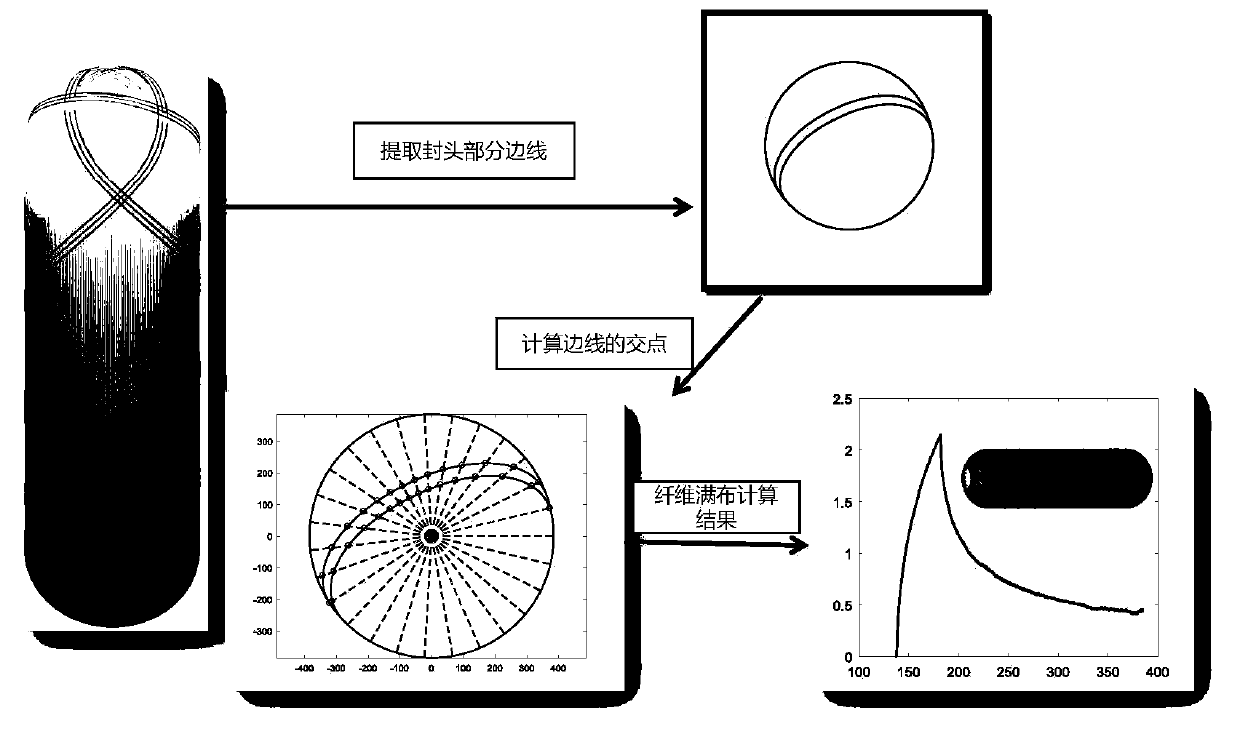
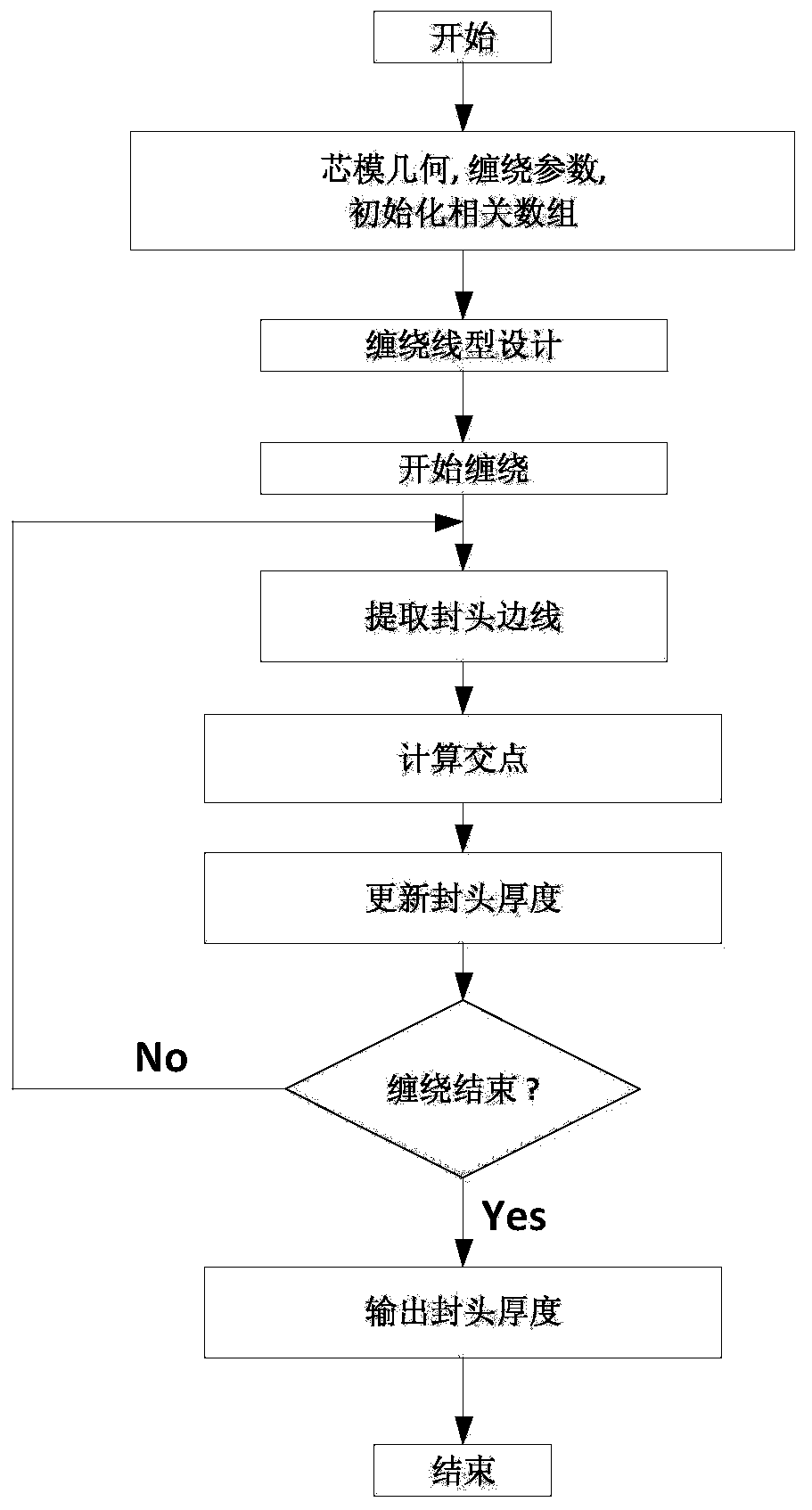
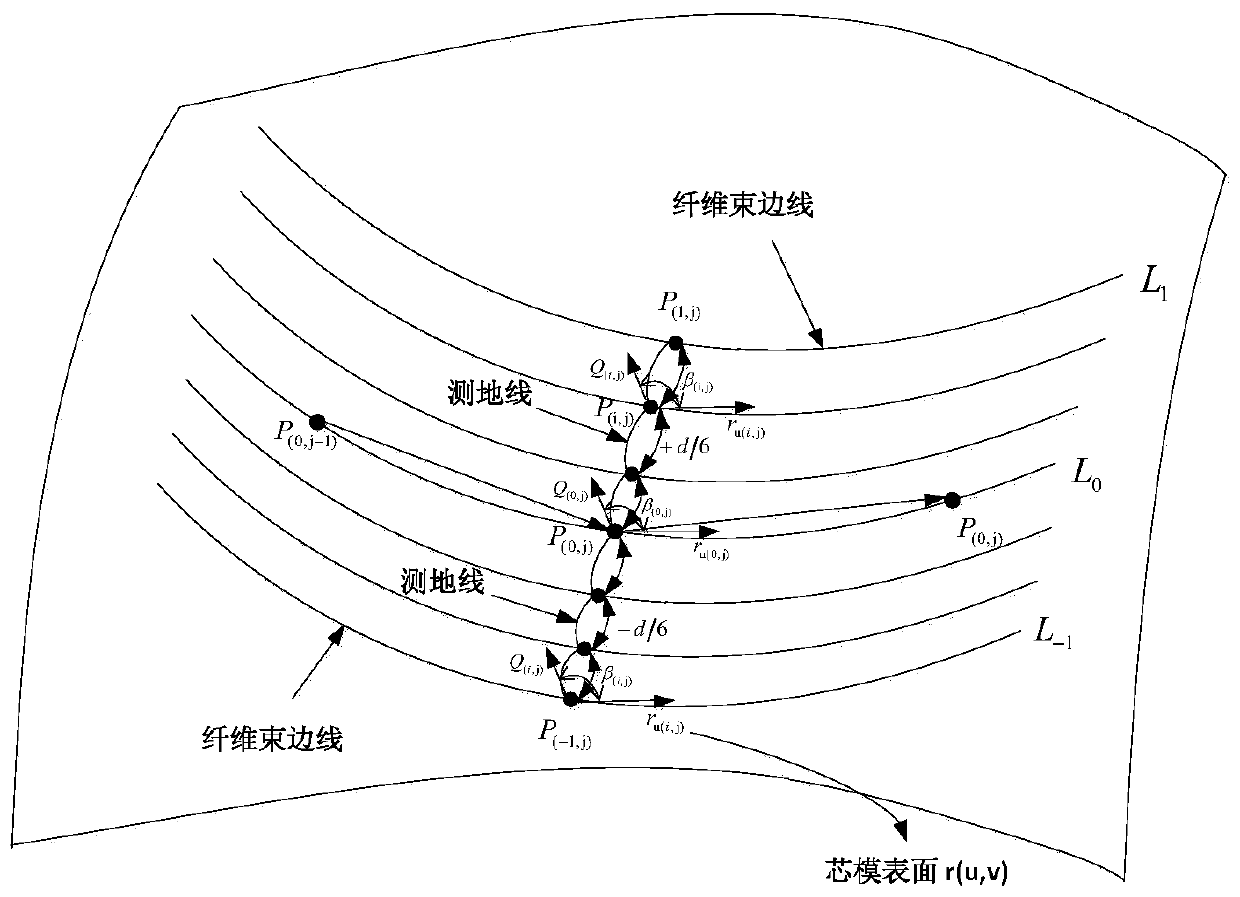
Method for calculating thickness of end socket of fiber wound composite shell
A technology of winding composite materials and calculation methods, which is applied in the field of calculation of the thickness of the head of the winding shell, can solve the problems that the actual winding line type cannot be considered
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] Now in conjunction with embodiment, accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
[0060] The present invention comprises following several parts:
[0061] 1. Obtain the winding parameters of the shell head section
[0062] During the filament winding process, the winding angle changes continuously along the axis of the mandrel. Obtaining an accurate winding angle distribution is the first step in calculating the fiber trajectory, and the calculation formula for the winding angle is as follows:
[0063]
[0064] In the formula, λ is the sliding line coefficient, α is the winding angle, r is the radius of the rotary section, r' and r″ are the first and second derivatives of the radius of the rotary section to the axis coordinate Z of the mandrel, respectively, and A is When λ=0, the equation degenerates into the Clairaut equation. When λ≠0, solving this equation can obtain the variation law of the non-geodesic winding angle along the axis ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com