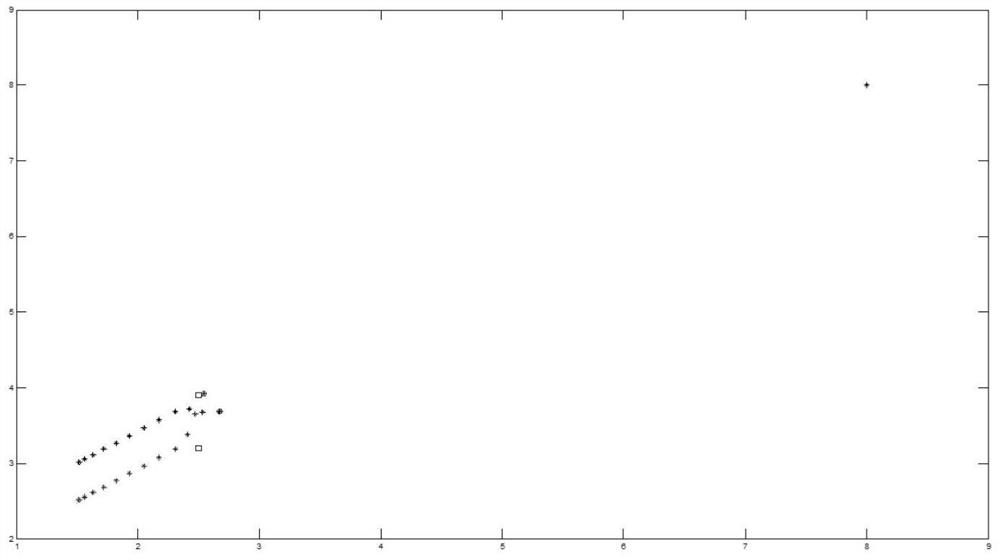
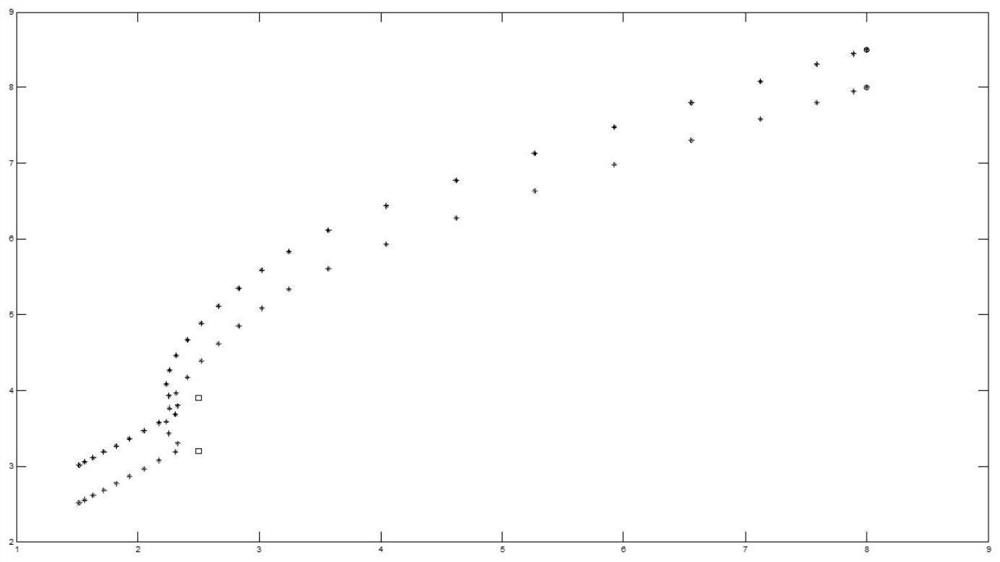
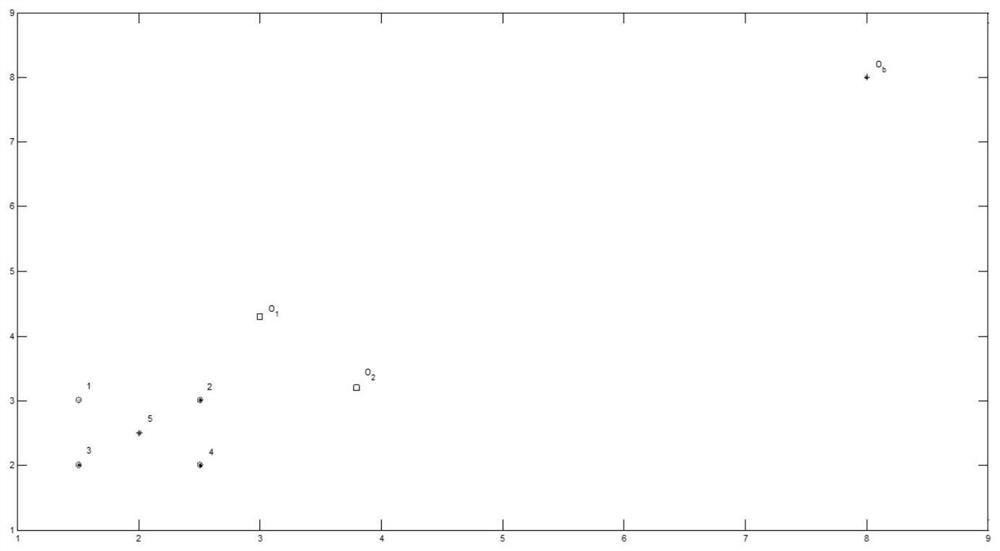
[0110] On the basis of the above embodiment, the present embodiment will illustrate the formation process as an example of five robots. figure 2 .
[0111] Step 1) Each robot checks whether to reach the target position, ie State, if the False is executed, it is performed, of which i = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, such as this example i = 1;
[0112] Step 2) Each robot gets its current position, speed, and acceleration of the last position. Your own target location STOP_P i , As well as the relative position of other robots in Position i [n] and initialize
[0113] Step 3) Robot I in Current Time K 0 Detect the surrounding environment to determine the position of the obstacle, and add the relative position of static obstacles to Adding a relative position of a dynamic obstacle to
[0114] Step 4) Robot I broadcast your obstacle collection For other robots J, J = 2, 3, 4, 5;
[0115] Step 5) The robot I judges whether or not the obstacle collection of all robots from the group is received...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com