Endovascular Surgical Instruments
A technology for surgical instruments and handles, applied in the field of medical instruments, can solve the problems of size limitation, increase of patient scars, and impact on appearance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
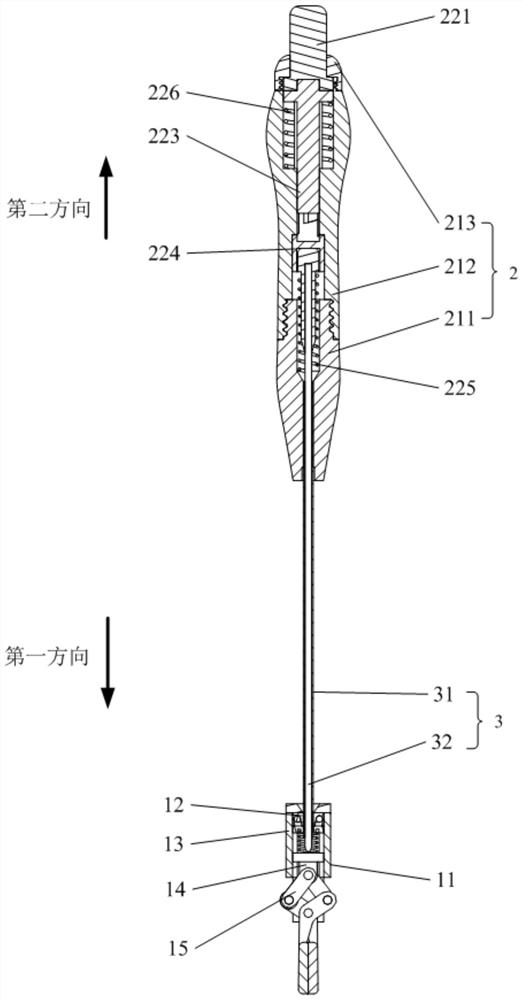
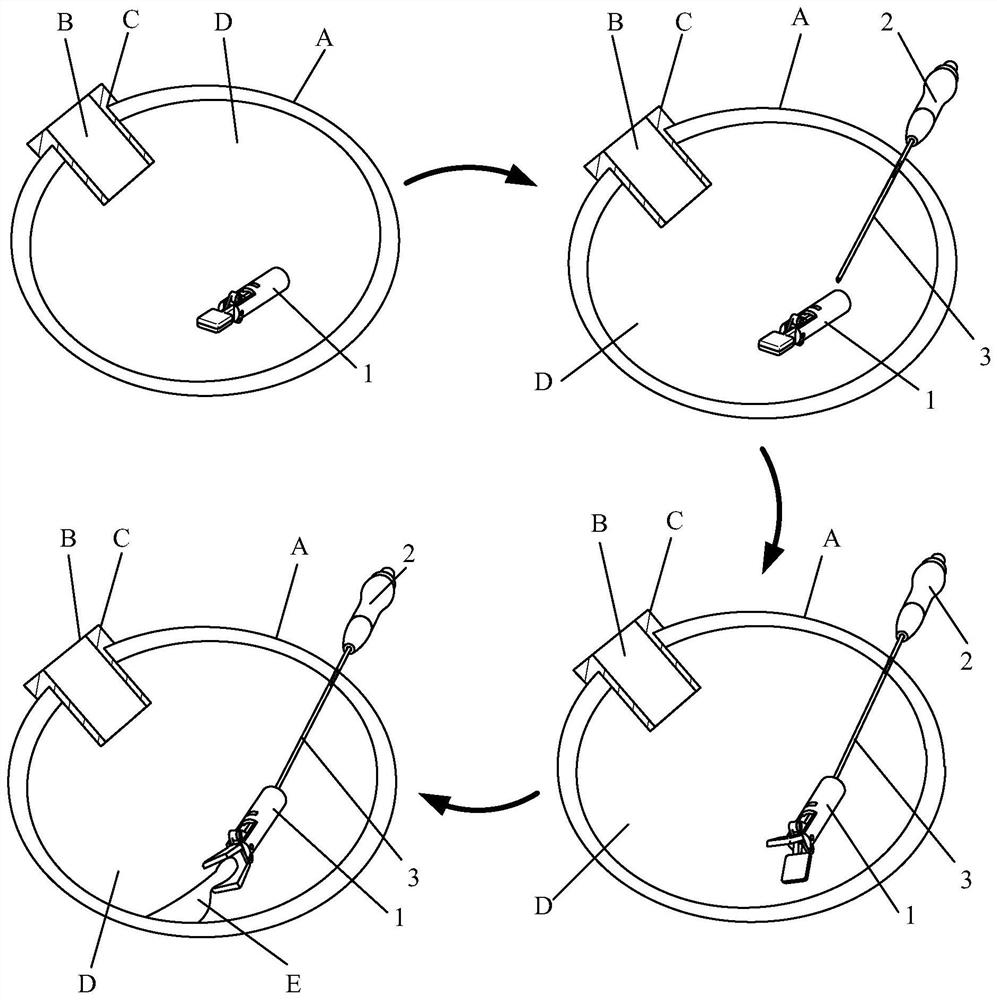
[0093] figure 1 is a schematic diagram of an intracavity surgical instrument according to an embodiment of the present invention. The intracavitary surgical instrument includes an operating device 1 and a handle 2, the handle 2 is provided with a connecting rod 3, and the connecting rod 3 includes a hollow sleeve rod 31 and a core rod 32 movably arranged in the sleeve rod 31, The connecting rod 3 has a pointed end. figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the operation of the intracavity surgical instrument according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 2 As shown, when performing intracavitary surgery, the doctor opens a puncture hole B on the patient's body surface A according to needs, and then inserts a puncture cannula C corresponding to the size of the puncture hole B into the puncture hole B to form a passage for surgical instruments to enter and exit , and then the operating device 1 is placed in the cavity D through the puncture cannula ...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Such as figure 2 As shown, the intracavitary surgical device includes an operating device 1 and a handle 2, the handle is provided with a connecting rod 3, and the connecting rod 3 includes a hollow sleeve rod 31 and a core rod movably arranged in the sleeve rod 31 32. The connecting rod 3 has a pointed end. Such as figure 2 As shown, when performing intracavitary surgery, the doctor opens an incision B on the patient's body surface A according to needs, and then inserts a puncture cannula C (trocar) corresponding to the size of the incision B into the incision B to form a channel for surgical instruments to enter and exit , and then place the operating device 1 in the cavity D through the puncture cannula C; the user holds the handle, and inserts the tip of the connecting rod 3 into the cavity D through other positions on the patient's body surface A; The operation is performed in the cavity D, and the connecting rod 3 is fixedly connected with the operating device...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Figure 21 It is a schematic diagram of the opened state of the operating device of the intracavitary surgical device in this embodiment, Figure 22 It is a schematic diagram of the closing state of the operating device of the intracavitary surgical device of this embodiment. Such as Figure 21 and Figure 22 As shown, the structure of the intracavitary surgical device of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the first or second embodiment, the only difference is:
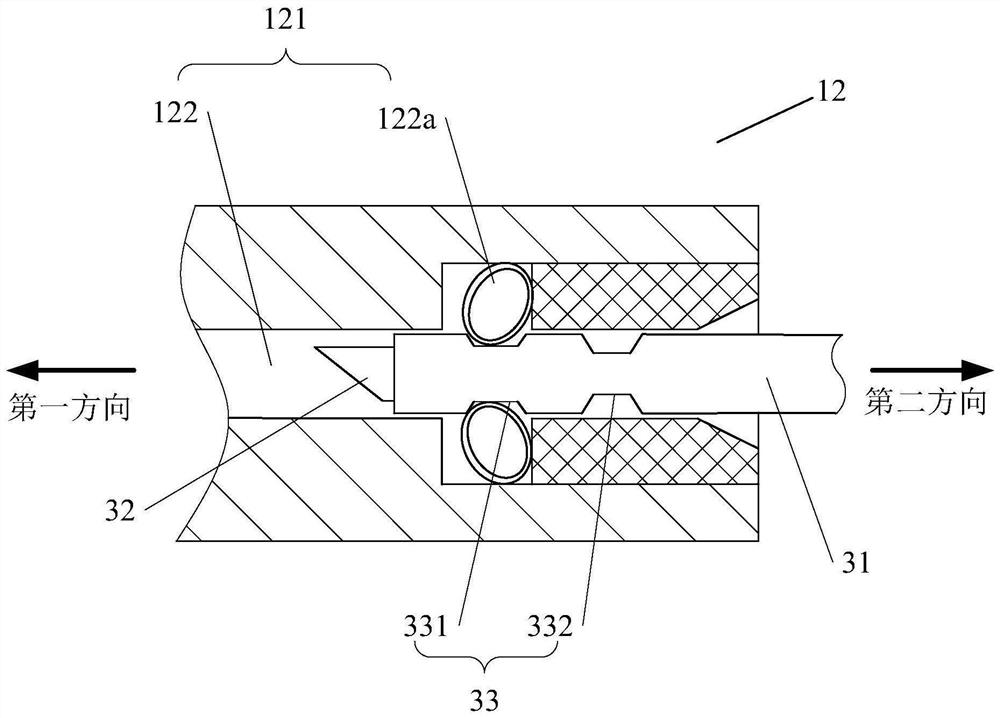
[0117] Such as Figure 21As shown, in the natural state (no external force), the push rod 14 is in the initial position, the angle between the two connecting arms 152b is small, and the distance between the two connecting points of the curved rod 152a and the connecting arm 152b is the shortest. The pliers head 15 is in an open state. When the core rod 32 is controlled to move in the first direction, the first end of the core rod 32 pushes the push rod 14 to move in the first direction, so th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com